Abstract
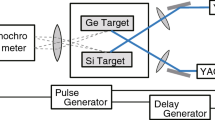
We collided silicon and germanium laser-induced plumes in helium background gas to clarify the behavior of the plumes after the collision. The expansion of the silicon and germanium species in the mixed plume after the collision was observed separately by spectroscopic measurements and the degree of mixing was evaluated by the experimental results. When the pressure of the background gas was 2000 Pa, the plumes moved backward after the collision with the counter-propagating shock wave, and no mixing of the plumes was observed. The effect of the counter-propagating shock wave was discussed by comparing with the results of numerical calculations based on the compressible Euler equations. At 300 Pa, the plumes concentrated at about 1 mm around the central region just after the collision and almost 100% mixing occurred in this region. The concentration and mixing of the plumes in the central region is a key to forming well-mixed plume. Stagnation and partial mixing of the plumes were observed at intermediate pressures. By decreasing the background helium gas pressure from 2000 to 300 Pa, the degree of mixing increased from 0 to about 100%. The results are compared with those in argon background gas to discuss effects of mean free path. The effects of counter-propagating shock wave, mean free path and the onset time of the collision on the backward movement and mixing of the plumes are discussed.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
D.B. Chrisey, G.K. Hubler, Pulsed laser deposition of thin films (Wiley, New York, 1994)
D. Bäuerle, Laser processing and chemistry (Springer, Berlin, 2000)
B.A. Remington, R.P. Drake, H. Takabe, D. Arnett, Phys. Plasmas 7, 1641 (2000)
K.F. Al-Shboul, S.S. Harilal, S.M. Hassan, A. Hassanein, J.T. Costello, T. Yabuuchi, K.A. Tanaka, Y. Hirooka, Phys. Plasmas 21, 013502 (2014)
Y. Yamada, T. Orii, I. Umezu, S.T.S. Takeyama, T.Y.T. Yoshida, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 35, 1361 (1996)
D.B. Geohegan, A.A. Puretzky, G. Duscher, S.J. Pennycook, Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 2987 (1998)
P.W. Rambo, J. Denavit, Phys. Plasmas 1, 4050 (1994)
J. Dardis, J.T. Costello, Spectrochim. Acta Part B 65, 627 (2010)
S.L. Gupta, P.K. Pandey, R.K. Thareja, Phys. Plasmas 20, 013511 (2013)
Z. Yang, W. Wei, J. Han, J. Wu, X. Li, S. Jia, Phys. Plasmas 22, 073511 (2015)
N. Gambino, P. Hayden, D. Mascali, J. Costello, C. Fallon, P. Hough, P. Yeates, A. Anzalone, F. Musumeci, Appl. Surf. Sci. 272, 69 (2013)
H. Luna, K.D. Kavanagh, J.T. Costello, J. Appl. Phys. 101, 033302 (2007)
P. Hough, C. McLoughlin, S.S. Harilal, J.P. Mosnier, J.T. Costello, J. Appl. Phys. 107, 024904 (2010)
A. Higo, K. Katayama, H. Fukuoka, T. Yoshida, T. Aoki, M. Yaga, I. Umezu, Appl. Phys. A 126, 304 (2020)
K. Katayama, Y. Horai, H. Fukuoka, T. Kinoshita, T. Yoshida, T. Aoki, I. Umezu, Appl. Phys. A 124, 150 (2018)
Y.B. Zel’Dovich, Y.P. Raizer, Physics of shock waves and high-temperature hydrodynamic phenomena (Academic Press, Cambridge, 1966)
N. Arnold, J. Gruber, J. Heitz, Appl. Phys. A 69, S87 (1999)
S.S. Harilal, G.V. Miloshevsky, P.K. Diwakar, N.L. LaHaye, A. Hassanein, Phys. Plasmas 19, 083504 (2012)
D.B. Geohegan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 60, 2732 (1992)
R.A. Smith, J. Lazarus, M. Hohenberger, A. Marocchino, J.S. Robinson, J.P. Chittenden, A.S. Moore, E.T. Gumbrell, M. Dunne, Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 49, B117 (2007)
T. Kinoshita, H. Fukuoka, I. Umezu, Mater. Sci. Forum 910, 96 (2018)
O.A. Ranjbar, Z. Lin, A.N. Volkov, Vacuum 157, 361 (2018)
T.E. Itina, J. Hermann, P. Delaporte, M. Sentis, Phys. Rev. E 66, 066406 (2002)
Z. Chen, D. Bleiner, A. Bogaerts, J. Appl. Phys. 99, 063304 (2006)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP 19K03815.
Funding
Japan Society for the Promotion of Science,KAKENHI Grant Number JP 19K03815,Ikurou Umezu
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
See supplementary material for the animation movie of Fig. 2 (MP4 3328 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Katayama, K., Kinoshita, T., Okada, R. et al. Mixing of laser-induced plumes colliding in a background gas. Appl. Phys. A 128, 1007 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-06136-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-06136-1