Abstract
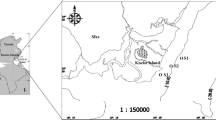
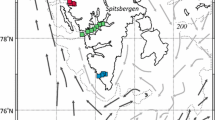
The aim of this study was to describe the microzooplankton composition under the sea ice in the Ross Sea (Antarctica) and its possible role as seed for the open-water community. We compared the under-sea-ice data to the communities present in the ice-free waters and at the retreating ice edge in order to test the hypothesis that the microzooplankton composition and abundance depend on the temporal development of the ecosystem. In December 2011, microzooplankton were sampled through two boreholes in sea ice, and 1 month later, in nearby stations that had been free from ice for a short time. The data from these samples were compared with a previous campaign (January 2011) when all of the area had been free of ice for a longer period. Our data indicate that under the sea ice the communities were very different from those of the ice-free waters, both in terms of abundance and diversity, with the prevalence of heterotrophic dinoflagellates and aloricate ciliates. Tintinnids were almost absent below the sea ice, and their abundance increased during the sampling at the intermediate depths. The present study provides evidence for the effect of the environment on the microzooplankton distributions, and indicates that the microzooplankton presence mainly depends on the sampling period. The community under the sea ice appears not to seed the open water community once the ice has retreated. The presence of the ice appears to influence the whole water-column production, which might thus not feed the deeper communities. The most important constraint appears to be the time that has lapsed from the presence of ice cover to the ice-free period.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alder VA (1999) Tintinnoinea. In: Boltovskoy D (ed) South Atlantic Zooplankton. Backhuys, Leiden, pp 321–384
Alder VA, Boltovskoy D (1991) Microplanktonic distributional patterns west to the Antarctic Peninsula, with special emphasis on the tintinnids. Polar Biol 11:103–112
Arrigo K, Weiss AM, JrWO Smith (1998) Physical forcing of phytoplankton dynamics in the southwestern Ross Sea. J Geophys Res 103:1007–1021
Balech E (1976) Clave ilustrada de dinoflagellados antarcticos. Publ Inst Antar Argent 11:1–99
Beaumont KL, Nash GV, Davidson AT (2002) Ultrastructure, morphology and flux of microzooplankton faecal pellets in an east Antarctic fjord. Marine Ecol Prog Series 245:133–148
Beers JR, Stewart GL (1970) Numerical abundance and estimated biomass of microzooplankton. In: Strickland JDH (ed) The ecology of the plankton off La Jolla, California, in the period April through September 1967. University of California press, Berkeley, pp 67–87
Boltovskoy D, Adler VA (1992) Microzooplankton and tintinnid species-specific assemblage structures: patterns of distribution and year-to-year variations in the Weddell Sea (Antarctica). J Plankton Res 14:1405–1423
Boltovskoy D, Adler V, Spinelli F (1989) Summer Weddel Sea microplankton: assemblage structure, distribution and abundance, with special emphasis on the tintinnina. Polar Biol 9:447–456
Buck KR, Garrison DL, Hopkins TL (1992) Abundance and distribution of tintinnid ciliates in an ice edge zone during the austral autumn. Antarct Sci 4:3–8
Calbet A (2008) The trophic roles of microzooplankton in marine systems. ICES J Mar Sci 65:325–331
Caron DA, Dennett MR, Lonsdale DJ, Moran DM, Shalapyonok L (2000) Microzooplankton herbivory in the Ross Sea, Antarctica. Deep-Sea Res 47:3249–3272
Celussi M, Bergamasco A, Cataletto B, Fonda Umani S, Del Negro P (2010) Water masses’ bacterial community structure and microbial activities in the Ross Sea, Antarctica. Antarct Sci 22:361–370
Choi JW, Stoecker DK (1989) Effects of Fixation on Cell Volume of Marine Planktonic Protozoa. App Environ Microbiol 55:1761–1765
Clarke KR, Gorley RN (2006) PRIMER v6: User Manual/Tutorial. PRIMER-E, Plymouth, pp 1–192
Comiso JC, Nishio F (2008) Trends in the sea ice cover using enhanced and compatible AMSR-E, SSM/I, and SMMR data. J Geophys Res 113:C02507
Delille D, Fiala M, Rosiers C (1995) Seasonal changes in phytoplankton and bacterioplankton distribution at the ice-water interface in the Antarctic neritic area. Marine Ecol Prog Series 123:225–233
Delille D, Fiala M, Kuparinen J, Kuosa H, Plessis C (2002) Seasonal changes in microbial biomass in the first-year ice of Terre Adélie area (Antarctica). Aquat Microb Ecol 28:257–265
Di Poi E, Blason C, Corinaldesi C, Danovaro R, Malisana E, Fonda Umani S (2013) Structure and interactions within the pelagic microbial food web (from viruses to microplankton) across environmental gradients in the Mediterranean Sea. Global Biogeochem Cycles 27:1034–1045
Dieckmann GS, Hellmer HH (2010) The importance of sea ice: and overview. In: Thomas DN, Dieckmann GS (eds) Sea ice. Blackwell Publishing, New Jersy, pp 1–22
Dolan JR, Pierce RW, Yang EJ, Kim SY (2012) Southern Ocean biogeography of tintinnid ciliates of the marine plankton. J Eukaryot Microbiol 59:511–519
Dolan JR, Yang EJ, Lee SH, Kim SY (2013) Tintinnid ciliates of Amundsen Sea (Antarctica) plankton communities. Polar Res 32:19784. doi:10.3402/polar.v32i0.19784
Edler L (1979) Recommendations for marine biological studies in the Baltic Sea. Phytoplankton and chlorophyll. Balt Marine Biol Publ 5:1–37
Fonda Umani S, Beran A (2003) Seasonal variations in the dynamics of microbial plankton communities: first estimates from experiments in the Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic Sea. Marine Ecol Prog Series 247:1–16
Fonda Umani S, Monti M, Nuccio C (1998) Microzooplankton biomass distribution in Terra Nova Bay, Ross Sea (Antarctica). J Mar Syst 17:289–303
Fonda Umani S, Accornero A, Budillon G, Cappello M, Tucci S, Cabrini M, Del Negro P, Monti M, De Vittor C (2002) Particulate matter and plankton dynamics in the Ross Sea Polynya of Terra Nova Bay during the Austral Summer 1997/98. J Mar Syst 36:29–49
Fonda Umani S, Monti M, Bergamasco A, Cabrini M, De Vittor C, Del Negro P (2005a) Plankton community structure and dynamics versus physical structure from Terra Nova Bay to Ross Ice Shelf (Antarctica). J Mar Syst 55:31–46
Fonda Umani S, Tirelli V, Beran A, Guardiani B (2005b) Relationships between microzooplankton and mesozooplankton: competition vs predation on natural assemblages in the Gulf of Trieste (northern Adriatic Sea). J Plankton Res 27(10):973–986
Garrison DL (1991) Antarctic sea ice biota. Amer Zool 31:17–33
Garrison DL, Buck KR (1989) The biota of Antarctic pack ice in the Weddell sea and Antarctic Peninsula regions. Polar Biol 10:211–219
Garrison DL, Close AR (1993) Winter ecology of the sea ice biota in Weddell sea pack ice. Marine Ecol Prog Series 96:17–31
Garrison DL, Close AR, Gordon LI (1993) Winter plankton assemblage in the ice edge zone of the Weddell and Scotia Seas: composition, biomass and spatial distributions. Deep Sea Res 40:311–338
Garrison DL, Gibson A, Coale SL, Gowing MM, Okolodkov YB, Fritsen CH, Jeffries MO (2005) Sea-ice microbial communities in the Ross Sea: autumn and summer biota. Marine Ecol Prog Series 300:39–52
Gugliemo L, Carrada GC, Catalano G, Dell’Anno A, Fabiano M, Lazara L, Mangoni O, Pusceddu A, Saggiomo V (2000) Structural and functional properties of sympagic communities in the annual sea ice at Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica). Polar Biol 23:137–146
Heinbokel JF, Coats DW (1986) Patterns of tintinnine abundance and reproduction near the edge of seasonal pack-ice in the Weddell Sea, November 1983. Marine Ecol Prog Series 33:71–80
Ichinomiya M, Honda M, Shimoda H, Saito K, Odate T, Fukuchi M, Taniguchi A (2007) Structure of the summer under fast ice microbial community near Syowa Station, eastern Antarctica. Polar Biol 30:1285–1293
Kramer M, Swadling KM, Meiners KM, Kiko R, Scheltz A, Nicolaus M, Werner I (2011) Antarctic sympagic meiofauna in winter: comparing diversity, abundance and biomass between perennially and seasonally ice-covered regions. Deep-Sea Res II 58:1062–1074
Larik O, Westheide W (2006) Coastal plankton. Verlag, Munchen, Photo guide for European seas 143 pp
Leakey RJG, Fenton N, Clarke A (1994) The annual cycle of planktonic ciliates in nearshore waters at Signy Island, Antarctica. J Plankton Res 16:841–856
Legendre P, Legendre L (1998) Numerical Ecology, 2nd, English edn. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam
Ligowski R, Godlewski M, Lukowski A (1992) Sea ice diatoms and ice edge planktonic diatoms at the northern limit of the Weddell Sea pack ice. Proc NIPR Symp Polar Biol 5:9–20
Margalef R (1982) Some thoughts on the dynamics of populations of ciliates. Annales Institut Océanographique Paris 58:15–18
Mc Manus GB, Santoferra LF (2012) Tintinnids in microzooplankton communities. In: Dolan JR et al (eds) The biology and ecology of tintinnid ciliates: models for marine plankton. Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford, pp 198–213
McMinn A, Scott FJ (2005) Dinoflagellates. In: Scott FJ, Marchant HJ (eds) Antarctic Marine Protists. ABRS Camberra and AAD Hobart, Goanna Print, pp 202–250
Meyer B (2012) The overwintering of Antarctic krill, Euphasia superba, from an ecophysiological perspective. Polar Biol 35:15–37
Michel C, Gissel Nielsen T, Noais C, Gosselin M (2002) Significance of sedimentation and grazing by ice micro and meiofauna for carbon cycling in annual sea ice (northern Baffin Bay). Aquat Microb Ecol 30:57–68
Mikrjukov KA, Siemensma FJ, Patterson DJ (2000) Heliozoa. In: Lee JJ, Leedale GF (eds) The illustrated guide to the protozoa. Bradbury P, pp 860-872
Modigh M, Castaldo S (2005) Effects of fixatives on ciliates as related to cell size. J Plankton Res 27:845–849
Monti M, Fonda Umani S (1995) Tintinnids in Terra Nova Bay—Ross Sea during two austral summer (1987/8 and 1989/90). Acta Protozool 34:193–201
Petz W (2005) Ciliates. In: Scott FJ, Marchant HJ (eds) Antarctic Marine Protists. ABRS Camberra and AAD Hobart, Goanna Print, pp 347–448
Petz W, Song W, Wilbert N (1995) Taxonomy and ecology of the ciliate fauna (Protozoa, Ciliophora) in the endopagial and pelagial of the Weddell Sea, Antarctica. Stapfia 40:1–223
Putt M, Stoecker DK (1989) An experimentally determined carbon: volume ratio for marine “oligotrichous” ciliates from estuarine and coastal waters. Limnol Oceanogr 34:1097–1107
Riebsell U, Schloss I, Smetacek V (1991) Aggregation of algae released from melting sea ice: implications for seeding and sedimentation. Polar Biol 11:239–248
Roberts D, Craven M, Minghong C, Allison I, Nash G (2007) Protists in the marine ice of the Amery Ice Shelf, East Antarctica. Polar Biol 30:143–153
Safi KA, Robinson KV, Hall JA, Scwarz J, Mass EW (2012) Ross Sea deep-ocean and epipelagic microzooplankton during the summer-autumn transition period. Aquat Microb Ecol 67:123–137
Schnack-Schiel SB, Dieckmann GS, Gradinger R, Melnikov IA, Spindler M, Thomas DN (2001) Meiofauna in sea ice of the Weddell Sea (Antarctica). Polar Biol 24:724–728
Sherr BF, Sherr EB, Fallon RD (1987) Use of monodispersed, fluorescently labeled bacteria to estimate in situ protozoan bacterivory. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:958–965
Sherr BF, Sherr EB, Pedrós-Alió C (1989) Simultaneous measurement of bacterioplankton production and protozoan bacterivory in estuarine water. Marine Ecol Prog Series 54:209–219
Sime-Ngando T, Gosselin M, Juniper SK, Levasseur M (1997) Changes in sea ice phagotrophic microprotists (20–200 µm) during the spring bloom, Canadian Arctic Archipelago. J Mar Syst 11:163–172
Spindler M (1994) Notes on the biology of sea ice in the Arctic and Antarctic. Polar Biol 14:319–324
Stoecker DK, Buck KR, Putt M (1993) Changes in the sea-ice brine community during the spring-summer transition, McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. II. Phagotrophic protists. Marine Ecol Prog Series 95:103–113
Stoecker DK, Gifford DJ, Putt M (1994) Preservation of marine planktonic ciliates: losses and cell shrinkage during fixation. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 110:293–299
Utermöhl H (1958) Zur Vervollkommung der quantitativen Phytoplankton-Methodik. Mitt Int Ver Theor Angew Limnol 9:1–38
Verity PG, Langdon C (1984) Relationship between lorica volume, carbon, nitrogen, and ATP content of tintinnids in Narragansett Bay. J Plankton Res 6(5):859–868
Wasik A, Mikolajczyk E (1990) Tintinnids near pack-ice between South Shetland and South Orkney Islands (26 Dec. 1988–18 Jan. 1989). Acta Protozoolo 29(3):229–244
Weissenberger J, Dieckmann GS, Gradinger R, Spindler M (1992) Sea ice: a cast technique to examine and analyze brine pockets and channel structure. Limnol Oceanogr 37:179–183
Wickham SA, Steinmair U, Kamennaya N (2011) Ciliate distributions and forcing factors in the Amundsen and Bellingshausen seas (Antarctica). Aquat Microb Ecol 62:215–230
Williams R, McCall H, Pierce RW, Turner JT (1994) Speciation of the tintinnid genus Cymatocylis by morphometric analysis of the loricae. Marine Ecol Prog Series 107:263–272
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Italian National Antarctic Research Program (PNRA). Thanks are due to Paolo Povero and Enrico Olivari for temperature, salinity and fluorescence data. The authors would like to thank Christopher Berrie for the language revision.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monti, M., Zoccarato, L. & Fonda Umani, S. Microzooplankton composition under the sea ice and in the open waters in Terra Nova Bay (Antarctica). Polar Biol 40, 891–901 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-016-2016-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-016-2016-9