Abstract
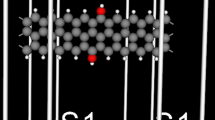
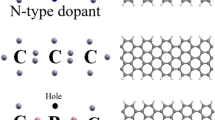
The electronic transport properties of zigzag graphene nanoribbons (ZGNRs) through covalent functionalization of gold (Au) atoms is investigated by using non-equilibrium Green’s function combined with density functional theory. It is revealed that the electronic properties of Au-doped ZGNRs vary significantly due to spin and its non-inclusion. We find that the DOS profiles of Au-adsorbed ZGNR due to spin reveal very less number of states available for conduction, whereas non-inclusion of spin results in higher DOS across the Fermi level. Edge Au-doped ribbons exhibit stable structure and are energetically more favorable than the center Au-doped ZGNRs. Though the chemical interaction at the ZGNR–Au interface modifies the Fermi level, Au-adsorbed ZGNR reveals semimetallic properties. A prominent qualitative change of the I–V curve from linear to nonlinear is observed as the Au atom shifts from center toward the edges of the ribbon. Number of peaks present near the Fermi level ensures conductance channels available for charge transport in case of Au-center-substituted ZGNR. We predict semimetallic nature of the Au-adsorbed ZGNR with a high DOS peak distributed over a narrow energy region at the Fermi level and fewer conductance channels. Our calculations for the magnetic properties predict that Au functionalization leads to semiconducting nature with different band gaps for spin up and spin down. The outcomes are compared with the experimental and theoretical results available for other materials.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.T. Pantelides, Y. Puzyrev, L. Tsetseris, B. Wang, MRS Bull. 37, 12 (2012)
K.S. Novoselov, V.I. Fal’ko, L. Colombo, P.R. Gellert, M.G. Schwab, K. Kim, Nature 490, 11 (2012)
J.S. Qi, J.Y. Huang, J. Feng, D.N. Shi, J. Li, ACS Nano 5(5), 3475 (2011)
H. Terrones, R. Lv, M. Terrones, M.S. Dresselhaus, Rep. Prog. Phys. 75(6), 062501 (2012)
J. Lan, X.H. Zheng, L.L. Song, R.N. Wang, Z. Zhang, Solid State Commn. 152, 1635 (2012)
Y. Gan, L. Sun, F. Banhart, Small 4, 5 (2008)
D. Ma, Z. Li, Z. Yang, Carbon 50, 1 (2012)
W. Zhang, L. Sun, Z. Xu, A.V. Krasheninnikov, P. Huai, Z. Zhu, F. Banhart, Phys. Rev. B 81(12), 125425 (2010)
K. Nakada, A. Ishii, N. Yamamoto, J. Kor, Phys. Soc. 63, 3 (2013)
S.-C. Zhu, K.L. Yao, G.Y. Gao, Y. Ni, Solid State Commun. 155, 40 (2013)
T. Chen, X.F. Li, L.L. Wang, Q. Li, K.W. Luo, X.H. Zhang, L. Xu, J. Appl. Phys. 115, 053707 (2014)
L.S. Wang, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 12, 31 (2010)
Y. Wu, W. Jiang, Y. Ren, W. Cai, W.H. Lee, H. Li, R.D. Piner, C.W. Pope, Y. Hao, R.S. Ruoff, Small 8, 20 (2012)
Y.-C. Zhou, H.L. Zhang, W.Q. Deng, Nanotech 24, 225705 (2013)
Atomistix ToolKit, A. S QuantumWise, www. quantumwise. com
S.M.M. Dubois, Z. Zanolli, X. Declerck, J.C. Charliera, Eur. Phys. J. B 72, 1 (2009)
X. Peng-Yang, Z. Gui-Lin, L. Yong-An, W. Jian-Guo, L. Xiao-Nian, J. Acta. Phys. Chim. Sin 28, 02 (2012)
K.T. Chan, J.B. Neaton, M.L. Cohen, Phys. Rev. B 77, 235430 (2008)
Principles of Semiconductor Devices, Bart Van Zeghbroeck. (2007)
N.K. Jaiswal, P. Srivastava, Solid State Commun. 152, 15 (2012)
N.K. Jaiswal, P. Srivastava, J. Comp. Theor. Nanosci. 10, 6 (2013)
R.S. Sundaram, M. Steiner, H.-Y. Chiu, M. Engel, A.H.A. Bol, R. Krupke, M. Burghard, K. Kern, P. Avouris. Nano. Lett. 11 (2011)
Z. Li, H. Qian, J. Wu, B.L. Gu, W. Duan, Phys. Rev. Letts. 100(20), 206802 (2008)
X. Hu, W. Zhang, L. Sun, A.V. Krasheninnikov, Phys. Rev. B. 86(19), 195418 (2012)
Z. Wang, J. Xiao, M. Li, Appl. Phys. A 110, 1 (2013)
N.K. Jaiswal, P. Srivastava, J Comp. Theor Nanosci. 9(4) (2012)
A.V. Krasheninnikov et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 102(12), 126807 (2009)
G. Yu et al., J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 46(37), 375303 (2013)
R. Varns, P. Strange, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 20(22), 225005 (2008)
W.H. Brito, R.H. Miwa, Phys. Rev. B 82(4), 045417 (2010)
R.S. Sundaram, M. Steiner, H.Y. Chiu, M. Engel, A.A. Bol, R. Krupke, M. Burghard, K. Kern, P. Avouris, Nano Lett. 11(9), 3833 (2011)
J.M. Xu, X.H. Hu, J. Sun, K.B. Yin, S.Y. Lei, L.T. Sun, Proceedings of 8th International Vacuum Electron Sources Conference and NANO carbon, (2010)
H. Peter Koch, R. Laskowski, P. Blaha, K. Schwarz, Phys. Rev. B 84, 245410 (2011)
C. Cao, M. Wu, J. Jiang, H.P. Cheng, Phys. Rev. B 81, 205424 (2010)
S. Gupta, G. Kaur, K. Dharamvir, AIP Conf. Proc. 1447, 1 (2012)
E.J.G. Santos, A. Ayuela, D. Sánchez-Portal, New J. Phys. 12, 053012 (2010)
M. Wei, L. Chen, N. Lun, Y. Sun, D. Li, H. Pan, Solid State Commn. 151, 20 (2011)
H. Wang, K. Li, Y. Cheng, Q. Wang, Y. Yao, U. Schwingenschlögl, W. Yang, Nanoscale 4, 9 (2012)
N.K. Jaiswal, P. Srivastava, IEEE Trans. Nanotech. 12, 5 (2013)
A. Ishii, M. Yamamoto, H. Asano, K. Fujiwara, J. Phys. Conf. Series 100(5), 052087 (2008)
K. Nakada, A. Ishii, Graphene Simulation, open access book edited by Jian Ru Gong, ISBN, 978–953 (2011)
H. Wang, K. Li, Y. Cheng, Q.X. Wang, Y. Yao, U. Schwingenschlögl, X. Zhang, W. Yang, Nanoscale 4(9), 2920 (2012)
T.P. Hardcastle et al., Phys. Rev. B 87(19), 195430 (2013)
A.V. Krasheninnikov, P.O. Lehtinen, A.S. Foster, P. Pyykkö, R.M. Nieminen, Phys. Rev. Letts. 102(12), 126807 (2009)
T.H. Seo, S.J. Chae, B.K. Kim, G. Shin, Y.H. Lee, E.K. Suh, App Phys Exp 5(11), 5101 (2012)
Semiconductor Today, Compounds &Advanced Silicon, 7,10,2012/2013
Morán-López, (Ed.). Physics of low dimensional systems (Vol. 7). Springer. (2001)
H. Mehrez, A. Wlasenko, B. Larade, J. Taylor, P. Grütter, H. Guo, Phys. Rev. B 65, 195419 (2002)
S.-L. Yan, M.-Q. Long, X.-J. Zhang, Xu Hui, Phys. Lett. A 378(13), 960 (2014)
T.P. Hardcastle, C.R. Seabourne, R. Zan, R.M.D. Brydson, U. Bangert, Q.M. Ramasse, K. Novoselov, A.J. Scott, Phys. Rev. B Conden. Matt. Mater. Phys. 87(19), 195430 (2013)
Y.Q. Wang, Y.E. Xie, Z.L. Zhang, Y. Zhang, Y.P. Chen, Eur. Phys. J. B 86, 34 (2013)
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Council of Scientific Research (CSIR), New Delhi for the financial assistance (Project No. 03(1202)/12/EMR-II) and the Computational Nanoscience and Technology Laboratory (CNTL), ABV-Indian Institute of Information Technology and Management, Gwalior for the computational and infrastructural facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srivastava, P., Dhar, S. & Jaiswal, N.K. Ab initio study of gold-doped zigzag graphene nanoribbons. Appl. Phys. A 117, 1997–2008 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-014-8608-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-014-8608-8