Abstract
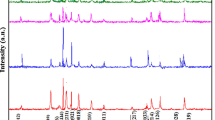
In this work, we synthesized the Co–Ti-substituted barium ferrite materials (Ba(CoTi)1.22Fe9.56O19) by sol–gel method (S1) and solid-state method (S2). The phase formation, structural and magnetic properties of both samples were investigated separately. Differential scanning calorimeter and thermo-gravimetric analysis curves showed changes in energy and weight with respect to temperatures during the sintering process—from room temperature to 1200 °C at a rate of 10 °C per min. X-ray diffractometer patterns indicate that both samples, with Co–Ti ions substitution, had single phase of M-type barium ferrite, and no clear structural changes or formation of second phase was observed. Grain size and shape of samples were exhibited in SEM images, from which S1 showed more regular-shaped particles than S2. Magnetic hysteresis loops of the samples were measured using a vibrating sample magnetometer and showed similar saturation magnetization (M s) and coercivity (H c). M s and H c are mainly determined by electron magnetic moment, ion occupation and particle size. Microwave absorption properties of the samples were characterized by a microwave vector network analyzer in the frequency range of 0.5–18 GHz. In terms of complex magnetic permeability, dielectric permittivity, maximum reflection loss, resonance peak and bandwidth, there were remarkable differences between two samples. We suggested that these different characteristics originate from the variation in particles size, surface state and oxygen vacancies, which determined the interfacial polarization and related microwave absorption performance of the samples.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.C. Pullar, Hexagonal ferrites: a review of the synthesis, properties and applications of hexaferrite ceramics. Prog. Mater. Sci. 57, 1191–1334 (2012)
D. Xu, F.F. Dong, Y.B. Chen, B.T. Zhao, S.M. Liu, M.O. Tade, Z.P. Shao, Cobalt-free niobium-doped barium ferrite as potential materials of dense ceramic membranes for oxygen separation. J. Membr. Sci. 455, 75–82 (2014)
J.L. Zhang, J.C. Fu, F.S. Li, E.Q. Xie, D.S. Xue, N.J. Mellors, Y. Peng, BaFe12O19 single-particle-chain nanofibers: preparation, characterization, formation principle, and magnetization reversal mechanism. Acs Nano 6, 2273–2280 (2012)
M. Manikandan, C. Venkateswaran, Effect of high energy milling on the synthesis temperature, magnetic and electrical properties of barium hexagonal ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 358, 82–86 (2014)
Y.Y. Meng, M.H. He, Q. Zeng, D.L. Jiao, S. Shukla, R.V. Ramanujan, Z.W. Liu, Synthesis of barium ferrite ultrafine powders by a sol–gel combustion method using glycine gels. J. Alloys Compd. 583, 220–225 (2014)
C.L. Yuan, Y.S. Tuo, Microwave adsorption of Sr(MnTi)(x)Fe12−2x O19 particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 342, 47–53 (2013)
J. Li, H.W. Zhang, Y.X. Li, Q. Li, G.L. Yu, Effect of La–Zn substitution on the structure and magnetic properties of low temperature Co-fired M-type barium ferrite. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 27, 793–797 (2014)
H.M. Khan, M.U. Islam, Y.B. Xu, M.A. Iqbal, I. Ali, Structural and magnetic properties of TbZn-substituted calcium barium M-type nano-structured hexa-ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 589, 258–262 (2014)
W.J. Zhang, Y. Bai, X. Han, L. Wang, X.F. Lu, L.J. Qiao, Magnetic properties of Co–Ti substituted barium hexaferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 546, 234–238 (2013)
T. Tsutaoka, N. Koga, Magnetic phase transitions in substituted barium ferrites BaFe12−x (Ti0.5Co0.5)(x)O19 (x = 0–5). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 325, 36–41 (2013)
E.D. Solov’eva, E.V. Pashkova, A.E. Perekos, B.S. Khomenko, A.G. Belous, Structural and magnetic properties of Ba0.7Sr0.3Fe12−2x Co x Ti x O19 M-type hexaferrites. Inorg. Mater. 49, 621–625 (2013)
I. Ali, M.U. Islam, M.S. Awan, M. Ahmad, Effects of Ga–Cr substitution on structural and magnetic properties of hexaferrite (BaFe12O19) synthesized by sol–gel auto-combustion route. J. Alloys Compd. 547, 118–125 (2013)
Z.F. Zi, Q.C. Liu, J.M. Dai, Y.P. Sun, Effects of Ce–Co substitution on the magnetic properties of M-type barium hexaferrites. Solid State Commun. 152, 894–897 (2012)
N. Koga, T. Tsutaoka, Preparation of substituted barium ferrite BaFe12−x (Ti0.5Co0.5)(x)O19 by citrate precursor method and compositional dependence of their magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 313, 168–175 (2007)
J.X. Qiu, M.Y. Gu, Magnetic nanocomposite thin films of BaFe12O19 and TiO2 prepared by sol–gel method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 252, 888–892 (2005)
C. Singh, S.B. Narang, I.S. Hudiara, Y. Bai, K. Marina, Hysteresis analysis of Co–Ti substituted M-type Ba–Sr hexagonal ferrite. Mater. Lett. 63, 1921–1924 (2009)
H.W. Zhang, J. Li, H. Su, T.C. Zhou, Y. Long, Z.L. Zheng, Development and application of ferrite materials for low temperature co-fired ceramic technology. Chin. Phys. B 22(117504), 117501–117521 (2013)
J.J. Liu, C.R. Gong, G.L. Fan, Preparation and properties of barium-ferrite-containing glass ceramic fibers via an electrospinning/sol–gel process. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 61, 185–191 (2012)
Z. Yang, C.S. Wang, X.H. Li, H.X. Zeng, (Zn, Ni, Ti) substituted barium ferrite particles with improved temperature coefficient of coercivity. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid 90, 142–145 (2002)
G.B. Teh, D.A. Jefferson, High-resolution transmission electron microscopy studies of sol–gel-derived cobalt-substituted barium ferrite. J. Solid State Chem. 167, 254–257 (2002)
W.J. Zhang, Y. Bai, X. Han, L. Wang, X.F. Lu, L.J. Qiao, J.L. Cao, D. Guo, Phase formation, sintering behavior and magnetic property of Bi–Co–Ti substituted M-type barium hexaferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 556, 20–25 (2013)
C.S. Wang, L.T. Li, J. Zhou, X.W. Qi, Z.X. Yue, X.H. Wang, Microstructures and high-frequency magnetic properties of low-temperature sintered Co–Ti substituted barium ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 257, 100–106 (2003)
H.T. Zhao, Y.C. Du, L.L. Kang, P. Xu, L. Du, Z.H. Sun, X.J. Han, Precursor-directed synthesis of quasi-spherical barium ferrite particles with good dispersion and magnetic properties. CrystEngComm 15, 808–815 (2013)
X.Z. Zhou, A.H. Morrish, Z. Yang, H.X. Zeng, Co–Sn substituted barium ferrite particles. J. Appl. Phys. 75, 5556–5558 (1994)
J. Lee, Y.K. Hong, W. Lee, G.S. Abo, J. Park, N. Neveu, W.M. Seong, S.H. Park, W.K. Ahn, Soft M-type hexaferrite for very high frequency miniature antenna applications. J. Appl. Phys. 111(07A502), 501–503 (2012)
C.J. Li, B. Wang, J.N. Wang, Magnetic and microwave absorbing properties of electrospun Ba(1−x)La x Fe12O19 nanofibers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 1305–1311 (2012)
A. Ghasemi, A. Hossienpour, A. Morisako, A. Saatchi, M. Salehi, Electromagnetic properties and microwave absorbing characteristics of doped barium hexaferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 302, 429–435 (2006)
Z.L. Zheng, H.W. Zhang, Complex permittivity and permeability of low-temperature sintered M-type barium hexaferrite in Ka-band frequency range. IEEE Trans. Magn. 49, 4230–4233 (2013)
H. Sozeri, H. Deligoz, H. Kavas, A. Baykal, Magnetic, dielectric and microwave properties of M–Ti substituted barium hexaferrites (M = Mn2+, Co2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, Zn2+). Ceram. Int. 40, 8645–8657 (2014)
S. Shakoor, M.N. Ashiq, M.A. Malana, A. Mahmood, M.F. Warsi, M. Najam-ul-Haq, N. Karamat, Electrical, dielectric and magnetic characterization of Bi–Cr substituted M-type strontium hexaferrite nanomaterials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 362, 110–114 (2014)
C.A. Stergiou, I. Manolakis, T.V. Yioultsis, G. Litsardakis, Dielectric and magnetic properties of new rare-earth substituted Ba-hexaferrites in the 2–18 GHz frequency range. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 1532–1535 (2010)
W. Chun-Yu, S. Xiang-Qian, S. Fu-Zhan, Double-layer microwave absorber of nanocrystalline strontium ferrite and iron microfibers. Chin. Phys. B 21, 028101 (2012)
N. Chen, K. Yang, M.Y. Gu, Microwave absorption properties of La-substituted M-type strontium ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 490, 609–612 (2010)
W.R. Agami, M.A. Ashmawy, A.A. Sattar, Structural, IR, and magnetic studies of annealed Li-ferrite nanoparticles. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 23, 604–610 (2014)
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support provided by the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Program) (Grant No. 2012CB933100). J. Li acknowledges the scholarship support from the Chinese Scholarship Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Li, J., Zhang, H. et al. Ba(CoTi)1.22Fe9.56O19 ferrites prepared by sol–gel method and solid-state method techniques. Appl. Phys. A 122, 306 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-9845-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-9845-9