Abstract
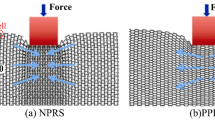
Using monophase core materials to design periodically acoustic metamaterials with vibration isolation properties and special acoustic properties that do not exist in natural bulk solids is a challenging and innovative work. In this paper, we proposed an innovative star-shaped acoustic metamaterials with periodic assemblies based on the double-negative properties generated by rotational resonance, monopolar resonance and dipole resonance. At the same time, the metastructures would generate broad and multiple omnidirectional band gaps through the rotational resonance of the spherical masses. In addition, the rationally designed arc-shaped ligaments could produce reversible deformations under the excitation of external strains, thereby realizing preliminary tuning of the band gaps. Numerical simulations with the finite element method provided effective data support for the above research, and proved that the proposed architected microstructures would provide reference for vibration reduction and the design of acoustic lens metamaterials.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Chen, W. Zhou, C. Lim, Active control for acoustic wave propagation in nonlinear diatomic acoustic metamaterials. Int. J. Nonlin. Mech. 125, 103535 (2020)
Y. Wu, Y. Lai, Z. Zhang, Elastic metamaterials with simultaneously negative effective shear modulus and mass density. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 105506 (2011)
Y. Sun, N. Pugno, In plane stiffness of multifunctional hierarchical honeycombs with negative Poisson’s ratio sub-structures. Compos. Struct. 106, 681–689 (2013)
S. Cui, B. Gong, Q. Ding, Y. Sun, F. Ren, X. Liu, Q. Yan, H. Yang, X. Wang, B. Song, Mechanical metamaterials foams with tunable negative Poisson’s ratio for enhanced energy absorption and damage resistance. Materials 11, 1869 (2018)
Y. Sun, Q. Chen, N. Pugno, Elastic and transport properties of the tailorable multifunctional hierarchical honeycombs. Compos. Struct. 107, 698–710 (2014)
K. Lu, Y. Tian, N. Gao, L. Li, H. Lei, M. Yu, Propagation of longitudinal waves in the broadband hybrid mechanism gradient elastic metamaterials rods. Appl. Acoust. 171, 107571 (2020)
X. Zhou, L. Wang, L. Qin, F. Peng, Improving sound insulation in low frequencies by multiple band-gaps in plate-type acoustic metamaterials. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 146, 109606 (2020)
S. Zhang, J. Wu, Low-frequency band gaps in phononic crystals with composite locally resonant structures. Acta. Phys. Sin. 62, 134302 (2013)
J. Zhou, L. Dou, K. Wang, D. Xu, H. Ouyang, A nonlinear resonator with inertial amplification for very low-frequency flexural wave attenuations in beams. Nonlinear Dyn. 96, 647–665 (2019)
Z. Liu, X. Zhang, Y. Mao, Y. Zhu, Z. Yang, C. Chan, P. Sheng, Locally resonant sonic materials. Phys. B 338, 201–205 (2000)
Q. Cheng, H. Guo, T. Yuan, P. Sun, F. Guo, Y. Wang, Topological design of honeycomb structure for broad and multiple band gaps in low-frequency range. Extreme Mech. Lett. 35, 100632 (2020)
X. Xu, M.V. Barnhart, X. Li, Y. Chen, G. Huang, Tailoring vibration suppression bands with hierarchical metamaterials containing local resonators. J. Sound Vib. 442, 237–248 (2019)
C. Cai, J. Zhou, L. Wu, K. Wang, D. Xu, H. Ouyang, Design and numerical validation of quasi-zero-stiffness metamaterials for very low-frequency band gaps. Compos. Struct. 236, 111862 (2020)
J. Zhou, X. Wang, D. Xu, S. Bishop, Nonlinear dynamic characteristics of a quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolator with cam-roller-spring mechanisms. J. Sound Vib. 346, 53–69 (2015)
K. Wang, J. Zhou, Q. Wang, H. Ouyang, D. Xu, Low-frequency band gaps in a metamaterial rod by negative-stiffness mechanisms: design and experimental validation. Appl.Phys. Lett. 114, 251902 (2019)
Y. Dong, H. Yao, J. Du, J. Zhao, C. Ding, Research on bandgap property of a novel small size multi-band phononic crystal. Phys. Lett. A 383, 283–288 (2019)
K. Wang, J. Zhou, H. Ouyang, L. Cheng, D. Xu, A semi-active metamaterial beam with electromagnetic quasi-zero-stiffness resonators for ultralow-frequency band gap tuning. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 176, 105548 (2020)
N. Kumar, S. Pal, Low frequency and wide band gap metamaterial with divergent shaped star units: Numerical and experimental investigations. Appl. Phys. Lett. 115, 254101 (2019)
Z. Yan, C. Zhang, Y. Wang, Elastic wave localization in two-dimensional phononic crystals with one-dimensional random disorder and aperiodicity. Phys. B 406, 1154–1161 (2011)
L. Alessandro, A. Krushynska, R. Ardito, N. Pugno, A. Corigliano, A design strategy to match the band gap of periodic and aperiodic metamaterials. Sci. Rep. 10, 16403 (2020)
X. Wu, Y. Li, S. Zuo, The study of a locally resonant beam with aperiodic mass distribution. Appl. Acoust. 165, 107306 (2020)
R. Zhu, X. Liu, G. Hu, C. Sun, G. Huang, Negative refraction of elastic waves at the deep-subwavelength scale in a single-phase metamaterial. Nat. Commun. 5, 5510 (2014)
J. Li, C. Chan, Double-negative acoustic metamaterial. Phys. Rev. E 70, 055602 (2004)
N. Fang, D. Xi, J. Xu, M. Ambati, W. Srituravanich, C. Sun, X. Zhang, Ultrasonic metamaterials with negative modulus. Nat. Mater. 5, 452–456 (2006)
X. Liu, G. Hu, G. Huang, C. Sun, An elastic metamaterial with simultaneously negative mass density and bulk modulus. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 251907 (2011)
Y. Wu, Y. Lai, Z. Zhang, Effective medium theory for elastic metamaterials in two dimensions. Phys. Rev. B 76, 205313 (2007)
Y. Lai, Y. Wu, P. Sheng, Z. Zhang, Hybrid elastic solids. Nat. Mater. 10, 620–624 (2011)
M. Chen, W. Xu, Y. Liu, K. Yan, H. Jiang, Y. Wang, Band gap and double-negative properties of a star-structured sonic metamaterial. Appl. Acoust. 139, 235–242 (2018)
M. Chen, H. Jiang, H. Zhang, D. Li, Y. Wang, Design of an acoustic superlens using single-phase metamaterials with a star-shaped lattice structure. Sci. Rep. 8, 1861 (2018)
Y. Huang, N. Gao, W. Chen, R. Bao, Extension/compression-controlled complete band gaps in 2D chiral square-lattice-like structures. Acta. Phys. Sin. 31, 51–65 (2018)
L. Jian, Y. Wang, W. Chen, Y. Wang, R. Bao, Harnessing inclusions to tune post-buckling deformation and bandgaps of soft porous periodic structures. J. Sound Vib. 459, 114848 (2019)
Y. Chen, T. Li, F. Scarpa, L. Wang, Lattice metamaterials with mechanically tunable poisson’s ratio for vibration control. Phys. Rev. Appl. 7, 024012 (2017)
K. Bertoldi, M.C. Boyce, Mechanically triggered transformations of phononic band gaps in periodic elastomeric structures. Phys. Rev. B 77, 052105 (2008)
K. Bertoldi, M.C. Boyce, S. Deschanel, S.M. Prange, T. Mullin, Mechanics of deformation-triggered pattern transformations and superelastic behavior in periodic elastomeric structures. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 56, 2642–2668 (2008)
K. Bertoldi, M.C. Boyce, Wave propagation and instabilities in monolithic and periodically structured elastomeric materials undergoing large deformations. Phys. Rev. B 78, 184107 (2008)
J. Shim, P. Wang, K. Bertoldi, Harnessing instability-induced pattern transformation to design tunable phononic crystals. Int. J. Solids Struct. 58, 52–61 (2015)
D. Mousanezhad, S. Babaee, R. Ghosh, E. Mahdi, K. Bertoldi, A. Vaziri, Honeycomb phononic crystals with self-similar hierarchy. Phys. Rev. B 92, 104304 (2015)
S. Ning, F. Yang, C. Luo, Z. Liu, Z. Zhuang, Low-frequency tunable locally resonant band gaps in acoustic metamaterials through large deformation. Extrem. Mech Lett 35, 100623 (2019)
S. Nanthakumar, X. Zhuang, H. Park, C. Nguyen, Y. Chen, T. Rabczuk, Inverse design of quantum spin hall-based phononic topological insulators. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 125, 550–571 (2019)
Funding
The project was supported by the National Natural Science of China (Grant No. 61690222, 12072222, 12021002, 11991032), the State Key Laboratory of Mechanical Behavior and System Safety of Traffic Engineering Structures (Grant No. SKLTESKF1901), the Aeronautical Science Foundation of China (Grant No. ASFC-201915048001) and the Project of Tianjin Natural Science Foundation (No.18JCQNJC05400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they do not have any financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that represent a conflict of interest in connection with the manuscript submitted.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Cheng, S., Wang, C. et al. Tunable band gaps and double-negative properties of innovative acoustic metamaterials. Appl. Phys. A 127, 495 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04612-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04612-8