Abstract
Objective
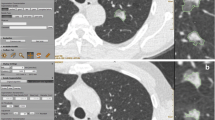
To evaluate the performance of software in segmenting ground-glass and solid components of subsolid nodules in pulmonary adenocarcinomas.
Method
Seventy-three pulmonary adenocarcinomas manifesting as subsolid nodules were included. Two radiologists measured the maximal axial diameter of the ground-glass components on lung windows and that of the solid components on lung and mediastinal windows. Nodules were segmented using software by applying five (-850 HU to -650 HU) and nine (-130 HU to -500 HU) attenuation thresholds. We compared the manual and software measurements of ground-glass and solid components with pathology measurements of tumour and invasive components.
Results
Segmentation of ground-glass components at a threshold of -750 HU yielded mean differences of +0.06 mm (p = 0.83, 95 % limits of agreement, 4.51 to 4.67) and -2.32 mm (p < 0.001, -8.27 to 3.63) when compared with pathology and manual measurements, respectively. For solid components, mean differences between the software (at -350 HU) and pathology measurements and between the manual (lung and mediastinal windows) and pathology measurements were -0.12 mm (p = 0.74, -5.73 to 5.55]), 0.15 mm (p = 0.73, -6.92 to 7.22), and -1.14 mm (p < 0.001, -7.93 to 5.64), respectively.
Conclusion
Software segmentation of ground-glass and solid components in subsolid nodules showed no significant difference with pathology.
Key Points
• Software can effectively segment ground-glass and solid components in subsolid nodules.
• Software measurements show no significant difference with pathology measurements.
• Manual measurements are more accurate on lung windows than on mediastinal windows.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goo JM, Park CM, Lee HJ (2011) Ground-glass nodules on chest CT as imaging biomarkers in the management of lung adenocarcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol 196:533–543
Naidich DP, Bankier AA, MacMahon H et al (2013) Recommendations for the management of subsolid pulmonary nodules detected at CT: a statement from the Fleischner Society. Radiology 266:304–317
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M et al (2011) International association for the study of lung cancer/american thoracic society/european respiratory society international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol 6:244–285
Hwang EJ, Park CM, Ryu Y et al (2015) Pulmonary adenocarcinomas appearing as part-solid ground-glass nodules: is measuring solid component size a better prognostic indicator? Eur Radiol 25:558–567
Revel MP, Bissery A, Bienvenu M, Aycard L, Lefort C, Frija G (2004) Are two-dimensional CT measurements of small noncalcified pulmonary nodules reliable? Radiology 231:453–458
Kakinuma R, Ashizawa K, Kuriyama K et al (2012) Measurement of focal ground-glass opacity diameters on CT images: interobserver agreement in regard to identifying increases in the size of ground-glass opacities. Acad Radiol 19:389–394
Goo JM (2011) A computer-aided diagnosis for evaluating lung nodules on chest CT: the current status and perspective. Korean J Radiol 12:145–155
Wormanns D, Kohl G, Klotz E et al (2004) Volumetric measurements of pulmonary nodules at multi-row detector CT: in vivo reproducibility. Eur Radiol 14:86–92
Goodman LR, Gulsun M, Washington L, Nagy PG, Piacsek KL (2006) Inherent variability of CT lung nodule measurements in vivo using semiautomated volumetric measurements. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186:989–994
Park CM, Goo JM, Lee HJ, Kim KG, Kang MJ, Shin YH (2010) Persistent pure ground-glass nodules in the lung: interscan variability of semiautomated volume and attenuation measurements. AJR Am J Roentgenol 195:W408–W414
Oda S, Awai K, Murao K et al (2010) Computer-aided volumetry of pulmonary nodules exhibiting ground-glass opacity at MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 194:398–406
Oda S, Awai K, Murao K et al (2011) Volume-doubling time of pulmonary nodules with ground glass opacity at multidetector CT: Assessment with computer-aided three-dimensional volumetry. Acad Radiol 18:63–69
de Hoop B, Gietema H, van de Vorst S, Murphy K, van Klaveren RJ, Prokop M (2010) Pulmonary ground-glass nodules: increase in mass as an early indicator of growth. Radiology 255:199–206
Scholten ET, Jacobs C, van Ginneken B et al (2015) Detection and quantification of the solid component in pulmonary subsolid nodules by semiautomatic segmentation. Eur Radiol 25:488–496
Kuhnigk JM, Dicken V, Bornemann L et al (2006) Morphological segmentation and partial volume analysis for volumetry of solid pulmonary lesions in thoracic CT scans. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 25:417–434
de Hoop B, Gietema H, van Ginneken B, Zanen P, Groenewegen G, Prokop M (2009) A comparison of six software packages for evaluation of solid lung nodules using semi-automated volumetry: what is the minimum increase in size to detect growth in repeated CT examinations. Eur Radiol 19:800–808
Lee KH, Goo JM, Park SJ et al (2014) Correlation between the size of the solid component on thin-section CT and the invasive component on pathology in small lung adenocarcinomas manifesting as ground-glass nodules. J Thorac Oncol 9:74–82
Gandara DR, Aberle D, Lau D et al (2006) Radiographic imaging of bronchioloalveolar carcinoma: screening, patterns of presentation and response assessment. J Thorac Oncol 1:S20–S26
Lee HY, Choi YL, Lee KS et al (2014) Pure ground-glass opacity neoplastic lung nodules: histopathology, imaging, and management. AJR Am J Roentgenol 202:W224–W233
Thunnissen E, Beasley MB, Borczuk AC et al (2012) Reproducibility of histopathological subtypes and invasion in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. An international interobserver study. Mod Pathol 25:1574–1583
Acknowledgments
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Prof. Jin Mo Goo. The authors of this manuscript declare relationships with the following companies: Prof. B. van Ginneken is affiliated with Fraunhofer MeVis, Bremen, Germany. This study was supported by a grant from the National R&D Program for Cancer Control, Ministry for Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (1520230). Julien G. Cohen acknowledges support from the Société Francaise de Radiologie (SFR) and Collège des Enseignants de Radiologie de France (CERF). No complex statistical methods were necessary for this paper. Institutional Review Board approval was obtained.
Written informed consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board. Methodology: retrospective, observational, performed at one institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cohen, J.G., Goo, J.M., Yoo, RE. et al. Software performance in segmenting ground-glass and solid components of subsolid nodules in pulmonary adenocarcinomas. Eur Radiol 26, 4465–4474 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-016-4317-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-016-4317-3