Abstract
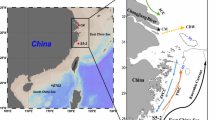
Marine dissolved organic matter (DOM) is one of the largest dynamic pools of organic carbon in the global carbon cycle, yet DOM is still chemically poorly characterized. To better understand the origin, composition, and cycling of DOM in the China marginal sea, dissolved humic substances (DHS) were isolated from seawaters in two locations in the Southern Yellow Sea. The DHS were subdivided into fulvic acids (FAs), humic acids (HAs) and the XAD-4 fractions. Complementary analytical approaches were used to characterize the isolated DHS samples including stable carbon isotopic composition, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), 13C cross polarization magic angle spinning (CP/MAS) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), and pyrolysis gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (Py-GC/MS). The results demonstrated that both DHS samples encountered the influences from marine source, indicating that algal and microbial-derived materials are the predominant precursors for the studied samples. The three fractions of DHS showed different properties. FAs presented more aromatic features, whereas HAs contained more aliphatic lipids and proteinaceous materials. The XAD-4 fractions were enriched in 13C and contained more carbohydrates but less aromatic compounds. The lower molecular weight and higher heteroatom content and number of carboxyl groups for the XAD-4 fractions may give them considerable geochemical significance for aspects of trace metal species, bioavailability of pollutants, mineral weathering and water acidification in marine environments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulla H A N, Minor E C, Dias R F, Hatcher P G. 2010. Changes in the compound classes of dissolved organic matter along an estuarine transect: a study using FTIR and 13C NMR. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 74 (13): 3815–3838.
Aiken G R, McKnight D M, Thorn K A, Thurman E M. 1992. Isolation of hydrophilic organic acids from water using nonionic macroporous resins. Org. Geochem., 18 (4): 567–573.
Aiken G R. 1985. Isolation and concentration techniques for aquatic humic substances. In: Aiken G R, McKnight D M, Wershaw R L, McCarthy P eds. Humic Substances in Soil, Sediment, and Water: Geochemistry, Isolation, and Characterization. John Wiley & Sons, New York. p.363–386.
Bai Y, Su R G, Shi X Y. 2014. Assessing the dynamics of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in the southern Yellow Sea by excitation-emission matrix fluorescence and parallel factor analysis (EEM-PARAFAC). Cont. Shelf Res., 88: 103–116.
Benner R, Fogel M L, Sprague E K, Hodson R E. 1987. Depletion of 13 C in lignin and its implications for stable carbon isotope studies. Nature, 329 (6141): 708–710.
Benner R, Pakulski J D, McCarthy M, Hedges J I, Hatcher P G. 1992. Bulk chemical characteristics of dissolved organic matter in the ocean. Science, 255 (5051): 1561–1564.
Buurman P, Nierop K G J, Kaal J, Senesi N. 2009. Analytical pyrolysis and thermally assisted hydrolysis and methylation of EUROSOIL humic acid samples-a key to their source. Geoderma, 150 (1-2): 10–22.
Cao X Y, Aiken G R, Spencer R G M, Butler K, Mao J D, Schmidt-Rohr K. 2016. Novel insights from NMR spectroscopy into seasonal changes in the composition of dissolved organic matter exported to the Bering Sea by the Yukon River. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 181: 72–88.
Chefetz B, Chen Y, Clapp C E, Hatcher P G. 2000. Characterization of organic matter in soils by thermochemolysis using tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAH). Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., 64 (2): 583–589.
de la Rosa J M, González-Pérez J A, González-Vila F J, Knicker H, Araújo M F. 2011. Molecular composition of sedimentary humic acids from South West Iberian Peninsula: a multi-proxy approach. Org. Geochem., 42 (7): 791–802.
Esteves V I, Otero M, Duarte A C. 2009. Comparative characterization of humic substances from the open ocean, estuarine water and fresh water. Org. Geochem., 40 (9): 942–950.
Esteves V I, Otero M, Santos E B H, Duarte A C. 2007. Stable carbon isotope ratios of tandem fractionated humic substances from different water bodies. Org. Geochem., 38 (6): 957–966.
Green N W, Perdue E M, Aiken G R, Butler K D, Chen H M, Dittmar T, Niggemann J, Stubbins A. 2014. An intercomparison of three methods for the large-scale isolation of oceanic dissolved organic matter. Mar. Chem., 161: 14–19.
Hatcher P G, Spiker E C, Szeverenyi N M, Maciel G E. 1983. Selective preservation and origin of petroleum-forming aquatic kerogen. Nature, 305 (5934): 498–501.
Hedges J I, Hatcher P G, Ertel J R, Meyers-Schulte K J. 1992. A comparison of dissolved humic substances from seawater with Amazon River counterparts by 13 C-NMR spectrometry. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 56 (4): 1753–1757.
Hedges J I, Keil R G, Benner R. 1997. What happens to terrestrial organic matter in the ocean? Org. Geochem., 27 (5-6): 195–212.
Hedges J I. 1992. Global biogeochemical cycles: progress and problems. Mar. Chem., 39 (1-3): 67–93.
Hertkorn N, Benner R, Frommberger M, Schmitt-Kopplin P, Witt M, Kaiser K, Kettrup A, Hedges J I. 2006. Characterization of a major refractory component of marine dissolved organic matter. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 70 (12): 2990–3010.
Jacobs G A, Hur H B, Riedlinger S K. 2000. Yellow and East China Seas response to winds and currents. J. Geophys. Res., 105 (C9): 21947–21968.
Kisand V, Gebhardt S, Rullkötter J, Simon M. 2013. Significant bacterial transformation of riverine humic matter detected by pyrolysis GC-MS in serial chemostat experiments. Mar. Chem., 149: 23–31.
Koch B P, Witt M, Engbrodt R, Dittmar T, Kattner G. 2005. Molecular formulae of marine and terrigenous dissolved organic matter detected by electrospray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 69 (13): 3299–3308.
Koprivnjak J F, Pfromm P H, Ingall E, Vetter T A, Schmitt-Kopplin P, Hertkorn N, Frommberger M, Knicker H, Perdue E M. 2009. Chemical and spectroscopic characterization of marine dissolved organic matter isolated using coupled reverse osmosis-electrodialysis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 73 (14): 4215–4231.
Lam B, Baer A, Alaee M, Lefebvre B, Moser A, Williams A, Simpson A J. 2007. Major structural components in freshwater dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol., 41 (24): 8240–8247.
Leenheer J A. 1981. Comprehensive approach to preparative isolation and fractionation of dissolved organic carbon from natural waters and wastewaters. Environ. Sci. Technol., 15 (5): 578–587.
Li H M, Shi X Y, Shang R N, Han X R. 2013. Distribution of dissolved organic carbon and its influence factors in the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea in autumn. Mar. Environ. Sci., 32 (2): 161–164, 181. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Mao J D, Cory R M, McKnight D M, Schmidt-Rohr K. 2007. Characterization of a nitrogen-rich fulvic acid and its precursor algae from solid state NMR. Org. Geochem., 38 (8): 1277–1292.
Mao J D, Fang X W, Lan Y Q, Schimmelmann A, Mastalerz M, Xu L, Schmidt-Rohr K. 2010. Chemical and nanometerscale structure of kerogen and its change during thermal maturation investigated by advanced solid-state 13C NMR spectroscopy. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 74 (7): 2110–2127.
Mao J D, Kong X Q, Schmidt-Rohr K, Pignatello J J, Perdue E M. 2012. Advanced solid-state NMR characterization of marine dissolved organic matter isolated using the coupled reverse osmosis/electrodialysis method. Environ. Sci. Technol., 46 (11): 5806–5814.
Meyers P A. 1994. Preservation of elemental and isotopic source identification of sedimentary organic matter. Chem. Geol., 114 (3-4): 289–302.
Mopper K, Stubbins A, Ritchie J D, Bialk H M, Hatcher P G. 2007. Advanced instrumental approaches for characterization of marine dissolved organic matter: extraction techniques, mass spectrometry, and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Chem. Rev., 107 (2): 419–442.
Nebbioso A, Piccolo A. 2013. Molecular characterization of dissolved organic matter (DOM): a critical review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 405 (1): 109–124.
Perdue E M, Benner R. 2009. Marine organic matter. In: Senesi N, Xing B S, Huang P M eds. Biophysico-Chemical Processes Involving Natural Nonliving Organic Matter in Environmental Systems. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey. p.407–449.
Reemtsma T, These A, Springer A, Linscheid M. 2006. Fulvic acids as transition state of organic matter: indications from high resolution mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol., 40 (19): 5839–5845.
Simjouw J P, Minor E C, Mopper K. 2005. Isolation and characterization of estuarine dissolved organic matter: comparison of ultrafiltration and C18 solid-phase extraction techniques. Mar. Chem., 96 (3-4): 219–235.
Stevenson F J. 1994. Humus Chemistry: Genesis, Composition, Reactions. 2 nd edn. John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Thurman E M, Malcolm R L. 1981. Preparative isolation of aquatic humic substances. Environ. Sci. Technol., 15 (4): 463–466.
Tremblay L, Alaoui G, Léger M N. 2011. Characterization of aquatic particles by direct FTIR analysis of filters and quantification of elemental and molecular compositions. Environ. Sci. Technol., 45 (22): 9671–9679.
Woods G C, Simpson M J, Kelleher B P, McCaul M, Kingery W L, Simpson A J. 2010. Online high-performance size exclusion chromatography-nuclear magnetic resonance for the characterization of dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol., 44 (2): 624–630.
Xie L P, Wang Z L, Wang B D, Sun X, Sun P X. 2010. Distribution and controlled factor of dissolved organic carbon in Southern Yellow Sea in spring. Mar. Environ. Sci., 29 (5): 636–640. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yuan H M, Song J M, Li X G, Li N, Duan L Q, Qu B X, Lu X, Chen X. 2015. Distribution and impact factors of dissolved organic carbon in the Southern Yellow Sea and the Changjiang Estuary in summer. J. Guangxi Acad. Sci., 31 (3): 155–160. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang Y L, Du J Z, Ding X P, Zhang F F. 2016. Comparison study of sedimentary humic substances isolated from contrasting coastal marine environments by chemical and spectroscopic analysis. Environ. Earth Sci., 75 (5): 378.
Zhang Y L, Du J Z, Peng B, Zhang F F, Zhao X, Zhang J. 2013a. Chemical and spectroscopic characterization of dissolved humic substances in a mangrove-fringed estuary in the eastern coast of Hainan Island, China. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol., 31 (2): 454–463.
Zhang Y L, Du J Z, Zhang F F, Yu Y H, Zhang J. 2011. Chemical characterization of humic substances isolated from mangrove swamp sediments: the Qinglan area of Hainan Island, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci., 93 (3): 220–227.
Zhang Y L, Du J Z, Zhao X, Wu W S, Peng B, Zhang J. 2014. A multi-proxy study of sedimentary humic substances in the salt marsh of the Changjiang Estuary, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci., 151: 295–301.
Zhang Y L, Green N W, Perdue E M. 2013b. Acid-base properties of dissolved organic matter from pristine and oil-impacted marshes of Barataria Bay, Louisiana. Mar. Chem., 155: 42–49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41403108), the West Light Foundation of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. Y412011004), and the Natural Science Foundation of Qinghai Province (No. 2014-ZJ-937Q)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Yang, K., Du, J. et al. Chemical characterization of fractions of dissolved humic substances from a marginal sea—a case from the Southern Yellow Sea. J. Ocean. Limnol. 36, 238–248 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-017-6202-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-017-6202-6