Abstract
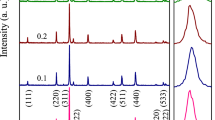
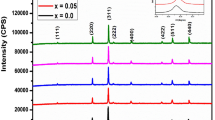
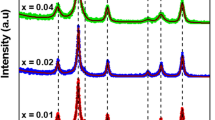
Unprecedented analysis of the impact of high-level Al3+ substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of low-coercivity Co0.5Zn0.5AlxFe2−xO4 (0.3 ≤ x ≤ 0.8) nanoferrites prepared via autocombustion method is presented. Single-phase cubic structure has been assured for all samples using XRD patterns and FTIR spectra. Due to the notable difference in the ionic radii of Fe3+ and Al3+, structural defects are created for high substitution levels, which is to be balanced by cation redistribution and/or the appearance of Fe2+ and Co3+ cations. Rietveld analysis and size-strain plots were used to explain the non-monotonic change of the lattice parameter, microstrain and crystallite size. For the as-prepared samples, the estimated size ranged from 9 to 19 nm, which was confirmed by HRTEM images. Magnetic properties were deduced from M–H loops traced at room temperature. Saturation magnetization (MS) decreased with increasing Al3+ content while coercivity (Hc) was fluctuating. Based on the experimental data of XRD, FTIR, and VSM, a cation distribution has been proposed and tightly correlated with the structural and magnetic properties. The significant reduction of the lattice parameter and coercivity for the sample with x = 0.8 upon sintering process has been explained in the light of the cation distribution.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Goldman, Modern Ferrite Technology, 2nd edn. (Springer, USA, 2006)
M. Arruebo, M. Rodrigo Fernández-Pacheco, R. Ibarra, J. Santamaría, Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nano Today 2.3, 22–32 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1748-0132(07)70084-1
Z.A. Gilani, M.S. Shifa, H.M.N.K. Asghar, M.A. Khan, M.N. Anjum, M.N. Usmani, R. Alic, M.F. Warsi, New LiCo0.5PrxFe2−xO4 nanoferrites: prepared via low cost technique for high density storage application. Ceram. Int. 44(2018), 1881–1885 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.10.126
J.H. Hankiewicz, J.A. Stoll, J. Stroud, J. Davidson, K.L. Livesey, K. Tvrdy, A. Roshko, S.E. Russek, K. Stupic, P. Bilski, R.E. Camley, Z.J. Celinski, Nano-sized ferrite particles for magnetic resonance imaging thermometry. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 469, 550–557 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.09.037
Wu Kaidi, J. Li, C. Zhang, Zinc ferrite based gas sensors: a review. Ceram. Int. 45, 11143–11157 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.03.086
D.R. Mane, S. Patil, D.D. Birajdar, A.B. Kadam, S.E. Shirsath, R.H. Kadam, Sol–gel synthesis of Cr3+ substituted Li0.5Fe2.5O4: cation distribution, structural and magnetic properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 126, 755–760 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.12.048
S.T. Alone, S.E. Shirsath, R.H. Kadam, K.M. Jadhav, Chemical synthesis, structural and magnetic properties of nano-structured Co–Zn–Fe–Cr ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 5055–5060 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.02.006
E. Erdem, Electron beam curing of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Hybrid Mater 1, 62–70 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2478/afpuc-2014-0003
Y. Köseoğlu, A. Baykal, F. Gözüak, H. Kavas, Structural and magnetic properties of CoxZn1−xFe2O4 nanocrystals synthesized by microwave method. Polyhedron 28, 2887–2892 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2009.06.061
P. Priyadharsini, A. Pradeep, P.S. Rao, G. Chandrasekaran, Structural, spectroscopic and magnetic study of nanocrystalline Ni–Zn ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 116, 207–213 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2009.03.011
A.M. Wahba, M.B. Mohamed, N.G. Imam, Correlating structural, magnetic, and luminescence properties with the cation distribution of Co0.5Zn0.5+xFe2–xO4 nanoferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 408, 51–59 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.02.027
D. Peddis, N Yaacoub, M. Ferretti, A. Martinelli, G. Piccaluga, A. Musinu, C. Cannas, G. Navarra, J. M. Greneche, D. Fiorani, Cationic distribution and spin canting in CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 23, 1–8 (2011) https://iopscience.iop.org/0953-8984/23/42/426004
E. Manova, D. Paneva, B. Kunev, C. Estournès, E. Riviere, K. Tenchev, A. Leaustic, I. Mitov, Mechanochemical synthesis and characterization of nanodimensional iron–cobalt spinel oxides. J. Alloys Compd. 485, 356–361 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.05.107
S.J. Kim, B.R. Myoung, C.S. Kim, Neutron diffraction and exchange interaction on CoAlxFe2–xO4 (x = 0.1, 0.2). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 272–276, 2161–2162 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2003.12.946
Y.M. Abbas, S.A. Mansour, M.H. Ibrahim, S.E. Ali, Microstructure characterization and cation distribution of nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 2748–2756 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.05.038
Y. Kim, D. Kim, C.S. Lee, Synthesis and characterization of CoFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles prepared by temperature-controlled coprecipitation method. Phys. B Condens Mater 337, 42–51 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-4526(03)00322-3
R. Arulmurugan, G. Vaidyanathan, S. Sendhilnathan, B. Jeyadevan, Thermomagnetic properties of Co1−xZnxFe2O4 (x = 0.1–0.5) nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 303, 131–137 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2005.10.237
T.R. Tatarchuk, N.D. Paliychuk, M. Bououdina, B. Al-Najar, M. Pacia, W. Macyk, A. Shyichuk, Effect of cobalt substitution on structural, elastic, magnetic and optical properties of zinc ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 731, 1256–1266 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.10.103
Y. Zhang, Z. Yang, D. Yin, Y. Liu, C. Fei, Composition and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles prepared by the co-precipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 3470–3475 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2010.06.047
A.R. Abbasian, M.S. Afarani, One-step solution combustion synthesis and characterization of ZnFe2O4 and ZnFe16O4 nanoparticles. Appl Phys A 125, 1–12 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3017-7
M.P. Vinardell, M. Mitjans, Antitumor activities of metal oxide nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 5, 1004–1021 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano5021004
J. Rodriguez-Carvajal, Recent advances in magnetic structure determination by neutron powder diffraction. Physica B (Amsterdam) 192, 55–69 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1748-0132(07)70084-1
M. Ferrari, L. Lutterotti, Method for the simultaneous determination of anisotropic residual stresses and texture by x-ray diffraction. J. Appl. Phys. 76(11), 7246–7255 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.358006
A.B. Kulkarni, S.N. Mathad, Synthesis and structural analysis of Co–Zn–Cd Ferrite by Williamson-Hall and size–strain plot methods. Int. J Self-Propag. High-Temp. Synth. 27, 37–43 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3103/S106138621801003X
L. Kumar, P. Kumar, M. Kar, Cation distribution by Rietveld technique and magnetocrystalline anisotropy of Zn substituted nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 551, 72–81 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.10.009
A.T. Raghavender, D. Pajic, K. Zadro, P. Tomislav Milekovic, K.M. Venkateshwar Rao, D.R. Jadhav, Synthesis and magnetic properties of NiFe2−xAlxO4 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 316, 1–7 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2007.03.204
H.M. Zaki, S. Al-Heniti, Synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline MgAlxFe2−xO4 ferrites. J. Mater. Res. 27, 2798–2805 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.310
S.J. Haralkar, R.H. Kadam, S.S. More, S.E. Shirsath, M.L. Mane, S. Patil, D.R. Mane, Intrinsic magnetic, structural and resistivity properties of ferromagnetic Mn0.5Zn0.5AlxFe2−xO4 nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 1189–1196 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.12.018
P.S. Aghav, V.N. Dhage, M.L. Mane, D.R. Shengule, R.G. Dorik, K.M. Jadhav, Effect of aluminum substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite synthesized by sol–gel auto combustion process. Phys. B 406, 4350–4354 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2011.08.066
E.V. Gopalan, P.A. Joy, I.A. Al-Omari, D.S. Kumar, Y. Yoshida, M.R. Anantharaman, On the structural, magnetic and electrical properties of sol–gel derived nanosized cobalt ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 485, 711–717 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.06.033
K.J. Standley, Oxide Magnetic Material (Clarendon, Oxford, 1972)
R.S. Turtelli, M. Atif, N. Mehmood, F. Kubel, K. Biernack, W. Linert, R. Grossinger, C. Kapusta, M. Sikora, Interplay between the cation distribution and production methods in cobalt ferrite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 132, 832–838 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.12.020
A.M. Wahba, M.B. Mohamed, Structural and magnetic characterization and cation distribution of nanocrystalline CoxFe3−xO4 ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 378, 246–252 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.10.164
P. Vlazan, M. Stefanescu, P. Barvinschi, M. Stoia, Study on the formation of CoxFe3−xO4 system using two low temperature synthesis methods. Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 4119–4125 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.08.050
R.N. Bhowmik, N. Naresh, Structure, ac conductivity and complex impedance study of Co3O4 and Fe3O4mixed spinel ferrites. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Tech. 8(2), 40–52 (2010). https://doi.org/10.4314/ijest.v2i8.63779
P. Tarte, Infrared spectra of inorganic aluminates and characteristic vibrational frequencies of AlO4 tetrahedra and AlO6 octahedra. Spectrochim Acta A-M (1967). https://doi.org/10.1016/0584-8539(67)80100-4
A.M. Wahba, N.G. Imam, M.B. Mohamed, Flower-like morphology of blue and greenish-gray ZnCoxAl2−xO4 nanopigments. J. Mol. Struct. 1105, 61–69 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2015.10.052
S.M. Patange, S.E. Shirsath, S.P. Jadhav, V.S. Hogade, S.R. Kamble, K.M. Jadhav, Elastic properties of nanocrystalline aluminum substituted nickel ferrites prepared by co-precipitation method. J. Mol. Struct. 1038, 40–44 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2012.12.053
A.M. Wahba, M.B. Mohamed, Structural, magnetic, and dielectric properties of nanocrystalline Cr-substituted Co0.8Ni0.2Fe2O4 ferrite. Ceram. Int. 40(4), 6127–6135 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.11.064
A.I. Borhan, A.R. Iordan, M.N. Palamaru, Correlation between structural, magnetic and electrical properties of nanocrystalline Al3+ substituted zinc ferrite. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 2549–2556 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.03.012
L. Kumar, M. Kar, Influence ofAl3+ ion concentration on the crystal structure and magnetic anisotropy of nanocrystalline spinel cobalt ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 2042–2048 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.03.010
M.H. Ehsani, S. Esmaeili, M. Aghazadeh, P. Kameli, F. Shariatmadar Tehrani, I. Karimzadeh, An investigation on the impact of Al doping on the structural and magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 125, 1–9 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2572-2
V. Rusanov, V. Gushterov, S. Nikolov, A.X. Trautwein, Detailed Mössbauer study of the cation distribution in CoFe2O4 ferrites. Hyperfine Interact. 191, 67–74 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-01370-6_52
P.A. Shaikh, R.C. Kambale, A.V. Rao, Y.D. Kolekar, Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of Co–Ni–Mn ferrites synthesized by co-precipitation method. J. Alloys Compd. 492, 590–596 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.11.189
P.G. Bercoff, H.R. Bertorello, Localized canting effect in Zn-substituted Ni ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 213, 56–62 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(00)00011-1
K.S. Rao, A.M. Kumar, M.C. Varma, G.S. Choudary, K.H. Rao, Cation distribution of titanium substituted cobalt ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 488, L6–L9 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.08.086
H.E. Zhang, B.F. Zhang, G.F. Wang, X.H. Dong, Y. Gao, The structure and magnetic properties of Zn1−xNixFe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel auto-combustion. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 312, 126–130 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2006.09.016
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wahba, A.M., Mohamed, M.B. Correlating cation distribution with the structural and magnetic properties of Co0.5Zn0.5AlxFe2–xO4 nanoferrites. Appl. Phys. A 126, 488 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03692-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03692-2