Abstract
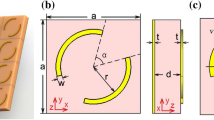
A novel tunable terahertz metamaterials polarization converter (PC) is presented in this paper, whose operating band can be extended by the innovative band splicing technology (combine different PCs with different bands to make the bands splice together) and adjusted into a broadband absorber via adjusting the temperature. Four different units are combined to form a supercell and the phases can be matched through the phase compensation optimization technology. It is a noteworthy finding that the working band becomes wider significantly as the four different working bands join together by the band splicing technology. At the same time, under the action of vanadium dioxide (VO2), the amplitude of reflectance is regulated through the temperature field. The simulation results display that below the critical temperature of 341 K (68 °C), VO2 is treated as an insulator (σ = 20 S/m), the cross-polarization conversion (CPC) can be achieved in the frequency range of 0.91–1.67 THz, whose relative bandwidth (RB) reaches 58.9%. The operating band is expanded compared with four single small units with similar basic structure but different parameters, whose bands are 1.11–1.714 THz, 1.08–1.68 THz, 1.13–1.7 THz, and 1.024–1.608 THz with polarization conversion ratios (PCRs) above 0.9. At high temperature which exceeds the critical temperature, VO2 turns into metal (σ = 200,000 S/m) and the PC is switched into an ultra-broadband absorber with the operating band of 0.744–1.782 THz (the relative bandwidth (RB) of 82.1%), which is significantly different from that at low temperature. Without complex geometry, the reflected PC can broaden the bandwidth on the existing basis. Besides, this metamaterial structure builds a bridge between the polarization converter and the absorber by taking advantage of the non-contact control method, which strengthens the degree of freedom of the electromagnetic metamaterials that would further create a greatly fertile ground for their applications.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Euler, V. Fusco, R. Dickie, R. Cahill, J. Verheggen, Sub-mm wet etched linear to circular polarization fss based polarization converters. IEEE Trans. Antenn. Propag. 59(8), 3103–3106 (2011)
C. Dietlein, A. Luukanen, Z. Popovi, E. Grossman, A w-band polarization converter and isolator. IEEE Trans. Antenna Propag. 55(6), 1804–1809 (2007)
D. Molter, G. Torosyan, G. Ballon, L. Drigo, R. Beigang, J. Léotin, Step-scan time-domain terahertz magneto-spectroscopy. OPT. Express 20(6), 5993–6002 (2012)
M. Beruete, M. Navarro-Cia, M. Sorolla, I. Campillo, Polarization selection with stacked hole array metamaterial. J. Appl. Phys. 103(5), 1353 (2008)
M. Mutlu, E. Ozbay, A transparent 90 polarization rotator by combining chirality and electromagnetic wave tunneling. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100(5), 051909 (2012)
D.R. Smith, Metamaterials and negative refractive index. Science 305(5685), 788–792 (2004)
J.B. Pendry, A.J. Holden, W.J. Stewart, I. Youngs, Extremely low frequency plasmons in metallic mesostructures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 4773–4776 (1996)
H. Chen, H. Ma, S. Qu, J. Wang, Y. Li, H. Yuan, Z. Xu, Ultra-wideband polarization conversion metasurfaces. IEEE 122(4), 1009–1011 (2014)
Y. Cheng, Y. Nie, X. Wang, R. Gong, An ultrathin transparent metamaterial polarization transformer based on a twist-split-ring resonator. Appl. Phys. A-Mater 111(1), 209–215 (2013)
A.R. Shelby, Experimental verification of a negative index of refraction. Science 292(5514), 77–79 (2001)
P.U. Jepsen, D.G. Cooke, M. Koch, Terahertz spectroscopy and imaging – modern techniques and applications. Laser Photon. Rev. 6(3), 418–418 (2012)
T. Kleine-Ostmann, T. Nagatsuma, A review on terahertz communications research. J. Infrared Millim. TE. 32(2), 143–171 (2011)
N. Yu, P. Genevet, M.A. Kats, F. Aieta, J.P. Tetienne, F. Capasso, Z. Gaburro, Light propagation with phase discontinuities: generalized laws of reflection and refraction. Science 334(6054), 333–337 (2011)
N.K. Grady, J.E. Heyes, D.R. Chowdhury, Y. Zeng, M.T. Reiten, A.K. Azad, A.J. Taylor, D.A.R. Dalvit, H.T. Chen, Terahertz metamaterials for linear polarization conversion and anomalous refraction. Science 340(6138), 1304–1307 (2013)
W.W. Liu, S.Q. Chen, Z.C. Li, H. Cheng, P. Yu, J.X. Li, Realization of broadband cross-polarization conversion in transmission mode in the terahertz region using a single-layer metasurface. Opt. Lett. 40, 13 (2015)
D.L. Markovich, A. Andryieuski, M. Zalkovskij, R. Malureanu, A.V. Lavrinenko, Metamaterial polarization converter analysis: limits of performance. Appl. Phys. B 112(2), 143–152 (2013)
J. Han, A. Lakhtakia, C.W. Qiu, Terahertz metamaterials with semiconductor split-ring resonators for magnetostatic tunability. Opt. Express 16(19), 14390–14396 (2012)
M. Nakajima, N. Takubo, Z. Hiroi, Y. Ueda, T. Suemoto, Photoinduced metallic state in vo2 proved by the terahertz pump-probe spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92(1), 6853 (2008)
S. Wang, L. Kang, D.H. Werner, Hybrid resonators and highly tunable terahertz metamaterials enabled by vanadium dioxide (vo2). Sci. Rep. 7(1), 4326 (2017)
D. Wang, L. Zhang, Y. Gu, M.Q. Mehmood, Y. Gong, A. Srivastava, L. Jian, T. Venkatesan, C. Qiu, M. Hong, Switchable ultrathin quarter-wave plate in terahertz using active phase-change metasurfac. Sci. Rep. 5, 15020 (2015)
M.J. Dicken, K. Aydin, I.M. Pryce, L.A. Sweatlock, H.A. Atwater, Frequency tunable near-infrared metamaterials based on vo2 phase transition. Opt. Express 17(20), 18330–18339 (2009)
Z. Yi, H. Qiuping, C. Honglei, L. Xiaoxia, L. Yalin, A broadband and switchable vo2-based perfect absorber at the thz frequency. Opt. Commun. 426, 443–449 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Open Research Program in China’s State Key Laboratory of Millimeter Waves (Grant No. K201927).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Ye, H., Zhao, Y. et al. A tunable ultra-wideband cross-polarization conversion based on the band splicing technology. Appl. Phys. B 127, 69 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-021-07622-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-021-07622-9