Abstract
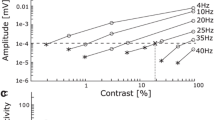
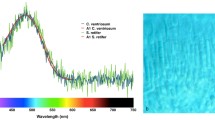
We used electroretinography (ERG) to determine spectral and luminous sensitivities, and the temporal resolution (flicker fusion frequency, FFF) in three sympatric (but phylogenetically distant) coastal shark species: Carcharhinus plumbeus (sandbar shark), Mustelus canis (smooth dogfish), and Squalus acanthias (spiny dogfish). Spectral sensitivities were similar (range ~400–600 nm, peak sensitivity ~470 nm), with a high likelihood of rod/cone dichromacy enhancing contrast discrimination. Spiny dogfish were significantly less light sensitive than the other species, whereas their FFF was ~19 Hz at maximum intensities; a value equal to that of sandbar shark and significantly above that of smooth dogfish (~9–12 Hz). This occurred even though experiments on spiny dogfish were conducted at 12 versus 25 °C and 20 °C for experiments on sandbar shark and smooth dogfish, respectively. Although spiny dogfish have a rod-dominated retina (rod:cone ratio 50:1), their visual system appears to have evolved for a relatively high temporal resolution (i.e., high FFF) through a short integration time, with the requisite concomitant reduction in luminous sensitivity. Our results suggest adaptive plasticity in the temporal resolution of elasmobranch visual systems which reflects the importance of the ability to track moving objects such as mates, predators, or prey.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AIC:
-
Akaike’s information criterion
- ERG:
-
Electroretinography
- FFF:
-
Flicker fusion frequency
- LLI:
-
Log light intensity
- MSP:
-
Microspectrophotometry
References
Able KW, Fahay MP (2010) Ecology of the estuarine fishes: temperate waters of the western North Atlantic. The John Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Alexander RL (1996) Evidence of brain-warming in the mobulid rays, Mobula tarapacana and Manta birostris (Chondrichthyes: Elasmobranchii: Batoidea: Myliobatiformes). Zool J Linn Soc-Lond 118:151–164
Ali MA, Muntz WRA (1973) Electroretinography as a tool for studying fish vision. In: Ali MA (ed) Vision in fishes, new approaches in research. NATO advanced study institute series, vol 1. Plenum Press, New York, pp 159–167
Ali MA, Anctil M, Cervetto L (1978) Photoreception. In: Ali MA (ed) Sensory ecology, review and perspectives. Plenum Press, New York, pp 467–502
Arendt MD, Olney JE, Lucy JA (2001) Stomach content analysis of cobia, Rachycentron canadum, from lower Chesapeake Bay. Fish Bull 99:665–670
Armington JC (1974) The Electroretinogram. Academic Press, New York
Bedore CN, Ellis R, Loew ER, Frank TM, Hueter RE, McComb DM, Kajiura SM (2013) A physiological analysis of color vision in batoid elasmobranchs. J Comp Physiol A 199:1129–1141
Bilotta J, Lynd FM, Powers MK (1998) Effects of mean luminance on goldfish temporal contrast sensitivity. Vis Res 38:55–59
Bleckmann H, Hofmann MH (1999) Special senses. In: Hamlett WC (ed) Sharks, skates, and rays: the biology of elasmobranch fishes. The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, pp 300–308
Block BA (1986) Structure of the brain and eye heater tissue in marlins, sailfish and spearfish. J Morphol 190:169–189
Block BA, Carey FG (1985) Warm brain and eye temperatures in sharks. J Comp Physiol B 156:229–236
Bowman RW, Stillwell CE, Michaels WL, Grosslein MD (2000) Food of northwest Atlantic fishes and two common species of squid. NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-NE-155. Northeast Region, Northeast Fisheries Science Center, Woods Hole, p 137
Bozzano A (2004) Retinal specializations in the dogfish Centroscymnus coelolepis from the Mediterranean deep-sea. Sci Mar 68(Suppl 3):185–195
Bozzano A, Collin SP (2000) Retinal ganglion cell topography in elasmobranchs. Brain Behav Evol 55:191–208
Bozzano A, Murgia R, Vallerga S, Hirano J, Archer S (2001) The photoreceptor system in the retinae of two dogfishes, Scyliorhinus canicula and Galeus melastomus: possible relationship with depth distribution and predatory lifestyle. J Fish Biol 50:1258–1278
Braekevelt CR (1994) Fine structure of the choroidal tapetum lucidum in the Port Jackson shark (Heterodontus phillipi). Anat Embryol (Berl) 190:591–596
Brill R, Magel C, Davis M, Hannah R, Rankin P (2008) Effects of rapid decompression and exposure to bright light on visual function in black rockfish (Sebastes melanops) and Pacific halibut (Hippoglossus stenolepis). Fish Bull 106:427–437
Brown KT (1968) The electroretinogram: its components and their origins. Vis Res 8:633–677
Bullock TH, Hofmann MH, New JG, Nahm FK (1991) Dynamic properties of visual evoked potentials in the tectum of cartilaginous and bony fishes, with neuroethological implications. J Exp Zool 256(Suppl 5):142–155
Burnham KP, Anderson DR (2002) Model selection and multimodel inference: a practical information-theoretic approach. Springer, New York
Carey FG (1982) A brain heater in the swordfish. Science 216:1327–1329
Casterlin ME, Reynolds WW (1979) Diel activity patterns of the smooth dogfish shark, Mustelus canis. Bull Mar Sci 29:440–442
Coates MM, Garm A, Theobald JC, Thompson SH, Nilsson DE (2006) The spectral sensitivity of the lens eyes of a box jellyfish, Tripedalia cystophora. J Exp Biol 209:3758–3765
Cohen JL (1991) Adapation for scotopic vision in the lemon shark (Negaprion brevirostris). J Exp Zool 5:76–84
Cohen JL, Gruber SH, Hamasaki DI (1977) Spectral sensitivity and purkinje shift in the retina of the lemon shark, Negaprion brevirostris (Poey). Vis Res 17:787–792
Collette BB, Klein-MacPhee G (2002) Bigelow and Schroeder’s Fishes of the Gulf of Maine, 3rd edn. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, DC
Compagno LJV (1984a) FAO Species Catalogue. Vol. 4. Sharks of the world: an annotated and illustrated catalogue of shark species known to date, Part 1 Hexanchiformes to Lamniformes. FAO Fish Synop 4(1):1–249
Compagno LJV (1984b) FAO Species Catalogue. Vol. 4. Sharks of the world: an annotated and illustrated catalogue of shark species known to date, Part 2 Carcharhiniformes. FAO Fish Synop 4(2):251–655
Compagno LJV (1990) Alternative live-history styles of cartilaginous fishes in time and space. Environ Biol Fishes 28:33–75
Compagno LJV (2003) Sharks of the order Carcharhiniformes. Blackburn Press, New Jersey
Conrath CL, Musick JA (2002) Reproductive biology of the smooth dogfish, Mustelus canis, in the northwest Atlantic Ocean. Environ Biol Fishes 64:367–377
Conrath CL, Musick JA (2008) Investigations into depth and temperature habitat utilization and overwintering grounds of juvenile sandbar sharks, Carcharhinus plumbeus: the importance of near shore North Carolina waters. Environ Biol Fish 82:123–131
Crescitelli F, McFall-Ngai M, Horwitz J (1985) The visual pigment sensitivity hypothesis: further evidence from fishes of varying habitats. J Comp Physiol A 157:323–333
Douglas RH (2001) The ecology of teleost fish visual pigments: a good example of sensory adaptation to the environment? In: Schmid A (ed) Ecology of Sensing. Springer, Berlin, pp 215–235
Evans LS, Peachy NS, Marchese AL (1993) Comparison of three methods of estimating the parameters of the Naka-Rushton equation. Doc Ophthalmol 84:19–30
Fishelson L, Baranes A (1999) Ocular development in the oman shark, Iago omanensis (Triakidae), Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Anat Rec 256:389–402
Fleisher KJ, Case JF (1995) Cephalopod predation facilitate by dinoflagellate luminescence. Biol Bull 189:263–271
Forward RB, Cronin TW, Douglas JK (1988) The visual pigments of carbs. II. Environmental adaptations. J Comp Physiol 162A:479–490
Frank TM (1999) Comparative study of temporal resolution in the visual systems of mesopelagic crustaceans. Biol Bull 196:137–144
Frank TM (2000) Temporal resolution in mesopelagic crustaceans. Philos Trans R Soc 355:1195–1198
Frank TM (2003) Effects of light adaptation on the temporal resolution of deep-sea crustaceans. Integr Comp Biol 43:559–570
Fritsches KA, Brill RW, Warrant EJ (2005) Warm eyes provide superior vision in swordfishes. Curr Biol 15:55–58
Gačić Z, Damjanovic I, Bajic A, Milosevic M, Mickovic B, Nikcevic M, Andjus PR (2007a) The d-wave in fish and the state of light adaptation. Gen Physiol Biophys 26:260–267
Gačić Z, Damjanović I, Mićković B, Hegediš A, Nikčević M (2007b) Spectral sensitivity of the dogfish shark Scyliorhinus canicula. Fish Physiol Biochem 33:21–27
Gelsleichter J, Musick JA, Nichols S (1999) Food habits of the smooth dogfish, Mustelus canis, dusky shark, Carcharhinus obscurus, Atlantic sharpnose shark, Rhizoprionodon terraenovae, and the sand tiger, Carcharias taurus, from the northwest Atlantic Ocean. Environ Biol Fishes 54:205–217
Govardovskii VI, Lychakov LV (1977) Visual cells and visual pigments in the Black Sea elasmobranchs. Zh Evol Biokhim Fiziol 13:162–166
Govardovskii VI, Fyhrquist N, Reuter T, Kuzmin DG, Donner K (2000) In search of the visual pigment template. Vis Neurosci 17:509–528
Grubbs RD, Musick JA (2007) Spatial delineation of summer nursery areas for juvenile sandbar sharks in Chesapeake Bay, Virginia. Am Fish Soc Symp 50:63–86
Grubbs RD, Musick JA, Conrath CL, Romaine JG (2007) Long-term movements, migration, and temporal delineation of summer nurseries for juvenile sandbar sharks in the Chesapeake Bay region. Am Fish Soc Symp 50:87–108
Gruber SH (1977) The visual system of sharks: adaptations and capability. Am Zool 17:453–469
Gruber SH, Gulley RL, Brandon J (1975) Duplex retina in seven elasmobranch species. Bull Mar Sci 25:353–358
Hamasaki DI, Bridges CDB (1965) Properties of the electroretinogram in three elasmobranch species. Vis Res 5:483–496
Hamasaki DI, Bridges CDB, Meneghini KA (1967) The electroretinogram of three species of elasmobranchs. In: Gilbert PW, Mathewson RF, Rall DP (eds) Sharks. skates, and rays. The Johns Hopkins Press, Baltimore, pp 447–463
Hanyu I, Ali MA (1964) Electroretinogram and its flicker fusion frequency at different temperatures in light-adapted salmon (Salmo salar). J Cell Comp Physiol 63:309–322
Harding JM, Mann R (2001) Diet and habitat use by bluefish, Pomatomus saltatrix, in a Chesapeake Bay estuary. Environ Biol Fish 60:401–409
Hart NS, Lisney TJ, Marshall NJ, Collin SP (2004) Multiple cone visual pigments and the potential for trichromatic colour vision in two species of elasmobranch. J Exp Biol 207:4587–4594
Hart NS, Lisney TJ, Collin SP (2006) Visual communication in elasmobranchs. In: Kapoor BG, Ladich F, Collin SP, Raschi WG (eds) Fish communication, vol 2. Science Publishers Inc., Enfield, pp 337–392
Hart NS, Theiss SM, Harahush BK, Collin SP (2011) Microspectrophotometric evidence for cone monochromacy in sharks. Naturwissenschaften 98:193–201
Healy K, McNally L, Ruxton GD, Cooper N, Jackson AL (2013) Metabolic rate and body size are linked with perception of temporal information. Anim Behav 86:685–696
Heath AR (1991) The ocular tapetum lucidum: a model system for interdisciplinary studies in elasmobranch biology. J Exp Zool 256(Suppl S5):41–45
Hodgson ES, Mathewson RF (1978) Sensory biology of sharks, skates, and rays. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC
Horodysky AZ, Brill RW, Warrant EJ, Musick JA, Latour RJ (2008) Comparative visual function in five sciaenid fishes inhabiting Chesapeake Bay. J Exp Biol 211:3601–3612
Horodysky AZ, Brill RW, Warrant EJ, Musick JA, Latour RJ (2010) Comparative visual function in four piscivorous fishes inhabiting Chesapeake Bay. J Exp Biol 213:1751–1761
Horodysky AZ, Brill RW, Crawford KC, Seagroves ES, Johnson AK (2013) Comparative visual ecophysiology of mid-Atlantic temperate reef fishes. Biol Open 2:1371–1381
Hueter RE (1991) Adaptations for spatial vision in sharks. J Exp Zool Suppl 5:130–141
Hueter RE, Mann DA, Maruska KP, Sisneros JA, Semski LS (2004) Sensory biology of elasmobranchs. In: Carrier JC, Musick JA, Heithaus MR (eds) Biology of sharks and their relatives. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 325–368
Jerlov NG (1968) Optical oceanography. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Jerlov NG (1974) Optical aspects of oceanography. Academic Press, London
Johnson ML, Shelton PMJ, Gaten E (2000) Temporal resolution in the eyes of marine decapods from coastal and deep-sea habitats. Mar Biol 136:243–248
Kajiura SJ (2010) Pupil dilation and visual field in the piked dogfish, Squalus acanthias. Enviorn Biol Fish 88:133–141
Kajiura SJ, Tallack SML (2009) Pupil dilation in the spiny dogfish. Bull Mt Desert Biol Lab 48:68
Klimley PA (2013) The Biology of sharks and rays. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Kobayashi H (1962) A comparative study on electroretinogram in fish, with special reference to ecological aspects. Contribution of the Shimonoseki College of Fisheries, No 253:171–248
Levine JS, MacNichol EF Jr (1979) Visual pigments in teleost fishes: effects of habitat, microhabitat, and behavior on visual system evolution. Sens Process 3:95–131
Lisney TJ, Collin SP (2008) Retinal ganglion cell distribution and spatial resolving power in elasmobranchs. Brain Behav Evol 72:59–77
Lisney TJ, Theiss SM, Collin SP, Hart NS (2012) Vision in elasmobranchs and their relatives: 21st century advances. J Fish Biol 80:2024–2054
Litherland, LE (2009) Neuroethological studies in shark vision. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Queensland, Sensory Neurobiology Group, School of Biomedical Sciences, Brisbane, Australia, pp 211
Litherland L, Collin SP (2008) Comparative visual function in elasmobranchs: spatial arrangement and ecological correlates of photoreceptor and ganglion cell distributions. Vis Neurosci 25:549–561
Litherland L, Collin SP, Fritsches KA (2009) Visual optics and ecomorphology of the growing shark eye: a comparison between deep and shallow water species. J Exp Biol 212:3583–3594
Loew ER, McFarland WN (1990) The underwater visual environment. In: Douglas RH, Djamgoz MBA (eds) The visual system of fish. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 3–43
Losey GS, McFarland WN, Loew ER, Zamzow JP, Nelson PA, Marshall NJ (2003) Visual biology of Hawaiian coral reef fishes. I. Ocular transmission and visual pigments. Copeia 2003:433–454
Lythgoe JN (1979) The ecology of vision. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Lythgoe JN (1978) Fishes: vision in dim light and surrogate senses. In: Ali MA (ed) Sensory ecology, review and perspectives. Plenum Press, New York, pp 155–168
Lythgoe JN (1988) Light and vision in the aquatic environment. In: Atema J, Fay RR, Popper AN, Tavolga WN (eds) Sensory biology of aquatic animals. Springer, New York, pp 57–82
Lythgoe JN, Partridge JC (1991) The modelling of optimal visual pigments of dichromatic teleosts in green coastal waters. Vis Res 31:361–371
Marshall JN, Cronin TW, Frank TM (2003) Visual adaptations in crustaceans: chromatic, developmental, and temporal aspects. In: Collin SP, Marshall JN (eds) Sensory processing in aquatic environments. Springer, New York, pp 343–372
McCandless CT, Pratt HL Jr, Kohler NE, Merson RR, Recksiek CW (2007) Distributions, localized abundance, movements and migrations of juvenile sandbar sharks tagged in Delaware Bay. Am Fish Soc Symp 50:45–62
McComb DM, Frank TM, Hueter RE, Kajiura SM (2010) Temporal resolution and spectral sensitivity of the visual system of three coastal shark species from different light environments. Physiol Biochem Zool 83:299–307
McComb DM, Kajiura SM, Horodysky AZ, Frank TM (2013) Comparative visual function in predatory fishes from the Indian River lagoon. Physiol Biochem Zool 86:285–297
McFarland WN (1986) Light in the sea-correlations with behaviors of fishes and invertebrates. Am Zool 26:389–401
McFarland W (1991) Light in the sea: the optical world of elasmobranchs. J Exp Zool Suppl 5:3–12
McFarland WN, Munz FW (1975a) Part II: the photic environment of clear tropical seas during the day. Vis Res 15:1063–1070
McFarland WN, Munz FW (1975b) Part III: the evolution of photopic visual pigments in fishes. Vis Res 15:1071–1080
McMillan DG, Morse WW (1999) Essential fish habitat source document: Spiny dogfish, Squalus acanthias, life history and habitat characteristics. NOAA Tech Memo NMFS-NE-150, Northeast Region, Northeast Fisheries Science Center, Woods Hole, pp 19
Mensinger AF, Case JF (1992) Dinoflagellate luminescence increases susceptibility of zooplankton to teleost predation. Mar Biol 112:207–210
Morishita H, Ohashi S, Oku T, Nakajima Y, Lokima S, Ryufuku M, Nakamura H, Ohmiya Y (2002) Cloning and characterization of an active fragment of luciferase from a luminescent marine alga, Pyrocystis lunula. Photochem Photobiol 75:311–315
Naka KI, Rushton WAH (1966) S-potentials from luminosity units in the retina of fish (Cyprinidae). J Physiol 185:587–599
Newman AS, Marshall JN, Collin SP (2013) Visual eyes: a quantitative analysis of the photoreceptor layer in deep-sea sharks. Brain Behav Evol 82:237–249
O’Gower AK, Mathewson RF (1967) Spectral sensitivity and flicker fusion frequency of the lemon shark, Negaprion brevirostris. In: Gilbert PW, Mathewson RF, Rall DP (eds) Sharks, skates, and rays. The Johns Hopkins Press, Baltimore, pp 433–446
R Development Core Team (2008) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Ross LG, Ross B (1999) Anesthetic and sedative techniques for aquatic animals. Blackwell Science Ltd., Oxford
Rountree RA, Able KW (1996) Seasonal abundance, growth, and foraging habits of juvenile smooth dogfish, Mustelus canis, in a New Jersey estuary. Fish Bull 94:522–534
Runcie RM, Dewar H, Hawn DR, Frank LR, Dickson KA (2009) Evidence for cranial endothermy in the opah (Lampris guttatus). J Exp Biol 212:461–470
Schieber NL, Collin SP, Hart NS (2012) Comparative retinal anatomy in four species of elasmobranch. J Morphol 273:423–440
Severns ML, Johnson MA (1993) The care and fitting of the Naka-Rushton functions to electroretinographic intensity data. Doc Ophthalmol 85:135–150
Siebeck UE, Marshall NJ (2001) Ocular media transmission in coral reef fish—can coral reef fish see ultraviolet light? Vis Res 41:133–149
Sillman AJ, Letsinger GA, Patel S, Loew ER, Klimley AP (1996) Visual pigments and photoreceptors in two species of shark, Triakis semifasciata and Mustelus henlei. J Exp Zool 276:1–10
Sloman KA, Wilson RW (2006) Anthropogenic impacts upon behavior and physiology. In: Sloman KA, Wilson RW, Balshine S (eds) Fish Physiology, Behavior and physiology of fish, vol 24. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 413–468
Stavenga DG, Smiths RP, Hoenders BJ (1993) Simple exponential functions describing the absorbance bands of visual pigment spectra. Vis Res 33:1011–1017
Stell WK (1972) The structure and morphologic relations of rods and cones in the retina of the spiny dogfish Squalus. Comp Biochem Physiol 42:141–152
Stell WK, Witkovsky P (1973) Retinal structure in the smooth dogfish, Mustelus canis: light microscopy of photoreceptor and horizontal cells. J Comp Neurol 148:33–46
Stillwell CE, Kohler NE (1993) Food habits of the sandbar shark Carcharhinus plumbeus off the U.S. northeast coast, with estimates of daily ration. Fish Bull 91:138–150
Thorpe A, Douglas RH, Truscott RJW (1993) Spectral transmission and short-wave absorbing pigments in the fish lens. I. Phylogenetic distribution and identity. Vis Res 33:289–300
Warrant EJ (1999) Seeing better at night: life style, eye design and the optimum strategy of spatial and temporal summation. Vis Res 39:1611–1630
Warrant E (2004) Vision in the dimmest habitats on earth. J Comp Physiol A 190:765–789
Water JF, Overton AS, Ferry KH, Mather ME (2003) Atlantic coast feeding habits of striped bass: a synthesis supporting a coast-wide understanding of trophic biology. Fish Manag Ecol 10:349–360
Weissburg MJ, Browman HI (2005) Sensory biology: linking the internal and external ecologies of marine organisms. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 287:263–307
Acknowledgments
All animal capture, care, and experimental protocols complied with relevant laws of the United States and were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees of the College of William and Mary, Nova Southeastern University, and the University of Massachusetts Dartmouth. The authors thank the staff at the Virginia Institute of Marine Science—Eastern Shore Laboratory for their continuing hospitality and help in acquiring sandbar sharks and smooth dogfish, D. Bernal (University of Massachusetts, Dartmouth) for making it possible to perform experiments on spiny dogfish, and L. Litherland for her support and discussions regarding experimental design, execution, and data analysis. M. Kalinoski’s participation was funded in part by a scholarship from the South Florida Chapter of the Explorer’s Club. This paper is contribution 3409 from the Virginia Institute of Marine Science, College of William & Mary. The opinions expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the U.S. Department of Commerce—National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) or any of its subagencies. Mention of trade names, products, or commercial companies is for identification purposes only and likewise does not imply endorsement by NOAA or any of its subagencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalinoski, M., Hirons, A., Horodysky, A. et al. Spectral sensitivity, luminous sensitivity, and temporal resolution of the visual systems in three sympatric temperate coastal shark species. J Comp Physiol A 200, 997–1013 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-014-0950-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-014-0950-y