Abstract
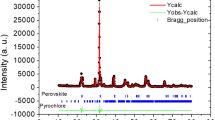
The lead-free ceramics K0.5Na0.5NbO3: x wt% Er3+ (x = 0, 1, 2, 3 and 4) were produced via solid-state method. The ceramic was sintered at 1100 °C to produce a pure-phase perovskite with an orthorhombic structure. No extra phases in the XRD spectra demonstrate that all the Er3+ ions have dispersed into the host lattice. At room temperature, PL emission spectra were examined under the wavelengths 488 and 980 nm. In both emission spectra, green emission bands (528 and 549 nm) and slightly faint red emission bands (662 nm) were found. Observing the effect of pump power revealed that two photons are involved in the emission process. The time decay profile indicates an average lifetime of Er3+ ions is 25.05 μs. The ferroelectric hysteresis loop at room temperature showed decent shapes with good remnant. Thus, by combining the optical and ferroelectric properties, KNN may have potential applications to be employed in optoelectronic devices.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The above-mentioned authors have all the relevant data associated with this research work and will be dedicated to sharing that if they are asked to do so in the future.
References
R. Groß, D. Bunke, C.-O. Gensch, S. Zangl, and A. Manhart, Study on Hazardous Substances in Electrical and Electronic Equipment, Not Regulated by the RoHS Directive Final Report Content, 2008
X. Vendrell, J.E. García, X. Bril, D.A. Ochoa, L. Mestres, G. Dezanneau, Improving the functional properties of (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3 piezoceramics by acceptor doping. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 35(1), 125–130 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2014.08.033
H. Wu, S. Shi, X. Liu, H. Wang, J. Xu, L. Yang, W. Qiu, S. Zhou, Photoluminescence and outstanding transparent in Er3+-doped (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3-(Sr0.5Ba0.5)(Bi0.5Nb0.5)O3 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 34, 612 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10021-9
J.P. Sharma, D. Kumar, A.K. Sharma, Structural and dielectric properties of pure potassium sodium niobate (KNN) lead-free ceramics. Solid State Commun. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2021.114345
Q. Zhang, L. Luo, J. Gong, P. Du, W. Li, G. Yuan, Photoluminescence, thermoluminescence and reversible photoluminescence modulation of multifunctional optical materials Pr3+ doped KxNa1-xNbO3 ferroelectric ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 40(12), 3946–3955 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2020.05.003
Y.Y.S. Cheng, L. Liu, Y. Huang, L. Shu, Y.X. Liu, L. Wei, J.F. Li, All-inorganic flexible (K, Na)NbO3-based lead-free piezoelectric thin films spin-coated on metallic foils. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13(33), 39633–39640 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c11418
M. Dolhen, A. Mahajan, R. Pinho, M.E. Costa, G. Trolliard, P.M. Vilarinho, Sodium potassium niobate (K0.5Na0.5NbO3, KNN) thick films by electrophoretic deposition. RSC Adv. 5(6), 4698–4706 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra11058g
W. Li, D. Wang, X. Li, P. Li, P. Fu, C. Hu, J. Hao, W. Li, Q. Zhang, Optical temperature sensing properties and thermoluminescence behavior in Er-modified potassium sodium niobate-based multifunctional ferroelectric ceramics. J. Mater. Chem. C. Mater. 10(33), 11891–11902 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1039/d2tc01268e
L. Xiang, H. Gangbin, W. Huangtao, S. Shaoyang, W. Hua, X. Jiwen, Y. Ling, Q. Wei, Transmittance, photoluminescence and electrical properties in Er-doped 0.98K0.5Na0.5NbO3-0.02Sr(Yb0.5Ta0.5)O3 ferroelectric ceramics. J. Electron. Mater. 51(7), 3476–3484 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-09626-3
X. Wu, S. Lu, K.W. Kwok, Photoluminescence, electro-optic response and piezoelectric properties in pressureless-sintered Er-doped KNN-based transparent ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 695, 3573–3578 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.11.409
A. Banwal, R. Bokolia, Efficient tunable temperature sensitivity in thermally coupled levels of Er3+/Yb3+ co-doped BaBi2Nb2O9 ferroelectric ceramic. J. Lumin. 263, 120071 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2023.120071
S. Kumar, N. Thakur, Effect of alkali metal (Na, K) ion ratio on structural, optical and photoluminescence properties of K0.5Na0.5NbO3 ceramics prepared by sol-gel technique. Bull. Mater. Sci. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-020-02341-x
S. Bairagi, S.W. Ali, Effects of surface modification on electrical properties of KNN nanorod-incorporated PVDF composites. J. Mater. Sci. 54, 11462–11484 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-03719-x
Y. Zhang, L. Duan, A. Zhang, D. Wang, R. Chu, Z. Xu, G. Li, C. Zhang, Photoluminescence, electrical properties and electron band structure of (Ho, Yb)3+ co-doped SrBi4Ti4O15 multifunctional ceramics. Ceram. Int. 48(7), 9248–9257 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.12.111
R. Bokolia, O.P. Thakur, V.K. Rai, S.K. Sharma, K. Sreenivas, Dielectric, ferroelectric and photoluminescence properties of Er3+ doped Bi4Ti3O12 ferroelectric ceramics. Ceram. Int. 41(4), 6055–6066 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.01.062
X. Wu, C.M. Lau, K.W. Kwok, Effect of phase transition on photoluminescence of Er-doped KNN ceramics. J. Lumin. 155, 343–350 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2014.07.005
M. Narwan, A. Banwal, R. Sharma, R. Bokolia, Non-invasive thermal sensing and improved recoverable energy storage density of Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3: Er3+ doped multifunctional ferroelectric ceramic. J. Lumin. 265, 120236 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2023.120236
J. Wangi, Y. Sun, S. Shi, H. Wang, J. Xu, L. Yang, W. Qi, Effects of Er3+ doping on the structure and electro-optical properties of 0.94(K0.5Na0.5)NbO3–0.06Sr(Zn1/3Nb2/3)O3 ceramics. Bull. Mater. Sci. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-021-02596-y
L.N. Liu, X.M. Chen, R.Y. Jing, H.L. Lian, W.W. Wu, Y.P. Mou, P. Liu, Electrical and photoluminescence properties of (Bi0.5−x/0.94Erx/0.94Na0.5)0.94Ba0.06TiO3 lead-free ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 5233–5239 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00822-2
C. Lin, X. Wu, M. Lin, Y. Huang, J. Li, Optical, luminescent and optical temperature sensing properties of (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3-ErBiO3 transparent ceramics. J. Alloy. Compd. 706, 156–163 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.02.245
Y.J. Du, L.I.D.J. Martin, D. Poelman, Reversible yellow-gray photochromism in potassium-sodium niobate-based transparent ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 41, 1925–1933 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2020.10.046
L.N. Liu, X.M. Chen, Y.D. Xu, H.L. Lian, P. Liu, Light-triggered “on-off” switchable dielectric constant in (Bi0.5Na0.5)0.94Ba0.06TiO3 lead-free ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 123, 022904 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0153351
M.S. El-Eskandarany, Mechanically induced solid-state reduction. Mech. Alloy. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-4557-7752-5.00006-1
L. Kozielski, K. Feliksik, B. Wodecka-Duś, D. Szalbot, S. Tutu, Hot pressed K0.5Na0.5NbO3 material for piezoelectric transformer for energy harvesting. Arch. Metall. Mater. 63(3), 1275–1280 (2018). https://doi.org/10.24425/123801
A. Banwal, R. Bokolia, Phase evolution and microstructure of BaBi2Nb2O9 ferroelectric ceramics. Mater. Today Proc. 46, 10121–10124 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.09.380
H.C. Thong, C. Zhao, Z. Zhou, C.F. Wu, Y.X. Liu, Z.Z. Du, J.F. Li, W. Gong, K. Wang, Technology transfer of lead-free (K, Na)NbO3-based piezoelectric ceramics. Mater. Today 29, 37–48 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2019.04.016
A. Dahiya, O. P. Thakur, and J. K. Juneja, Sensing and actuating applications of potassium sodium niobate: Use of potassium sodium niobate in sensor and actuator, in Proc. of the Int. Conf. on Sens. Tech. ICST, pp. 383–386, (2013), doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSensT.2013.6727680
Q. Jin, M. Jiang, S. Han, Y. Yan, Microstructure, optical and electrical properties of Bi and Ba co-doped K0.52Na0.48NbO3 transparent ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29(15), 13407–13417 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9466-5
S. Dwivedi, T. Pareek, S. Kumar, Structure, dielectric, and piezoelectric properties of K0.5Na0.5NbO3-based lead-free ceramics. RSC Adv. 8(43), 24286–24296 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra04038a
L. Gao, Z. Liu, P. Ren, R. Liang, T. Li, K. Guo, B. Xie, J. Lu, P. Mao, J. Tian, L. Shu, Inhibiting oxygen vacancies and twisting NbO6 octahedron in erbium modified KNN-based multifunctional ceramics. J. Materiomics (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmat.2023.05.007
E. Makagon, O. Kraynis, R. Merkle, J. Maier, I. Lubomirsky, Non-classical electrostriction in hydrated acceptor doped BaZrO3: proton trapping and dopant size effect. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2104188 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202104188
H. Sun, Q. Zhang, X. Wang, M. Gu, Green and red upconversion luminescence of Er3+-doped K0.5Na0.5NbO3 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 40(2), 2581–2584 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.10.089
A. Banwal, R. Bokolia, Enhanced upconversion luminescence and optical temperature sensing performance in Er3+ doped BaBi2Nb2O9 ferroelectric ceramic. Ceram. Int. 48(2), 2230–2240 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CERAMINT.2021.09.314
W.U. Xiao, Rare-earth-doped KNN-based ceramics for photoluminescent and electro-optic applications (The Hong Kong Polytechnic College, Hong Kong, 2015)
D. Peng, H. Zou, Upconversion luminescence, ferroelectrics and piezoelectrics of Er doped SrBi4Ti4O15. AIP Adv. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4773318
W. Li, Z. Xu, R. Chu, P. Fu, G. Zang, Improved piezoelectric property and bright upconversion luminescence in Er doped (Ba0.99Ca0.01)(Ti0.98Zr0.02)O3 ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 583, 305–308 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.08.103
H. Liu, J. Wang, H. Wang, J. Xu, C. Zhou, W. Qiu, Er3+ and Sr(Bi0.5Nb0.5)O3-modified (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3: a new transparent fluorescent ferroelectric ceramic with high light transmittance and good luminescence performance. Ceram. Int. 48(3), 4230–4237 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.10.215
Z. Cao, J. Wang, C. Zhang, X. Mao, L. Luo, Flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator based on the Er3+ doped lead-free (Na0.5Bi0.5)TiO3-BaTiO3 piezoelectric nanofibers with strong upconversion luminescence. J. Alloys Compd. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.165766
M.K. Mahata, T. Koppea, T. Mondal, C. Brüsewitza, K. Kumar, V.K. Rai, H. Hofsässa, U. Vetter, Incorporation of Zn2+ ions into BaTiO3:Er3+/Yb3+ nanophosphor: an effective way to enhance upconversion, defect luminescence and temperature sensing. PCCP 17(32), 20741–20753 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cp01874a
D.B. Paulaviciene, N. Traskina, R. Vargalis, A. Katelnikovas, S. Sakirzanovas, Thermal decomposition synthesis of Er3+-activated NaYbF4 upconverting microparticles for optical temperature sensing. J. Lumin. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2019.116672
R. Bokolia, O.P. Thakur, V.K. Rai, S.K. Sharma, K. Sreenivas, Electrical properties and light up conversion effects in Bi3.79Er0.03Yb0.18Ti3-xWxO12 ferroelectric ceramics. Ceram. Int. 42(5), 5718–5730 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.12.103
A. Banwal, R. Bokolia, Thermometric sensing performance in Erbium modified SrBi2-xNb2ErxO9 ferroelectric ceramic for optoelectronic devices. Ceram. Int. 48(23), 34405–34414 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.08.019
Q. Zhang, K. Chen, L. Wang, H. Sun, X. Wang, X. Hao, A highly efficient, orange light-emitting (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3:Sm3+/Zr4+ lead-free piezoelectric material with superior water resistance behavior. J. Mater. Chem. C. Mater. 3(20), 5275–5284 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4tc02995j
L. Wang, B. Lua, X. Liu, Y. Shi, J. Li, Y. Liu, Fabrication and upconversion luminescence of novel transparent Er2O3 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2019.11.048
Y.A. Genenko, J. Glaum, M.J. Hoffmann, K. Albe, Mechanisms of aging and fatigue in ferroelectrics. MSEB 192(C), 52–82 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2014.10.003
Acknowledgements
We thank the Department of Applied Physics, Delhi Technological University, for letting us use research facilities. The authors, MV and SS, would like to extend their sincere appreciation to their supervisor, Dr. RB, for her guidance, patience, and constant encouragement throughout their research work. They also wish to express their gratitude to AB for her valuable contributions to the experiment and manuscript writing, her kindness and friendship, and for creating a positive research environment. Finally, the authors would like to thank their family and friends for their unwavering support, understanding, inspiration, and love.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Muskan Varshney: Conceptualization, data curation, writing-original draft, made all the measurements, Shreya Soni: Conceptualization, data curation, writing-original draft, made all the measurements, Ankita Banwal: Data curation, writing-editing, Megha Narwan: Data curation, writing-editing, Manoj Verma: XRD analysis, writing-editing, Renuka Bokolia: Supervision, reviewing and editing of the original draft.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Varshney, M., Soni, S., Banwal, A. et al. Effect of Er3+ ion incorporation on the structural, photoluminescence, and ferroelectric properties of K0.5Na0.5NbO3 ceramic for optoelectronic applications. Appl. Phys. A 130, 267 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07447-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07447-1