Abstract
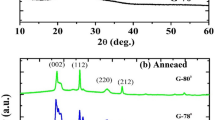
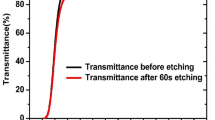
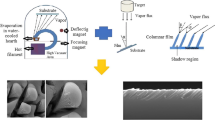
The columnar growth angle-dependent tungsten oxide (WO3) thin films were grown by using the Glancing angle sputter deposition (GLAD) technique with varying different substrate angles (00, 700, 750, and 800) on Fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) and Corning glass (CG) corning glass substrates at room temperature. The surface morphology, crystallographic structure, optical, and electrochemical properties were determined using X-ray diffraction (XRD), Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), Ultraviolet–Visible (UV–Vis) spectrometer, and electrochemical analyzer, respectively. The structural properties reveal that the films are amorphous in nature. FE-SEM studies observed the columnar growth of the nano-rods and surface porosity. The optical transmittance of the deposited films was decreased from 83 to 78%, and the optical bandgap decreased from 3.08 to 2.88 eV with increasing GLAD angle. The electrochemical studies reveal that the GLAD angle influenced the coloration efficiency (CE). The highest CE of 32 cm2/C at 600 nm and highest Diffusion coefficient (DC) of 6.529 × 10–9 cm2 s−1 of the films was observed for the films deposited at an angle of 750.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- WO3 :
-
Tungsten oxide
- GLAD:
-
Glancing angle sputter deposition
- RF:
-
Radio frequency
- FTO:
-
Fluorine doped tin oxide
- CG:
-
Corning glass
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
- FE-SEM:
-
Field emission scanning electron microscope
- CE:
-
Coloration efficiency
- TMO:
-
Transition metal oxides
- CV:
-
Cyclic voltammograms
- DC:
-
Diffusion coefficient
- WE:
-
Working electrode
- RE:
-
Reference electrode
- CE:
-
Counter electrode
References
D. Shao, M. Yu, J. Lian, S. Sawyer, An ultraviolet photodetector fabricated from WO3 nanodiscs/reduced graphene oxide composite material. Nanotechnology 24(29), 295701 (2013)
H. Simchi, B.E. McCandless, T. Meng, W.N. Shafarman, Structural, optical, and surface properties of WO3 thin films for solar cells. J Alloys Compd. 617(302), 609–615 (2014)
J.L. Solis, S. Saukko, L. Kish, C.G. Granqvist, V. Lantto, Semiconductor gas sensors based on nanostructured tungsten oxide. Thin Solid Films 391(2), 255–260 (2001)
V. Lokhande, A. Lokhande, G. Namkoong, J.H. Kim, T. Ji, Charge storage in WO 3 polymorphs and their application as supercapacitor electrode material. Results Phys. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.02.012
M. Bb, K. VM., Structural, morphological and optical properties of electron beam evaporated WO 3 thin films. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 11(6), 1232–1237 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtusci.2016.12.003
Y. Djaoued, S. Balaji, R. Brüning, Electrochromic devices based on porous tungsten oxide thin films. J. Nanomater. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/674168
M. Meenakshi, V. Gowthami, P. Perumal, R. Sivakumar, C. Sanjeeviraja, Influence of dopant concentration on the electrochromic properties of tungsten oxide thin films. Electrochim. Acta. 174, 302–314 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.05.187
R. Sivakumar, R. Gopalakrishnan, M. Jayachandran, C. Sanjeeviraja, Preparation and characterization of electron beam evaporated WO3 thin films. Opt. Mater. (Amst). 29(6), 679–687 (2007)
S. Park, H. Kim, C. Jin, C. Lee, Intense ultraviolet emission from needle-like WO 3 nanostructures synthesized by noncatalytic thermal evaporation. Nanoscale Res. Lett. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-6-451
S. Badilescu, P.V. Ashrit, Study of sol-gel prepared nanostructured WO3 thin films and composites for electrochromic applications. Solid State Ionics 158(1–2), 187–197 (2003)
K. Naveen Kumar, H. Shaik, M.V. Sathish, S.S. Abdul, On the bonding and electrochemical performance of sputter deposited WO3 thin films. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 872(1), 01247 (2020)
M.B. Johansson, B. Zietz, G.A. Niklasson, L. Österlund, Optical properties of nanocrystalline WO3 and WO3-x thin films prepared by DC magnetron sputtering. J. Appl. Phys. 115(21), 213510 (2014)
K. Naveen Kumar, H. Shaik, L.N. Chandrashekar, P. Aishwarya, S. Abdul Sattar, G. Nithya et al., On ion transport during the electrochemical reaction on plane and GLAD deposited WO3 thin films. Mater. Today Proc. 59, 275–282 (2021)
K. Naveen Kumar, H. Shaik, A. Pawar, L.N. Chandrashekar, S.A. Sattar, G. Nithya et al., Effect of annealing and oxygen partial pressure on the RF sputtered WO3 thin films for electrochromic applications. Mater. Today. Proc. 59, 339–344 (2021)
V.V. Kondalkar, R.R. Kharade, S.S. Mali, R.M. Mane, P.B. Patil, P.S. Patil et al., Nanobrick-like WO3 thin films: Hydrothermal synthesis and electrochromic application. Superlattices Microstruct. 73, 290–295 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2014.05.039
N.E. Stankova, P.A. Atanasov, T.J. Stanimirova, A.O. Dikovska, R.W. Eason, Thin (0 0 1) tungsten trioxide films grown by laser deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 247(1–4), 401–405 (2005)
R. Levinas, N. Tsyntsaru, M. Lelis, H. Cesiulis, Synthesis, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study and photoelectrochemical behaviour of as-deposited and annealed WO3 films. Electrochim. Acta 225, 29–38 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.12.112
V. Madhavi, P. Kondaiah, H. Shaik, K.N. Kumar, T.S.S. Kumar Naik, G.M. Rao et al., Fabrication of porous 1D WO3 NRs and WO3/BiVO4 hetero junction photoanode for efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting. Mater. Chem. Phys. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.125095
J. Gupta, H. Shaik, K.N. Kumar, A review on the prominence of porosity in tungsten oxide thin films for electrochromism. Ionics (Kiel). 27(6), 2307–2334 (2021)
C. Charles, N. Martin, M. Devel, J. Ollitrault, A. Billard, Correlation between structural and optical properties of WO3 thin films sputter deposited by glancing angle deposition. Thin Solid Films 534, 275–281 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2013.03.004
K. Robbie, Advanced techniques for glancing angle deposition. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Microelectron. Nanom. Struct. 16(3), 1115 (1998)
M. Layani, P. Darmawan, W.L. Foo, L. Liu, A. Kamyshny, D. Mandler et al., Nanostructured electrochromic films by inkjet printing on large area and flexible transparent silver electrodes. Nanoscale 6(9), 4572–4576 (2014)
A. Rydosz, K. Dyndał, K. Kollbek, W. Andrysiewicz, M. Sitarz, K. Marszałek, Structure and optical properties of the WO3 thin films deposited by the GLAD magnetron sputtering technique. Vacuum (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2020.109378
J.J. Steele, M.J. Brett, Nanostructure engineering in porous columnar thin films: Recent advances. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 18(4), 367–379 (2007)
L. Xiao, Y. Lv, W. Dong, N. Zhang, X. Liu, Dual-functional WO3 nanocolumns with broadband antireflective and high-performance flexible electrochromic properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8(40), 27107–27114 (2016)
J. Yuan, B. Wang, H. Wang, Y. Chai, Y. Jin, H. Qi et al., Electrochromic behavior of WO 3 thin films prepared by GLAD. Appl. Surf. Sci. 447, 471–478 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.03.248
J. Wang, E. Khoo, P.S. Lee, J. Ma, Controlled synthesis of WO3 nanorods and their electrochromic properties in H2SO4 electrolyte. J. Phys. Chem. C. 113(22), 9655–9658 (2009)
Y.M. Lu, C.P. Hu, The colored and bleached properties of tungsten oxide electrochromic films with different substrate conductivities. J. Alloys Compd. 449(1–2), 389–392 (2008)
M. Laurenti, S. Bianco, M. Castellino, N. Garino, A. Virga, C.F. Pirri et al., toward plastic smart windows: optimization of indium tin oxide electrodes for the synthesis of electrochromic devices on polycarbonate substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8(12), 8032–8042 (2016)
V. Madhavi, P. Kondaiah, O.M. Hussain, S. Uthanna, Structural, optical and electrochromic properties of RF magnetron sputtered WO3 thin films. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 454, 141–147 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2014.07.029
Acknowledgements
The author acknowledges AICTE (8-39/RIFD/RPS/POLICY-1/2016) in New Delhi, India for financial support.
Funding
AICTE, 8-39/RIFD/RPS/POLICY-1/2016, Habibuddin Shaik.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Naveen Kumar, K., Shaik, H., Madhavi, V. et al. Glancing angle sputter deposited tungsten trioxide (WO3) thin films for electrochromic applications. Appl. Phys. A 128, 985 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-06124-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-06124-5