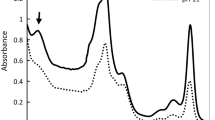
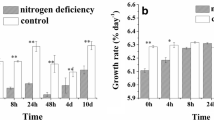
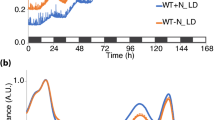
Abstract
Raphidiopsis raciborskii can cause harmful cyanobacterial blooms when concentrations of environmental phosphorus (P) are very low, thus the physiological and molecular mechanisms involved in the acclimation to P need to be characterized better. The growth, chlorophyll fluorescence, alkaline phosphatase, and expression of genes directly involved in P assimilation were compared in the R. raciborskii FACHB 1496 strain grown with and without inorganic P. The specific growth rate (μ), Chl a, and six fluorescence parameters (minimal fluorescence (F0), maximal fluorescence (Fm), maximal variable fluorescence (Fv), electron transport flux (further than QA) per RC (ET0/RC), quantum yield of the electron transport in PSII (ØE0), and the probability that an electron from a trapped exciton is moved into the electron transport chain beyond Q −A (ψ0)) markedly decreased in R. raciborskii in response to experimental P-deficiency. In contrast, the relative variable fluorescence at the J-step (VJ), trapped energy flux (leading to QA reduction) per RC (TR0/RC), and alkaline phosphatase activity significantly increased. In addition, gene expressions involved in the alkaline phosphatase (phoA1 and phoA2), high-affinity inorganic P transporter (pstS1), phosphonate transporter and metabolism (phnD and phnM), and nucleotidase (nucH) were significantly upregulated under P deficiency. However, physiological and molecular responses were resumed rapidly after P re-supplementation following P-deficient conditions. Our results highlight that R. raciborskii can perform coordinated and complex cellular and physiological responses to cope with P deficiency, reflecting R. raciborskii’s multi-faceted machinery to respond to environmental P fluctuations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The authors declare that all data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article. The raw data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Alexander H, Rouco M, Haley S T et al. 2015. Functional group-specific traits drive phytoplankton dynamics in the oligotrophic ocean. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(44): E5972–E5979.
Amaral V, Bonilla S, Aubriot L. 2014. Growth optimization of the invasive cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in response to phosphate fluctuations. European Journal of Phycology, 49(1): 134–141.
Bai F, Liu R, Yang Y J et al. 2014. Dissolved organic phosphorus use by the invasive freshwater diazotroph cyanobacterium, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Harmful Algae, 39: 112–120.
Bai F, Shi J Q, Yang S Q et al. 2020. Interspecific competition between Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and Microcystis aeruginosa on different phosphorus substrates. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(34): 42264–42275.
Beszteri S, Yang I, Jaeckisch N et al. 2012. Transcriptomic response of the toxic prymnesiophyte Prymnesium parvum (N. Carter) to phosphorus and nitrogen starvation. Harmful Algae, 18: 1–15.
Burford M A, Beardall J, Willis A et al. 2016. Understanding the winning strategies used by the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Harmful Algae, 54: 44–53.
Burford M A, Davis T W, Orr P T et al. 2014. Nutrient-related changes in the toxicity of field blooms of the cyanobacterium, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 89(1): 135–148.
Burford M A, Willis A, Chuang A et al. 2018. Recent insights into physiological responses to nutrients by the cylindrospermopsin producing cyanobacterium, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 36(4): 1032–1039.
Carpenter S R, Caraco N F, Correll D L et al. 1998. Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecological Applications, 8(3): 559–568.
Chislock M F, Sharp K L, Wilson A E. 2014. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii dominates under very low and high nitrogen-to-phosphorus ratios. Water Research, 49: 207–214.
Downing J A, McCauley E. 1992. The nitrogen: phosphorus relationship in lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 37(5): 936–945.
Droop M R. 1973. Some thoughts on nutrient limitation in algae. Journal of Phycology, 9(3): 264–272.
Dyhrman S T, Chappell P D, Haley S T et al. 2006. Phosphonate utilization by the globally important marine diazotroph Trichodesmium. Nature, 439(7072): 68–71.
Dyhrman S T, Jenkins B D, Rynearson T A et al. 2012. The transcriptome and proteome of the diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana reveal a diverse phosphorus stress response. PLoS One, 7(3): e33768.
Dyhrman S T, Palenik B. 2003. Characterization of ectoenzyme activity and phosphate-regulated proteins in the coccolithophorid Emiliania huxleyi. Journal of Plankton Research, 25(10): 1215–1225.
Dyhrman S T. 2016. Nutrients and their acquisition: phosphorus physiology in microalgae. In: Borowitzka M A, Beardall J, Raven J A eds. The Physiology of Microalgae. Springer, Cham. p.155–183.
Elser J J, Elser M M, MacKay N A et al. 1988. Zooplanktonmediated transitions between N- and P-limited algal growth. Limnology and Oceanography, 33(1): 1–14.
Frischkorn K R, Harke M J, Gobler C J et al. 2014. De novo assembly of Aureococcus anophagefferens transcriptomes reveals diverse responses to the low nutrient and low light conditions present during blooms. Frontiers in Microbiology, 5: 375.
Fuentes-Valdés J J, Plominsky A M, Allen E E et al. 2016. Complete genome sequence of a Cylindrospermopsin-Producing cyanobacterium, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii CS505, containing a circular chromosome and a single extrachromosomal element. Genome Announcements, 4(4): e00823–16.
González-Gil S, Keafer B A, Jovine R V M et al. 1998. Detection and quantification of alkaline phosphatase in single cells of phosphorus-starved marine phytoplankton. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 164: 21–35.
Guedes I A, Pacheco A B F, Vilar M C P et al. 2019. Intraspecific variability in response to phosphorus depleted conditions in the cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa and Raphidiopsis raciborskii. Harmful Algae, 86: 96–105.
Hamilton D P, Salmaso N, Paerl H W. 2016. Mtigating harmful cyanobacterial blooms: strategies for control of nitrogen and phosphorus loads. Aquatic Ecology, 50(3): 351–366.
Harke M J, Berry D L, Ammerman J W et al. 2012. Molecular response of the bloom-forming cyanobacterium, Microcystis aeruginosa, to phosphorus limitation. Microbial Ecology, 63(1): 188–198.
Harke M J, Gobler C J. 2013. Global transcriptional responses of the toxic cyanobacterium, Microcystis aeruginosa, to nitrogen stress, phosphorus stress, and growth on organic matter. PLoS One, 8(7): e69834.
Ichimura T. 1979. Isolation and culture methods of algae. In: Nishizawa K, Chihara M eds. Methods in Phycological Studies. Kyoritsu Shuppan, Tokyo. p.294–305. (in Japanese)
Ilikchyan I N, McKay R M L, Zehr J P et al. 2009. Detection and expression of the phosphonate transporter gene phnD in marine and freshwater picocyanobacteria. Environmental Microbiology, 11(5): 1314–1324.
Isvánovics V, Shafik H M, Présing M et al. 2000. Growth and phosphate uptake kinetics of the cyanobacterium, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanophyceae) in throughflow cultures. Freshwater Biology, 43(2): 257–275.
Jacob J, Lawlor D W. 1993. In vivo photosynthetic electron transport does not limit photosynthetic capacity in phosphate-deficient sunflower and maize leaves. Plant, Cell & Environment, 16(7): 785–795.
Jacob J. 1995. Phosphate deficiency increases the rate constant of thermal dissipation of excitation energy by Photosystem II in intact leaves of sunflower and maize. Australian Journal of Plant Physiology, 22(3): 417–424.
Karl D M. 2014. Microbially mediated transformations of phosphorus in the sea: new views of an old cycle. Annual Review of Marine Science, 6: 279–337.
Li M Z, Shi X G, Guo C T et al. 2016. Phosphorus deficiency inhibits cell division but not growth in the dinoflagellate Amphidinium carterae. Frontiers in Microbiology, 7: 826.
Lin S J, Litaker R W, Sunda W G. 2016. Phosphorus physiological ecology and molecular mechanisms in marine phytoplankton. Journal of Phycology, 52(1): 10–36.
Lin X, Zhang H, Huang B Q et al. 2012. Alkaline phosphatase gene sequence characteristics and transcriptional regulation by phosphate limitation in Karenia brevis (Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae, 17: 14–24.
Liu Z F, Koid A E, Terrado R et al. 2015. Changes in gene expression of Prymnesium parvum induced by nitrogen and phosphorus limitation. Frontiers in Microbiology, 6: 631.
Liu Z Y, Wu C D. 2012. Response of alkaline phosphatases in the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. FACHB 709 to inorganic phosphate starvation. Current Microbiology, 64(6): 524–529.
Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the method. Methods, 25(4): 402–408.
Lu Z, Lei L M, Lu Y et al. 2021. Phosphorus deficiency stimulates dominance of Cylindrospermopsis through facilitating cylindrospermopsin-induced alkaline phosphatase secretion: integrating field and laboratory-based evidences. Environmental Pollution, 290: 117946.
Luo H, Lin X, Li L et al. 2017. Transcriptomic and physiological analyses of the dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi reveal non-alkaline phosphatase-based molecular machinery of ATP utilisation. Environmental Microbiology, 19(11): 4506–4518.
Moore L R, Ostrowski M, Scanlan D J et al. 2005. Ecotypic variation in phosphorus-acquisition mechanisms within marine picocyanobacteria. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 39(3): 257–269.
Nausch M, Nausch G, Wasmund N. 2004. Phosphorus dynamics during the transition from nitrogen to phosphate limitation in the central Baltic Sea. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 266: 15–25.
Nusch E A. 1980. Comparison of different methods for chlorophyll and phaeopigment determination. Archiv für Hydrobiologie-Beiheft Ergebnisse der Limnologie, 14: 14–36.
Padisák J. 1997. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszaynska) Seenaya et Subba Raju, an expanding, highly adaptive cyanobacterium: worldwide distribution and review of its ecology. Archiv für Hydrobiologie, 107(S1): 563–593.
Paerl H W, Xu H, McCarthy M J et al. 2011. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): the need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Research, 45(5): 1973–1983.
Perron M C, Qiu B S, Boucher N et al. 2012. Use of chlorophyll a fluorescence to detect the effect of microcystins on photosynthesis and photosystem II energy fluxes of green algae. Toxicon, 59(5): 567–577.
Piccini C, Aubriot L, Fabre A et al. 2011. Genetic and eco-physiological differences of South American Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii isolates support the hypothesis of multiple ecotypes. Harmful Algae, 10(6): 644–653.
Pierangelini M, Stojkovic S, Orr P T et al. 2014. Photosynthetic characteristics of two Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii strains differing in their toxicity. Journal of Phycology, 50(2): 292–302.
Posselt A J, Burford M A, Shaw G. 2009. Pulses of phosphate promote dominance of the toxic cyanophyte Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in a subtropical water reservoir. Journal of Phycology, 45(3): 540–546.
Prentice M J, Hamilton D P, Willis A et al. 2019. Quantifying the role of organic phosphorus mineralisation on phytoplankton communities in a warm-monomictic lake. Inland Waters, 9(1): 10–24.
Prentice M J, O’Brien K R, Hamilton D P et al. 2015. High- and low-affinity phosphate uptake and its effect on phytoplankton dominance in a phosphate-depauperate lake. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 75(2): 139–153.
Qin B Q, Xu P Z, Wu Q L et al. 2007. Environmental issues of Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia, 581(1): 3–14.
Saker M L, Griffiths D J. 2001. Occurrence of blooms of the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszynska) Seenayya and Subba Raju in a north Queensland domestic water supply. Marine and Freshwater Research, 52(6): 907–915.
Sebastian M, Ammerman J W. 2009. The alkaline phosphatase PhoX is more widely distributed in marine bacteria than the classical PhoA. The ISME Journal, 3(5): 563–572.
Shen H, Song L R. 2007. Comparative studies on physiological responses to phosphorus in two phenotypes of bloom-forming Microcystis. Hydrobiologia, 592(1): 475–486.
Shi X G, Lin X, Li L et al. 2017. Transcriptomic and microRNAomic profiling reveals multi-faceted mechanisms to cope with phosphate stress in a dinoflagellate. The ISME Journal, 11(10): 2209–2218.
Sinha R, Pearson L A, Davis T W et al. 2014. Comparative genomics of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii strains with differential toxicities. BMC Genomics, 15: 83.
Smith V H. 1983. Low nitrogen to phosphorus ratios favor dominance by blue-green algae in lake phytoplankton. Science, 221(4611): 669–671.
Strasser B J, Strasser R J. 1995. Measuring fast fluorescence transients to address environmental questions: the JIP test. In: Mathis P ed. Photosynthesis: from Light to Biosphere. KAP Press, Dordrecht. p.977–980.
Stucken K, John U, Cembella A et al. 2010. The smallest known genomes of multicellular and toxic cyanobacteria: comparison, minimal gene sets for linked traits and the evolutionary implications. PLoS One, 5(2): e9235.
Su Z C, Dam P, Chen X et al. 2003. Computational inference of regulatory pathways in microbes: an application to phosphorus assimilation pathways in Synechococcus sp. WH8102. Genome Informatics, 13: 3–13.
Su Z S, Olman V, Xu Y. 2007. Computational prediction of Pho regulons in cyanobacteria. BMC Genomics, 8: 156.
Suzuki S, Ferjani A, Suzuki L et al. 2004. The SphS-SphR two component system is the exclusive sensor for the induction of gene expression in response to phosphate limitation in Synechocystis. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279(13): 13234–13240.
Tetu S G, Brahamsha B, Johnson D A et al. 2009. Microarray analysis of phosphate regulation in the marine cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. WH8102. The ISME Journal, 3(7): 835–849.
Vershinina O A, Znamenskaya L V. 2002. The Pho regulons of bacteria. Microbiology, 71(5): 497–511.
Wan L L, Chen X Y, Deng Q H et al. 2019. Phosphorus strategy in bloom-forming cyanobacteria (Dolichospermum and Microcystis) and its role in their succession. Harmful Algae, 84: 46–55.
Welch E B, Cooke G D. 1995. Internal phosphorus loading in shallow lakes: importance and control. Lake and Reservoir Management, 11(3): 273–281.
Willis A, Adams M P, Chuang A W et al. 2015. Constitutive toxin production under various nitrogen and phosphorus regimes of three ecotypes of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii ((Wołoszyńska) Seenayya et Subba Raju). Harmful Algae, 47: 27–34.
Willis A, Chuang A W, Dyhrman S et al. 2019. Differential expression of phosphorus acquisition genes in response to phosphorus stress in two Raphidiopsis raciborskii strains. Harmful Algae, 82: 19–25.
Willis A, Posselt A J, Burford M A. 2017. Variations in carbon-to-phosphorus ratios of two Australian strains of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. European Journal of Phycology, 52(3): 303–310.
Willis A, Woodhouse J N, Ongley S E et al. 2018. Genome variation in nine co-occurring toxic Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii strains. Harmful Algae, 73: 157–166.
Wu J F, Sunda W, Boyle E A et al. 2000. Phosphate depletion in the western North Atlantic Ocean. Science, 289(5480): 759–762.
Wu J R, Shien J H, Shieh H K et al. 2007. Cloning of the gene and characterization of the enzymatic properties of the monomeric alkaline phosphatase (phoX) from Pasteurella multocida strain X-73. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 267(1): 113–120.
Wu Z X, Shi J Q, Li R H. 2009. Comparative studies on photosynthesis and phosphate metabolism of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii with Microcystis aeruginosa and Aphanizomenon flos-aquae. Harmful Algae, 8(6): 910–915.
Wu Z X, Shi J Q, Lin S et al. 2010. Unraveling molecular diversity and phylogeny of Aphanizomenon (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria) strains isolated from China. Journal of Phycology, 46(5): 1048–1058.
Wu Z X, Zeng B, Li R H et al. 2012. Physiological regulation of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria) in response to inorganic phosphorus limitation. Harmful Algae, 15: 53–58.
Xiao M, Hamilton D P, Chuang A et al. 2020. Intra-population strain variation in phosphorus storage strategies of the freshwater cyanobacterium Raphidiopsis raciborskii. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 96(6): fiaa092.
Xu H, Paerl H W, Qin B Q et al. 2010. Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnology and Oceanography, 55(1): 420–432.
Yang Y J, Shi J Q, Jia Y L et al. 2020. Unveiling the impact of glycerol phosphate (DOP) in the dinoflagellate Peridinium bipes by physiological and transcriptomic analysis. Environmental Sciences Europe, 32(1): 38.
Young E B, Tucker R C, Pansch L A. 2010. Alkaline phosphatase in freshwater Cladophora-epiphyte assemblages: regulation in response to phosphorus supply and localization. Journal of Phycology, 46(1): 93–101.
Zhang C Y, Chen G F, Wang Y Y et al. 2018. Physiological and molecular responses of Prorocentrum donghaiense to dissolved inorganic phosphorus limitation. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 129(2): 562–572.
Zhang S F, Yuan C J, Chen Y et al. 2016. Comparative transcriptomic analysis reveals novel insights into the adaptive response of Skeletonema costatum to changing ambient phosphorus. Frontiers in Microbiology, 7: 1476.
Zhang S F, Yuan C J, Chen Y et al. 2019. Transcriptomic response to changing ambient phosphorus in the marine dinoflagellate Prorocentrum donghaiense. Science of the Total Environment, 692: 1037–1047.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 42177055, 41877410) and the Chongqing Postgraduate Scientific Research Innovation Project (Nos. CYS21106, CYS20105)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, J., He, S., Zhao, L. et al. Physiological and molecular responses of invasive cyanobacterium Raphidiopsis raciborskii to ambient phosphorus deficiency. J. Ocean. Limnol. 40, 1792–1803 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-022-1314-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-022-1314-z