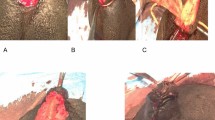
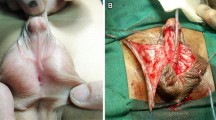
Abstract
Purpose
We have studied outcome of double-face preputial island flap (DFPIF) technique in severe types of hypospadias: penoscrotal, scrotal and perineal.
Methods
We have used DFPIF in 75 boys at a median age of 1.1 years (1.0–1.5). The meatus was penoscrotal, scrotal or perineal after de-gloving the penis. The inner face of the foreskin was used for urethroplasty and the outer face for ventral skin covering. Modifications were added: proximal anastomosis was protected by a spongioplasty; in case of urethral plate transection, we anastomosed on onlay proximal and distal segments of the flap (onlay-tube-onlay) and the tubularized part was sutured to corpus cavernosa. FU was scheduled at one month then every 3 months for a year then annually. At each consultation, the surgeon filled out a detailed cosmetic and functional sheet including flowmeter.
Results
Thirty-four patients had onlay preputial flap repair with urethral plate preservation. Forty-one had the onlay-tube-onlay technique. All children had a curvature, 19 had a significant residual curvature after dissection, corrected by dorsal plication (n = 9) and ventral lengthening (n = 10). Median FU was 4.2 years (2.7–6.5). 36 children (48%) had complications and needed redo surgery: 12 fistulas, 11 diverticula, 7 meatal stenosis, 3 strictures and 2 residual curvatures. All children but three voided within the normal limits for their age.
Conclusion
DFPIF remains a good option for a one-stage repair of severe hypospadias. After a median of 1.8 procedures, the final success rate was 96%. The healthy well-vascularized ventral skin allows safe redo surgery when needed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Castagnetti M, El-Ghoneimi A (2010) Surgical management of primary severe hypospadias in children: systematic 20-year review. J Urol 184(4):1469–1474
Long CJ, Canning DA (2016) Hypospadias: are we as good as we think when we correct proximal hypospadias? J Pediatr Urol 12(4):196.e1–5
Elder JS, Duckett JW, Snyder HM (1987) Onlay island flap in the repair of mid and distal penile hypospadias without chordee. J Urol 138(2):376–379
Snodgrass WT (2005) Snodgrass technique for hypospadias repair. BJU Int 95(4):683–693
Duckett JW (1981) The island flap technique for hypospadias repair. Urol Clin North Am 8(3):503–511
Hayashi Y, Sasaki S, Mogami T, Yamada Y, Tsugaya M, Kohri K (1996) One-stage urethroplasty with the modified OUPF IV for proximal hypospadias. Nihon Hinyokika Gakkai Zasshi 87(1):56–60
Bracka A (1995) Hypospadias repair: the two-stage alternative. Br J Urol 76(Suppl 3):31–41
Hinman F Jr (1991) The blood supply to preputial island flaps. J Urol 145(6):1232–1235
Jordan GH (1999) Penile reconstruction, phallic construction, and urethral reconstruction. Urol Clin North Am 26(1):1–13
Duckett JW Jr (1980) Transverse preputial island flap technique for repair of severe hypospadias. Urol Clin North Am 7(2):423–430
Hodgson NB (1970) A one-stage hypospadias repair. J Urol 104(2):281–283
Asopa R, Asopa HS (1984) One stage repair of hypospadias using double island preputial skin tube. Indian J Urol 1(1):41–43
Standoli L (1982) One-stage repair of hypospadias: preputial island flap technique. Ann Plast Surg 9(1):81–88
Gonzalez R, Lingnau A, Ludwikowski BM (2018) Results of onlay preputial flap urethroplasty for the single-stage repair of mid- and proximal hypospadias. Front Pediatr 6:19
Lee PA, Mazur T, Danish R, Amrhein J, Blizzard RM, Money J et al (1980) Micropenis. I. criteria, etiologies and classification. Johns Hopkins Med J 146(4):156–163
Kiss A, Sulya B, Szasz AM, Romics I, Kelemen Z, Toth J et al (2011) Long-term psychological and sexual outcomes of severe penile hypospadias repair. J Sex Med 8(5):1529–1539
Prasad MM, Marks A, Vasquez E, Yerkes EB, Cheng EY (2012) Published surgical success rates in pediatric urology—fact or fiction? J Urol 188(4 Suppl):1643–1647
Patel RP, Shukla AR, Snyder HM 3rd (2004) The island tube and island onlay hypospadias repairs offer excellent long-term outcomes: a 14-year followup. J Urol 172(4 Pt 2):1717–1719 (discussion 9)
Wiener JS, Sutherland RW, Roth DR, Gonzales ET Jr (1997) Comparison of onlay and tubularized island flaps of inner preputial skin for the repair of proximal hypospadias. J Urol 158(3 Pt 2):1172–1174
Sedberry-Ross S, Stisser BC, Henderson CG, Rushton HG, Belman AB (2007) Split prepuce in situ onlay hypospadias repair: 17 years of experience. J Urol 178(4 Pt 2):1663–1667
Baskin LS, Duckett JW, Ueoka K, Seibold J, Snyder HM 3rd (1994) Changing concepts of hypospadias curvature lead to more onlay island flap procedures. J Urol 151(1):191–196
Silva e EDM, Gorduza DB, Catti M, Valmalle AF, Demede D, Hameury F et al (2009) Outcome of severe hypospadias repair using three different techniques. J Pediatr Urol 5(3):205–211 (discussion 12–4)
Wallis MC, Braga L, Khoury A (2008) The role of flaps and grafts in modern hypospadiology. Indian J Urol 24(2):200–205
Rigamonti W, Castagnetti M (2011) Onlay on albuginea: modified onlay preputial island flap urethroplasty for single-stage repair of primary severe hypospadias requiring urethral plate division. Urology 77(6):1498–1502
Braga LH, Lorenzo AJ, Bagli DJ, Dave S, Eeg K, Farhat WA et al (2008) Ventral penile lengthening versus dorsal plication for severe ventral curvature in children with proximal hypospadias. J Urol 180(4 Suppl):1743–1747 (discussion 7–8)
Benson CR, Hoang L, Clavell-Hernandez J, Wang R (2018) Sexual dysfunction in urethral reconstruction: a review of the literature. Sex Med Rev 6(3):492–503
Moriya K, Kakizaki H, Tanaka H, Furuno T, Higashiyama H, Sano H et al (2006) Long-term cosmetic and sexual outcome of hypospadias surgery: norm related study in adolescence. J Urol 176(4 Pt 2):1889–1892 (discussion 92-93)
Blanc T, Ayedi A, El-Ghoneimi A, Abdoul H, Aigrain Y, Paris F et al (2011) Testicular function and physical outcome in young adult males diagnosed with idiopathic 46 XY disorders of sex development during childhood. Eur J Endocrinol 165(6):907–915
Badawy H, Orabi S, Hanno A, Abdelhamid H (2018) Posterior hypospadias: evaluation of a paradigm shift from single to staged repair. J Pediatr Urol 14(1):28.e1–28.e8
Castagnetti M, El-Ghoneimi A (2011) The influence of perioperative factors on primary severe hypospadias repair. Nat Rev Urol 8(4):198–206
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TB: project development, Data collection, Data analysis, Manuscript writing/editing, MP: Statistical analysis, Manuscript writing/editing, MS: Data collection, CM: Data collection, APJ: Data collection, Data analysis, AEG: project development, Data analysis, Manuscript writing/editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Ethical approval was waived by the local Ethics Committee of the university hospital Robert Debré, in view of the retrospective nature of the study and all the procedures being performed were part of the routine care. Meanwhile, a written consent for photography use for research was obtained for each photography shown in the manuscript and signed by the parents.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blanc, T., Peycelon, M., Siddiqui, M. et al. Double-face preputial island flap revisited: is it a reliable one-stage repair for severe hypospadias?. World J Urol 39, 1613–1624 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-020-03324-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-020-03324-7