Abstract
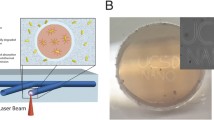
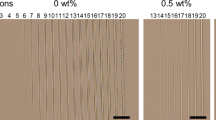
Polyacrylamide (PAA) hydrogels have applications as biochip materials due to their unique optical properties, including high transparency and low refractive indices similar to that of water, as well as their low cost. However, it is difficult to carry out microfabrication using these materials because they undergo nonuniform shrinkage when exposed to the air as water is lost via evaporation. The present study demonstrates the surface microfabrication of PAA hydrogels using a femtosecond laser under two different processing conditions. In some trials, the PAA hydrogel was swollen completely in water and then irradiated with the laser to fabricate a microgroove. In others, a dried hydrogel containing glycerol and having undergone uniform shrinkage was irradiated in air to fabricate the microgroove. Following the fabrication process, the dried gel was again swollen in water to reduce its refractive index. In both scenarios, microgrooves were fabricated by both single and multiple laser scanning. The results show that, for both processing conditions, single laser scanning generated narrow grooves with minimal depths as a consequence of the flexibility and swelling behavior of the hydrogel. In the case of multiple laser scanning, the shape of a microgroove having an aspect ratio of approximately 1.0 was retained on the surface of a PAA hydrogel with a refractive index of 1.34.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Nakajima, S. Ishihara, D. Imoto, S. Sawai, Nat. Commun. 5, 5367 (2014)
J. Zhou, C. Tu, Y. Liang, B. Huang, Y. Fang, X. Liang, X. Ye, Analyst 145, 1706 (2020)
Y.S. Torisawa, A. Takagi, Y. Nashimoto, T. Yasukawa, H. Shiku, T. Matsue, Biomaterials 28, 559 (2007)
H.N. Kim, N. Choi, BioChip J. 13, 8 (2019)
P. Gogoi, S. Sepehri, Y. Zhou, M.A. Gorin, C. Paolillo, E. Capoluongo, K. Gleason, A. Payne, B. Boniface, M. Cristofanilli, T.M. Morgan, P. Fortina, K.J. Pienta, K. Handique, Y. Wang, PLoS ONE 11, e0147400 (2016)
D.H. Kim, C.H. Seo, K. Han, K.W. Kwon, A. Levchenko, K.Y. Suh, Adv. Funct. Mater. 19, 1579 (2009)
M. Ghibaudo, L. Trichet, J. Le Digabel, A. Richert, P. Hersen, B. Ladoux, Biophys. J. 97, 357 (2009)
J. Zhou, A.V. Ellis, N.H. Voelcker, Electrophoresis 31, 2 (2010)
T. Fujii, Microelectron. Eng. 61–62, 907 (2002)
M.S. Giridhar, K. Seong, A. Schulzgen, P. Khulbe, N. Peyghambarian, M. Mansuripur, Appl. Opt. 43, 4584 (2004)
Y. Hanada, K. Sugioka, H. Kawano, T. Tsuchimoto, I. Miyamoto, A. Miyawaki, K. Midorikawa, Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 9885 (2009)
Y. Liao, J. Song, E. Li, Y. Luo, Y. Shen, D. Chen, Y. Cheng, Z. Xu, K. Sugioka, K. Midorikawa, Lab Chip 12, 746 (2012)
Y. Hanada, K. Sugioka, H. Kawano, I.S. Ishikawa, A. Miyawaki, K. Midorikawa, Biomed. Microdevices 10, 403 (2008)
G.-L. Roth, C. Esen, R. Hellmann, Opt. Exp. 25, 18442 (2017)
S. Ho, P.R. Herman, J.S. Aitchison, Appl. Phys. A 106, 5 (2012)
Y. Hanada, T. Ogawa, K. Koike, K. Sugioka, Lab Chip 16, 2481 (2016)
Y. Bai, B. Chen, F. Xiang, J. Zhou, H. Wang, Z. Suo, Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 151903 (2014)
M.L. Byron, E.A. Variano, Exp. Fluids 54, 1456 (2013)
T. Matsumura, A. Kazama, T. Yagi, Appl. Phys. A 81, 1393 (2005)
K.L. Choo, Y. Ogawa, G. Kanbargi, V. Otra, L.M. Raff, R. Komanduri, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 372, 145 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest relevant to the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nagao, R., Yamada, S. & Hanada, Y. Microfabrication on low-refractive-index hydrogels using femtosecond laser direct writing. Appl. Phys. A 128, 761 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05913-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05913-2