Abstract
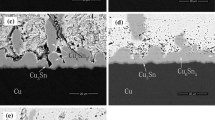
The interfacial reactions between Cu and Sn3Ag0.5Cu (SAC305) solder reflowed under various cooling rates were investigated. It is found that the cooling rate is an important parameter in solder reflow process because it influences not only microstructure of solder alloy but also the morphology and growth of intermetallic compounds (IMCs) formed between solder and Cu substrate. The experimental results indicate that only scallop-like Cu6Sn5 IMC layer is observed between solder and Cu substrate in case of water cooling and air cooling, while bilayer composed of scallop-like Cu6Sn5 and thin layer-like Cu3Sn is detected under furnace cooling due to sufficient reaction time to form Cu3Sn between Cu6Sn5 IMC and Cu substrate which resulted from slow cooling rate. Samples with different reflow cooling rates were further thermal-aged at 423 K. And it is found that the thickness of IMC increases linearly with square root of aging time. The growth constants of interfacial IMC layer during aging were obtained and compared for different cooling rates, indicating that the IMC layer thickness increased faster in samples under low cooling rate than in the high cooling rate under the same aging condition. The long prismatic grains were formed on the existing interfacial Cu6Sn5 grains to extrude deeply into solder matrix with lower cooling rate and long-term aging, and the Cu6Sn5 grains coarsened linearly with cubic root of aging time.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Zhang, L.L. Gao, Interfacial compounds growth of SnAgCu (nano La2O3)/Cu solder joints based on experiments and FEM. J. Alloys Compd. 635, 55–60 (2015)
J. Wang, H.M. Wei, P. He, T.S. Lin, F.J. Lu, Microstructure and mechanical properties of tin–bismuth solder reinforced by aluminum borate whiskers. J. Electron. Mater. 44, 3872–3879 (2015)
L. Zhang, L. Sun, Y.H. Guo, Microstructures and properties of Sn58Bi, Sn35Bi0.3Ag, Sn35Bi1.0Ag solder and solder joints. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26, 7629–7634 (2015)
X.W. Hu, Q. Huang, Y.L. Li, Y. Liu, Z.X. Min, A study on the interfacial reaction of Sn58Bi/Cu soldered joints under various cooling and aging conditions. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26, 5140–5151 (2015)
Q.K. Zhang, W.M. Long, X.Q. Yu, Y.Y. Pei, P.X. Qiao, Effects of Ga addition on microstructure and properties of Sn–Ag–Cu/Cu solder joints. J. Alloys Compd. 622, 973–978 (2015)
A. Sharma, B.G. Baek, J.P. Jung, Influence of La2O3 nanoparticle additions on microstructure, wetting, and tensile characteristics of Sn–Ag–Cu alloy. Mater. Des. 87, 370–379 (2015)
X.W. Hu, Y.L. Li, Z.X. Min, Interfacial reaction and growth behavior of IMCs layer between Sn–58Bi solders and a Cu substrate. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24, 2027–2034 (2013)
X.W. Hu, Y.L. Li, Z.X. Min, Interfacial reaction and IMC growth between Bi-containing Sn0.7Cu solders and Cu substrate during soldering and aging. J. Alloys Compd. 582, 341–347 (2014)
X.C. Lv, T.S. Lin, J. Wang, J. An, P. He, Morphology characterization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in Sn–58Bi/CNTs composites. Mater. Trans. 54, 1228–1231 (2013)
P. He, X.C. Lv, T.S. Lin, H.X. Li, J. An, X. Ma, J.C. Feng, Y. Zhang, Q. Li, Y.Y. Qian, Improvement of mechanical properties of Sn–58Bi alloy with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 22, s692–s696 (2012)
X.W. Hu, Y.L. Li, Y. Liu, Y. Liu, Z.X. Min, Microstructure and shear strength of Sn37Pb/Cu solder joints subjected to isothermal aging. Microelectron. Reliab. 54, 1575–1582 (2014)
X.W. Hu, W.J. Chen, X. Yu, Y.L. Li, Y. Liu, Z.X. Min, Shear strengths and fracture behaviors of Cu/Sn37Pb/Cu soldered joints subjected to different displacement rates. J. Alloys Compd. 600, 13–20 (2014)
K. Maslinda, A.S. Anasyida, M.S. Nurulakmal, Effect of Al addition to bulk microstructure, IMC formation, wetting and mechanical properties of low-Ag SAC solder. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2015). doi:10.1007/s10854-015-3780-y
L. Yang, Z.F. Zhang, Growth behavior of intermetallic compounds in Cu/Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu solder joints with different rates of cooling. J. Electron. Mater. 44, 590–596 (2015)
H.K. Kim, K.N. Tu, Kinetic analysis of the soldering reaction between eutectic SnPb alloy and Cu accompanied by ripening. Phys. Rev. B 53(23), 16027–16033 (1996)
X.W. Hu, Z.R. Ke, Growth behavior of interfacial Cu–Sn intermetallic compounds of Sn/Cu reaction couples during dip soldering and aging. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. 25, 936–945 (2014)
X.W. Hu, Y.L. Li, K. Li, Z.X. Min, Effect of Bi segregation on the asymmetrical growth of Cu–Sn intermetallic compounds in Cu/Sn–58Bi/Cu sandwich solder joints during isothermal. Aging 42, 3567–3572 (2013)
M. Yang, M.Y. Li, J. Kim, Texture evolution and its effects on growth of intermetallic compounds formed at eutectic Sn37Pb/Cu interface during solid-state aging. Intermetallics 31, 177–185 (2012)
M. He, Z. Chen, G.J. Qi, C.C. Wong, S.G. Mhaisalkar, Effect of post-reflow cooling rate on intermetallic compound formation between Sn–3.5Ag solder and Ni–P under bump metallization. Thin Solid Films 462–463, 363–369 (2004)
J. Hu, A.M. Hu, M. Li, D.L. Mao, Depressing effect of 0.1 wt% Cr addition into Sn–9Zn solder alloy on the intermetallic growth with Cu substrate during isothermal aging. Mater. Character. 61, 355–361 (2010)
M. Yang, Y. Cao, S. Joo, H. Chen, X. Ma, M. Li, Cu6Sn5 precipitation during Sn-based solder/Cu joint solidification and its effects on the growth of interfacial intermetallic compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 582, 688–695 (2014)
M.Y. Li, M. Yang, J. Kim, Textured growth of Cu6Sn5 grains formed at a Sn3.5Ag/Cu interface. Mater. Lett. 66, 135–137 (2012)
A.M. Gusak, K.N. Tu, Kinetic theory of flux-driven ripening. Phys. Rev. B 66, 115403-1–11540314 (2002)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 51465039), Nature Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (20151BAB206041), Science and Technology project of Jiangxi Department of Education (GJJ14108) and Fund of the State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing in NWPU (SKLSP201508).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Xu, T., Jiang, X. et al. Effects of post-reflow cooling rate and thermal aging on growth behavior of interfacial intermetallic compound between SAC305 solder and Cu substrate. Appl. Phys. A 122, 278 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-9893-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-9893-1