Abstract
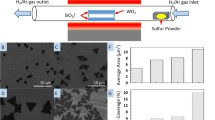
WS2 flakes have been grown successfully on SiO2 substrate via chemical vapor deposition method by reduction and sulfurization of WO3 using Ar/H2 gas and sulfur evaporated from solid sulfur powder. The prepared samples were characterized by optical microscopy, atomic force microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, Raman spectra and photoluminescence (PL). WS2 monolayers are obtained by extending the growth time. The perfect triangular single-crystalline WS2 flakes with an average length of more than 35 µm were achieved. The sharp PL peak (∼ 1.98 eV) and two distinct Raman peaks (E2g and A1g) with a ∼ 71.5 cm−1 peak split indicating that relatively high quality WS2 crystals with a regular triangle shape can be synthesized. Higher growth time shows larger triangular-shaped of WS2.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.Z. Butler, S.M. Hollen, L.Y. Cao, Y. Cui, J.A. Gupta, H.R. Gutierrez, T.F. Heinz, S.S. Hong, J.X. Huang, A.F. Ismach, E. Johnston-Halperin, M. Kuno, V.V. Plashnitsa, R.D. Robinson, R.S. Ruoff, S. Salahuddin, J. Shan, L. Shi, M.G. Spencer, M. Terrones, W. Windl, Goldberger, progress, challenges, and opportunities in two-dimensional materials beyond graphene. ACS Nano 7(4), 2898–2926 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn400280c
Q.H. Wang, K. Kalantar-Zadeh, A. Kis, J.N. Coleman, M.S. Strano, Electronics and optoelectronics of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. Natl. Nanotechnol. 7(11), 699–712 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2012.193
M.J. Allen, V.C. Tung, R.B. Kaner, Honeycomb carbon: a review of grapheme. Chem. Rev. 110(1), 132–145 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr900070d
A.H.C. Neto, F. Guinea, N.M.R. Peres, K.S. Novoselov, A.K. Geim, The electronic properties of grapheme. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81(1), 109–162 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.81.109
D. Jariwala, V.K. Sangwan, L.J. Lauhon, T.J. Marks, M.C. Hersam, Emerging device applications for semiconducting two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. ACS Nano 8(2), 1102–1120 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn500064
Y. Zhang, Y.F. Zhang, Q.Q. Ji, J. Ju, H.T. Yuan, J.P. Shi, T. Gao, D.L. Ma, M.X. Liu, Y.B. Chen, Controlled growth of high-quality monolayer WS2 layers on sapphire and imaging its grain boundary. ACS Nano 7, 8963–8971 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn403454e
G. Eda, S.A. Maier, Two-dimensional crystals: managing light for optoelectronics. ACS Nano 7(7), 5660–5665 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn403159y
W. Zhang, Z. Huang, W. Zhang, Y. Li, Two dimensional semiconductors with possible high room temperature mobility. Nano Res. 7(12), 1731–1737 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0532-x
X. Guo, X. Tong, Y. Wang, C. Chen, G. Jina, X. Guo, High photoelectrocatalytic performance of a MoS2–SiC hybrid structure for hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 1(15), 4657–4661 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta10600d
D. Raichman, D.A. Strawser, J.P. Lellouche, Covalent unctionalization/polycarboxylation of tungsten disulfide inorganic nanotubes (INTs-WS2). Nano Res. 8(5), 1454–1463 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0630-9
C. Ballif, M. Regula, P.E. Schmid, M. Remškar, R. Sanjinés, F. Lévy, Preparation and characterization of highly oriented, photoconducting WS2 thin films. Appl. Phys. A 62(6), 543–546 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01571690
H.R. Gutierrez, N. Perea-López, A. Laura Elías, A. Berkdemir, B. Wang, R. Lv, F. López-Urías, V.H. Crespi, H. Terrones, M. Terrones, Extraordinary room-temperature photoluminescence in triangular WS2 monolayers. Nano Lett. 13(8), 3447–3454 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl3026357
C.L. Choi, J. Feng, Y.G. Li, J. Wu, A. Zak, R. Tenne, H.J. Dai, WS2 nanoflakes from nanotubes for electrocatalysis. Nano Res. 6, 921–928 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-013-0369-8
J.D. Mehew, S. Unal, E.T. Alonso, G.F. Jones, S.F. Ramadhan, M.F. Craciun, S. Russo, Fast and highly sensitive ionic-polymergated WS2-graphene photodetectors. Adv. Mater. 29(23), 1700222 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201700222C
B.H. Kim, H.H. Gu, Y.J. Yoon, Large-area and low-temperature synthesis of few-layered WS2 films for photodetectors. 2D Mater. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1583/aadef8
H.R. Gutierrez, N. Perea-Lopez, A.L. Elıas et al., Extraordinary room-temperature photoluminescence in triangular WS2 monolayers. Nano Lett. 13(8), 3447–3454 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl302635
W. Zhao, Z. Ghorannevis, L. Chu, M. Toh, C. Kloc, P.H. Tan, G. Eda, Evolution of electronic structure in atomically thin sheets of WS2 and WSe2. ACS Nano 7(1), 791–797 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn305275h
H. Zeng, G.B. Liu, J. Dai, Y. Yan, B. Zhu, R. He, L. Xie, S. Xu, X. Chen, W. Yao, X. Cui, Optical signature of symmetry variations and spin-valley coupling in atomically thin tungsten dichalcogenides. Sci. Rep. 3, 1608–1612 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep01608
T.A. Loh, D.H. Chua, A.T. Wee, One-step synthesis of fewlayer WS2 by pulsed laser deposition. Sci. Rep. 5(18116), 1–9 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18116
K. Kang, S. Xie, L. Huang, Y. Han, P.Y. Huang, K.F. Mak, C.J. Kim, D. Muller, J. Park, High-mobility three-atom-thick semiconducting films with wafer-scale homogeneity. Nature 520(7549), 656–660 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14417
D.K. Nandi, U.K. Sen, A. Dhara, S. Mitra, S.K. Sarkar, Intercalation based tungsten disulfide (WS2) Li-ion battery anode grown by atomic layer deposition. RSC Adv. 6(44), 38024–38032 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra00468g
D. Fu, X. Zhao, Y.Y. Zhang, L. Li, H. Xu, A.R. Jang, S.I. Yoon, P. Song, S.M. Poh, T. Ren, Z. Ding, W. Fu, T.J. Shin, H.S. Shin, S.T. Pantelides, W. Zhou, K.P. Loh, Molecular beam epitaxy of highly crystalline monolayer molybdenum disulfide on hexagonal boron nitride. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139(27), 9392–9400 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b05131
Q.H. Wang, K. Kalantar-Zadeh, A. Kis, J.N. Coleman, M.S. Strano, Electronics and optoelectronics of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Nanotechnol. 7(11), 699–712 (2012)
A. Splendiani, L. Sun, Y. Zhang, T. Li, J. Kim, C.Y. Chim, G. Galli, F. Wang, Emerging photoluminescence in monolayer MoS2. Nano Lett. 10(4), 1271–1275 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl903868w
M. Okada, T. Sawazaki, K. Watanabe, T. Taniguch, H. Hibino, H. Shinohara, R. Kitaura, Direct chemical vapor deposition growth of WS2 atomic layers on hexagonal boron nitride. ACS Nano 8(8), 8273–8277 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn503093k
C.X. Cong, J.Z. Shang, X. Wu, B.C. Cao, N. Peimyoo, C.Y. Qiu, L.T. Sun, T. Yu, Synthesis and optical properties of large-area single-crystalline 2D semiconductor WS2 monolayer from chemical vapor deposition. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2(2), 131–136 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.201300428
Y. Rong, Y. Fan, A.L. Koh, A.W. Robertson, K. He, S. Wang, H. Tan, R. Sinclairc, J.H. Warner, Controlling sulphur precursor addition for large single crystal domains of WS2. Nanoscale 6(20), 12096 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4nr04091k
Y. Sheng, H. Tan, X. Wang, J.H. Warner, Hydrogen addition for centimeter-sized monolayer tungsten disulfide continuous films by ambient pressure chemical vapor deposition. Chem. Mater. 29(11), 4904–4911 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b00954
Y. Gao, Y.L. Hong, L.C. Yin, Z. Wu, Z. Yang, M.I. Chen, Z. Liu, T. Ma, D.M. Sun, Z. Ni, X.L. Ma, H.M. Cheng, W. Ren, Ultrafast Growth of High-Quality Monolayer WSe2 on Au. Adv. Mater. 29(29), 1700990–1700998 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201700990
H.R. Gutiérrez, N. Perea-López, A.L. Elías, A. Berkdemir, B. Wang, R. Lv, F. López-Urías, V.H. Crespi, H. Terrones, M. Terrones, Extraordinary room-temperature photoluminescence in triangular WS2 monolayers. Nano Lett. 13(8), 3447–3454 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl3026357
Z. Chen, L.W. Wang, Material genome explorations and new phases of two-dimensional MoS2, WS2 and ReS2 monolayers. Chem. Mater. 30, 6242–6248 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b00525
J. Han, R. Fang, L. Zhu, Z. Geng, X. He, CVD growth of monolayer WS2 through controlled growth temperature and time. Ferroelectrics 562(1), 51–57 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150193.2020.1760592
F. Lan, R. Yang, Y. Xu, S. Qian, S. Zhang, H. Cheng, Y. Zhang, Synthesis of large-scale single-crystalline monolayer WS2 using a semi-sealed method. Nanomaterials 8(2), 100–107 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020100
F. Chen, S. Ding, W.T.A. Su, A feasible approach to fabricate two dimensional WS2 flakes: from monolayer to multilayer. Ceram. Int. 44(18), 22108–22112 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.08.322
A. Molina-Sanchez, L. Wirtz, Phonons in single-layer and few-layer MoS2 and WS2. Phys. Rev. B 84(15), 155413 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.84.155413
N. Peimyoo, J. Shang, W. Yang, Y. Wang, C. Cong, T. Yu, Thermal conductivity determination of suspended mono- and bilayer ws2 by Raman spectroscopy. Nano Res. 8(4), 1210–1221 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0602-0
J.H. Parker, D.W. Feldman, M. Ashkin, Raman scattering by silicon and germanium. Phys. Rev. 155(3), 712–714 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrev.155.712
K. Uchinokura, T. Sekine, E. Matsuura, Raman scattering by silicon. Solid State Commun. 11(1), 47–49 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-1098(72)91127-1
S. Hussain, M. Farooq Khan, M.A. Shehzad, D. Vikraman, M.Z. Iqbal, D.C. Choi, W. Song, K.S. An, Y. Seo, J. Eom, W.G. Lee, J. Jung, Layer-modulated, wafer scale and continuous ultra-thin WS2 films grown by RF sputtering via post-deposition annealing. J. Mater. Chem. C 4(33), 7846–7852 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6tc01954d
P.S.G. Anand, P.S. Gaur, S. Sahoo, J.F. Scott, R.S. Katiyar, Electron-phonon interaction and double-resonance raman studies in monolayer ws2. J. Mater. Chem. C 119(9), 5146–5151 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp512540u
D. Dumcenco, D. Ovchinnikov, K. Marinov, P. Lazic, M. Gibertini, N. Marzari, O.L. Sanchez, Y.C. Kung, D. Krasnozhon, M.W. Chen et al., Large-area epitaxial monolayer MoS2. ACS Nano 9(4), 4611–4620 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b01281
H. Li, Q. Zhang, C.C.R. Yap, B.K. Tay, T.H.T. Edwin, A. Olivier, D. Baillargeat, Bulk to monolayer MoS2: evolution of Raman scattering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 22(7), 1385–1390 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201102111
Y. Gao, Z. Liu, D.M. Sun, L. Huang, L.P. Ma, L.C. Yin, T. Ma, Z. Zhang, X.L. Ma, L.M. Peng, Large-area synthesis of high-quality and uniform monolayer WS2 on reusable Au foils. Nat. Commun. 6(1), 8569 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9569
L. Liang, V. Meunier, First-principles raman spectra of MoS2, WS2 and their heterostructures. Nanoscale 6(10), 5394–5401 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3nr06906k
K.N. Kang, K. Godin, E.H. Yang, The growth scale and kinetics of WS2 monolayers under varying H2 concentration. Sci. Rep. 5(1), 1–9 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep13205
H. Peng, W. Dang, J. Cao, Y.L. Chen, D. Wu, W.S. Zheng, H. Li, Z.X. Shen, Z.F. Liu, Topological insulator nanostructures for near-infrared transparent flexible electrodes. Nat. Chem. 4(4), 281–286 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.1277
H. Tan, W. Xu, Y. Sheng, C.S. Lau, Y. Fan, Q. Chen, M. Tweedie, X. Wang, Y. Zhou, J.H. Warner, Lateral graphene-contacted vertically stacked WS2/MoS2 hybrid photodetectors with large gain. Adv. Mater. 29(46), 1702917–1702925 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.20170291
W. Zhao, R. Ribeiro, M. Toh, A. Carvalho, C. Kloc, A. Castro Neto, G. Eda, Origin of indirect optical transitions in few-layer MoS2, WS2, and WSe2. Nano Lett. 13(11), 5627–5634 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl403270k
S. Wang, M. Pacios, H. Bhaskaran, J.H. Warner, Substrate control for large area continuous films of monolayer MoS2 by atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition. Nanotechnology 27(8), 085604–085613 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/27/8/085604
J. Park, W. Lee, T. Choi, S.H. Hwang, J.M. Myoung, J.H. Jung, S.H. Kimc, H. Kim, Layer-modulated synthesis of uniform tungsten disulfide nanosheet using gas-phase precursors. Nanoscale 7(4), 1308–1313 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4nr04292a
K.M. McCreary, A.T. Hanbicki, G.G. Jernigan, J.C. Culbertson, B.T. Jonker, Synthesis of large-area WS2 monolayers with exceptional photoluminescence. Sci. Rep. 6(1), 1–7 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19159
A. Matthäus, A. Ennaoui, S. Fiechter, S. Tiefenbacher, T. Kiesewetter, K. Diesner, I. Sieber, W. Jaegermann, T. Tsirlina, R. Tenne, Highly textured films of layered metal disulfide 2H-WS2 preparation and optoelectronic properties. J. Electron. Mater. 144(3), 1013–1019 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1837522
W. Zhou, X. Zou, S. Najmaei, Z. Liu, Y. Shi, J. Kong, J. Lou, P.M. Ajayan, B.I. Yakobson, J.C. Idrobo, Intrinsic structural defects in monolayer molybdenum disulfide. Nano Lett. 13(6), 2615 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl4007479
Acknowledgements
We thank from West Tehran Branch Azad University for financial support of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have not any conflict of interest that may have influenced either the conduct or the presentation of the research to the editors.
Ethical approval
Our paper is just a research paper on nanostructure material and has no ethical problem.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asgary, S., Ramezani, A.H. & Ebrahimi Nejad, Z. Characterization of high quality, monolayer WS2 domains via chemical vapor deposition technique. Appl. Phys. A 128, 139 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05270-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05270-0