Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate shear-wave elastographic (SWE) features of triple negative breast cancers (TNBC) and determine useful discriminators from other types of invasive breast cancers.
Methods
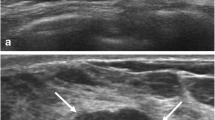
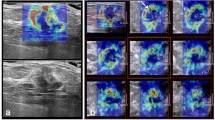
SWE features of 26 TNBC were reviewed and compared to 32 non-TNBC. Qualitative SWE features of lesion colour appearance, shape and homogeneity were analysed. Quantitative features were measured: mean (El mean), maximum (El max) and minimum (El min) elasticity value of the stiffest portion of the mass, mean elasticity of the surrounding tissue (El mean surr) and lesion to fat elasticity ratio (E ratio).
Results
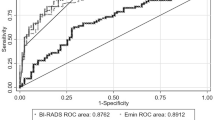
TNBC are more often regularly shaped (57.7 % vs. 6.2 %), while non-TNBC are more commonly red (93.7 % vs 42.3 %) and heterogeneous (68.7 % vs 42.3 %). The stiffness of TNBC is significantly lower compared to non-TNBC. The two groups could be distinguished on the basis of El max (p = 0.001), El mean (p = 0.001), El min (p = 0.001) and E ratio (p = 0.0017). Lesion to fat elasticity ratio in TNBC group was statistically significantly lower than in the non-TNBC control group (p = 0.009).
Conclusions
TNBC often demonstrate benign morphological features, are softer on SWE and have a lower lesion to fat stiffness ratio compared to the other, more common types of invasive breast cancers.
Key Points
• TNBC often demonstrate benign morphological features on SWE.
• TNBC present on elastography mostly as red, regularly shaped, heterogeneous lesions.
• TNBC are less stiff compared to other invasive breast cancers.
• TNBC have lower lesion to fat stiffness ratio than other breast cancers.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AUC:
-
Area under curve
- BBC:
-
Basal-like breast cancer
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- El mean:
-
Mean elasticity value
- El max:
-
Maximum elasticity value
- El min:
-
Minimum elasticity value
- El mean surr:
-
Mean elasticity value of surrounding tissue
- E ratio:
-
Lesion to fat elasticity ratio
- ER:
-
Oestrogen receptor
- HR+:
-
Hormone receptor positive
- HR−:
-
Hormone receptor negative
- HER2:
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
- kPa:
-
Kilopascals
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- PR:
-
Progesterone receptor
- SWE:
-
Shear-wave elastography
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- TNBC:
-
Triple negative breast cancers
- TN:
-
Triple negative
References
Reis-Filho JS, Tutt ANJ (2008) Triple negative tumors: a critical review. Histopathology 52:108–118
Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R et al (2001) Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:10869–10874
Weigelt B, Horlings HM, Kreike B et al (2008) Refinement of breast cancer classification by molecular characterization of histological special types. J Pathol 216:141–150
Tavassoli FA, Devilee P (2003) World Health Organisation classification of tumors. Pathology and genetics of tumors of the breast and female genital organs. IARC, Lyon
Page DL (2003) Special types of invasive breast cancer, with clinical implications. Am J Surg Pathol 27:832–835
Morris SR, Carey LA (2007) Gene expression profiling in breast cancer. Curr Opin Oncol 19:547–551
Dogan BE, Turnbull LW (2012) Imaging of triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Oncol 23:23–29
Dogan BE, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Gilcrease M, Dryden MJ, Yang WT (2010) Multimodality imaging of triple receptor-negative tumors with mammography, ultrasound and MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol 194:1160–1166
Uematsu T, Kasami M, Yuen S (2009) Triple-negative breast cancer: correlation between MR imaging and pathologic findings. Radiology 250:638–647
Ko ES et al (2010) Triple-negative breast cancer: correlation between imaging and pathological findings. Eur Radiol 20:1111–1117
Kojima Y et al (2011) Radiographic features for triple negative ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Breast Cancer 18:213–220
Kojima Y, Tsunoda H (2011) Mammography and ultrasound features of triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer 18:146–151
Youk JH, Son EJ, Chung J, Kim JA, Kim EK (2012) Triple-negative invasive breast cancer on dynamic contrast enhanced and diffusion weighted MR imaging: comparison with other brest cancer subtypes. Eur Radiol 22:1724–1734
Choi YJ, Seong MH, Choi SH et al (2011) Ultrasound and clinicopathological characteristics of triple receptor-negative breast cancers. J Breast Cancer 14:119–123
Wen SY et al (2012) Mammographic and pathological features of triple-negative breast cancer. Zhongzhua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 34:291–295
Boisserie-Lacroix M et al (2012) Radiological features of triple-negative breast cancers (73 cases). Diagn Interv Imaging 93:183–190
Krizmanich-Conniff KM et al (2012) Triple receptor-negative breast cancer: imaging and clinical characteristics. AJR Am J Roentgenol 199:458–464
Yang et al (2008) Mammographic features of triple receptor-negative primary breast cancers in young premenopausal women. Breast Cancer Res Treat 111:405–410
Wojcinski S et al (2012) Sonographic features of triple-negative and non-triple-negative breast cancer. J Ultrasound Med 31:1531–1541
Athanasiou A et al (2010) Breast lesions: quantitative elastography with supersonic shear imaging—preliminary results 1. Radiology 256:297–303
Cosgrove D, Berg WA, Doré CJ, Gay J, Henry JP, Cohen-Bacrie C (2012) Shear wave elastography for breast masses is highly reproducible. Eur Radiol 22:1023–1032
Berg WA et al (2012) Shear-wave elastography improves the specificity of breast US: the BE1 multinational study of 939 masses. Radiology 262:435–439
Chang JM, Park IA, Lee SH et al (2013) Stiffness of tumours measured by shear-wave elastography correlated with subtypes of breast cancer. Eur Radiol 23:2450–2458
Youk JH, Gweon HM, Son EJ, Kim JA, Jeong J (2013) Shear-wave elastography of invasive breast cancer: correlation between quantitative mean elasticity value and immunohistochemical profile. Breast Cancer Res Treat 138:119–126
Evans A et al (2012) Invasive breast cancer: relationship between shear-wave elastographic findings and histologic prognostic factors. Radiology 263:673–677
Brkljacic B, Ivanac G (2014) Ultrasonography of the breast. Ultrasound Clin 9:391–427
Evans A, Whelehan P, Thomson K et al (2010) Quantitative shear wave ultrasound elastography: initial experience in solid breast masses. Breast Cancer Res 12:104
Youk JH, Gweon HM, Son EJ, Han KH, Kim JA (2013) Diagnostic value of commercially available shear-wave elastography for breast cancers: integration into BI-RADS classification with subcategories of category 4. Eur Radiol 23:2695–2704
Lee EJ, Jung HK, Ko KH, Lee JT, Yoon JH (2013) Diagnostic performances of shear wave elastography: which parameter to use in differential diagnosis of solid breast masses? Eur Radiol 23:1803–1811
Chamming's F et al (2013) Shear wave elastography of tumor growth in a human breast cancer model with pathological correlation. Eur Radiol 23:2079–2086
Mori M, Tsunoda H, Kawauchi N et al (2012) Elastographic evaluation of mucinous carcinoma of the breast. Breast Cancer 19:60–63
Plodinec M, Loparic M, Monnier CA et al (2012) The nanomechanical signature of breast cancer. Nat Nanotechnol 7:757–765
Chang JM, Won JK, Lee KB, Park IA, Yi A, Moon WK (2013) Comparison of shear-wave and strain ultrasound elastography in the differentiation of benign and malignant breast lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol 201:W347–W356
Acknowledgments
The scientific guarantor of this publication is Boris Brkljacic. The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article. The authors state that this work has not received any funding. One of the authors has significant statistical expertise. Institutional review board approval was obtained. Written informed consent was waived by the institutional review board. Some study subjects have been previously reported and were presented as a poster at ECR 2014. Methodology: retrospective, cross-sectional study, performed at one institution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Džoić Dominković, M., Ivanac, G., Kelava, T. et al. Elastographic features of triple negative breast cancers. Eur Radiol 26, 1090–1097 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-015-3925-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-015-3925-7