Abstract
Introduction
Work disability is a major consequence of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), associated not only with traditional disease activity variables, but also more significantly with demographic, functional, occupational, and societal variables. Recent reports suggest that the use of biologic agents offers potential for reduced work disability rates, but the conclusions are based on surrogate disease activity measures derived from studies primarily from Western countries.
Methods
The Quantitative Standard Monitoring of Patients with RA (QUEST-RA) multinational database of 8,039 patients in 86 sites in 32 countries, 16 with high gross domestic product (GDP) (>24K US dollars (USD) per capita) and 16 low-GDP countries (<11K USD), was analyzed for work and disability status at onset and over the course of RA and clinical status of patients who continued working or had stopped working in high-GDP versus low-GDP countries according to all RA Core Data Set measures. Associations of work disability status with RA Core Data Set variables and indices were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analyses.
Results
At the time of first symptoms, 86% of men (range 57%-100% among countries) and 64% (19%-87%) of women <65 years were working. More than one third (37%) of these patients reported subsequent work disability because of RA. Among 1,756 patients whose symptoms had begun during the 2000s, the probabilities of continuing to work were 80% (95% confidence interval (CI) 78%-82%) at 2 years and 68% (95% CI 65%-71%) at 5 years, with similar patterns in high-GDP and low-GDP countries. Patients who continued working versus stopped working had significantly better clinical status for all clinical status measures and patient self-report scores, with similar patterns in high-GDP and low-GDP countries. However, patients who had stopped working in high-GDP countries had better clinical status than patients who continued working in low-GDP countries. The most significant identifier of work disability in all subgroups was Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) functional disability score.
Conclusions
Work disability rates remain high among people with RA during this millennium. In low-GDP countries, people remain working with high levels of disability and disease activity. Cultural and economic differences between societies affect work disability as an outcome measure for RA.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Work disability is a major consequence of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) [1–4]. Although RA is cumulative over time, 20% to 30% of patients become permanently work-disabled in the first 2 to 3 years of the disease [5]. Rapid remission in early disease appears to be a beneficial strategy against work disability in RA [6].
The availability of biologic agents during the past decade has led to expectations of reduced work disability rates in RA [7], according to observations in clinical trials [8–12]. However, reports of clinical cohorts indicate that work disability remains a major problem in RA [13–16]. Possible explanations are that the timing of biologic agents after joint damage is seen may be too late in many cases or that the use of biologic agents is unusual in many countries for financial reasons or both [17].
The risk of work disability in RA is associated not only with traditional articular, radiographic, and laboratory measures of disease activity and severity but as much or more with demographic, socioeconomic, vocational, functional, and social policy variables [1, 18]. Although work disability is one of the most important outcomes in RA, cultural and economical differences between societies [19] may compromise its value as an outcome measure.
Most studies concerning work disability in RA have been conducted in North America and Western Europe, and little is known about the employability of RA patients in other countries. A multinational database, Quantitative Standard Monitoring of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (QUEST-RA) [20, 21], was established to assess 100 unselected consecutive RA patients per clinic in different countries, including countries outside Western Europe and North America. In June 2009, the QUEST-RA database included 8,039 patients from 86 clinics in 32 countries. The QUEST-RA database was analyzed for work status at the onset of RA and discontinuation of work due to RA, as recalled by the patients. Current clinical status of patients who continued to work or who had stopped working in high-gross domestic product (high-GDP) and low-GDP countries was analyzed.
Materials and methods
Establishment of database
QUEST-RA was established in 2005 with the objectives to promote quantitative assessment in usual rheumatology care and to develop a baseline cross-sectional database of consecutive RA patients seen outside of clinical trials in regular care in many countries. Three or more rheumatologists were asked to enroll 100 consecutive unselected patients in each country [20]. As of June 2009, the program enrolled 8,039 patients from 86 sites in 32 countries, including Argentina, Brazil, Canada, Denmark, Egypt, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, India, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Kenya, Kosovo, Latvia, Lithuania, Morocco, The Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Romania, Russia, Serbia, Spain, Sweden, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, the UK, and the US [21].
Ethics committee approvals
The study was carried out in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethics committees or internal review boards of participating institutes approved the study, and written informed consent was obtained from the patients.
Physician assessment measures
All patients were assessed according to a standard protocol to evaluate RA (SPERA) [22]. The physician review included four RA Core Data Set measures: a formal examination of swollen joints (swollen joint count using 28 joints, or SJC28) and tender joints (tender joint count using 28 joints, or TJC28), global estimate of disease activity, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). Rheumatoid factor (RF) positivity according to local reference values was reported as well as whether the patient had radiographic erosions. All courses of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologic agents were listed. The number of DMARDs over disease course was calculated.
Patient self-report questionnaire measures
Patients completed a 4-page self-report questionnaire, which included three RA Core Data Set measures - physical function, pain, and patient global estimate (PTGL) - as well as demographic data, fatigue, and psychological distress. A standard Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) [23] assesses physical function in activities of daily living and has four response categories: 0 = without any difficulty, 1 = with some difficulty, 2 = with much difficulty, 3 = unable to do. Visual analog scales (VASs) (0 = best to 10 = worst) were completed for pain, fatigue, and PTGL. Psychological distress was queried as the capacity to cope with sleep, stress, anxiety, and depression in the HAQ format with response options 0 to 3 (seen above) for each question. The mean of the responses of these four questions was calculated for PS-HAQ (Psychological HAQ) of 0 to 3 [24].
Data concerning work or disability status were based on a patient self-report questionnaire that included queries about work status at the time of the first symptoms of RA and currently and that had the following response alternatives: working full-time, working part-time, unemployed, student, homemaker, retired, and disabled. Full-time workers, part-time workers, students, and unemployed individuals were classified as working in these analyses as these groups had the potential to be employed in the workforce. Homemakers, retirees, and disabled individuals were classified as non-working, although individuals in these groups may perform valuable non-paid work. Patient self-perceived work disability was queried with the questions, 'Are you work-disabled because of RA?' (with response options 'yes' or 'no') and 'If so, since when?'
Gross domestic product
The GDP of each country in 2005 was obtained from a database of the International Monetary Fund [25] and is expressed in units of 1,000 US dollars (USD) per capita. GDP ranged from 3.5 to 49K USD but was either less than 11K USD or greater than 24K USD in all countries. In this report, the 16 countries with a GDP per capita of greater than 24K USD are classified as 'high-GDP' whereas the 16 countries with a GDP per capita of less than 11K USD are classified as 'low-GDP'.
Statistical methods
Descriptive results are presented as mean, median, and percentages. The disease activity score using 28 joint counts (DAS28) [26] was calculated from the formula 0.56*v(TJC28) + 0.28*v(SJC28) + 0.70*ln(ESR) + 0.014*(PTGL) and ranged from 0 to 9.1 (low to high). Comparisons of demographic variables, clinical characteristics, RA disease activity measures, and treatment-related variables were performed using parametric and non-parametric tests for continuous variables and the chi-square test for categorical variables. Kaplan-Meier statistics were applied; those who reached age 65 after the onset of RA were censored at that date.
Regressions were performed to analyze which demographic and clinical measures were independently significant to identify work disability status. Variables in the model included age, sex, education level, HAQ physical function, radiographic erosions, RF, ESR, and SJC28. Data of all individuals from all countries were pooled together; regressions were performed in four independent categories for all countries: in low-GDP countries, with onset prior to 2000 and after 2000, and in high-GDP countries, with onset prior to 2000 and after 2000. The year 2000 was chosen as a milestone because the first biologic agent for treatment of RA was approved in 1999.
Results
Patients
The mean age of 8,039 patients in the QUEST-RA database, from 86 clinics in 32 countries, was 55 years; 80% were females, and the mean disease duration was 11 years (Table 1). Patients in low-GDP countries were younger and were more likely to be female and have RF and radiographic erosions compared with those in high-GDP countries, as described in detail previously [27]. Patients in low-GDP countries had statistically significantly higher disease activity levels of all individual RA Core Data Set measures, including physician-derived measures and patient self-report scores, compared with patients in high-GDP countries. The number of DMARDs taken, and especially the percentage of patients who had ever taken biologic agents, differed significantly, with 31% in high-GDP countries and 9.4% in low-GDP countries (Table 1).
Work status at baseline
At the time of first symptoms, 68% of patients who were 65 years old or younger, including 85% of men (57% to 100% among countries) and 64% of women (19% to 83%), reported that they were working (Table 2). Among women, the proportion working at onset ranged from greater than 80% in Sweden, Finland, Estonia, and Lithuania to not more than 50% in Turkey, Kosovo, Morocco, Greece, and Egypt (Table 2).
Rate of work disability
A third of the patients (37%) who were younger than 65 years old and working at the onset of symptoms reported that they subsequently became work-disabled because of RA, over the median (interquartile range) observation period of 9 (4 to 16) years. Among 1,754 patients whose symptoms had begun during the 2000s and were working at the baseline, the rates of probability (95% confidence interval) to continue working were 80% (78% to 82%) at 2 years and 68% (65% to 71%) at 5 years, in a similar pattern to women and men in high-GDP and low-GDP countries (Figure 1).
Clinical status variables in people younger than 65 years old who were working versus those who had stopped working
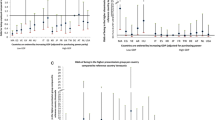
People who had stopped working had poorer clinical status according to all disease activity and patient self-report measures compared with people who were working (Table 3). Although better clinical status was seen in patients who were working than in those who were not working within high-GDP countries and within low-GDP countries, patients who were working in low-GDP countries had significantly better clinical status according to most measures than patients in high-GDP countries who had stopped working (Table 3). Among patients who were younger than 65 years old at the evaluation visit and reported that they are working, the current mean HAQ levels in high-GDP versus low-GDP countries were 0.43 versus 0.82 in men and 0.62 versus 0.95 in women. The mean DAS28 values in high-GDP versus low-GDP countries were, respectively, 3.1 versus 4.6 in men and 3.4 versus 4.8 in women (Figure 2), indicating that women continue working at higher disability and disease activity levels compared with men.
Disease activity (DAS28) and physical function (HAQ) in men and women who were younger than 65 years old and continued working in high-GDP and low-GDP countries. CI, confidence interval; DAS28, disease activity score using 28 joint counts; GDP, gross domestic product; HAQ, Health Assessment Questionnaire.
Differences in drug treatments
Among individuals who were younger than 65 years old at the evaluation, the rates of use of biologic agents were higher in those who had discontinued versus continued working and were 39% versus 32% in high-GDP countries and 13% versus 8.3% in low-GDP countries.
Identifiers of work disability
A series of logistic regressions was performed to analyze the independent capacity of age, sex, education, RF, radiographic erosions, HAQ physical function, ESR, and SJC28 to identify people who reported that they were work-disabled due to RA (Table 4). In the entire database, HAQ physical function, radiographic erosions, and sex were the three significant variables in these regressions (Table 4).
Discussion
The multinational QUEST-RA study provides several important observations concerning work-related outcomes in RA: (a) work disability rates remain high among patients with RA during this millennium; (b) major differences are seen in the proportion of women and men working at the onset of RA in different countries; (c) people continue working in low-GDP countries with levels of disease activity as high as or higher than those of work-disabled people with RA in high-GDP countries; and (d) in both high-GDP and low-GDP nations, the most significant identifier of work disability is the HAQ functional disability score.
Work disability rates remain high among patients with rheumatoid arthritis during this millennium
The availability of biologic agents over the past decade has increased expectations of reduced work disability rates in RA [7], based on results of clinical studies [8–11]. However, reports based on clinical cohorts have not indicated major effects of biologic agents on patients' work status [13–15]. The timing of treatment with biologic agents may not be optimal in many situations, and biologic agents are used infrequently in many countries for financial reasons (Tables 1 and 3) [17]. In QUEST-RA, a greater proportion of those who had discontinued versus continued working had taken biologic agents. Perhaps the early use of biologic agents will be associated with prevention of work disability in the future. However, at this time in actual clinics, the use of biologic agents appears to be primarily a surrogate for disease severity. In an ideal world, a reduction of work disability rates in RA patients might be achieved by initiating early and aggressive treatment within some weeks or months of the first symptoms [28]. The Finnish Rheumatoid Arthritis Combination Trial (FIN-RACo) [6] documented that early remission is critical concerning subsequent work or disability status: All patients who were in remission 6 months after baseline continued to work at 5 years compared with less than 80% with ACR20 (American College of Rheumatology 20% improvement criteria) and ACR50 responses and less than 50% with less than ACR20 responses [6]. FIN-RACo also indicated that traditional DMARDs, without biologic agents, can prevent work disability in early RA.
Work disability as an outcome measure of rheumatoid arthritis
It has become a fashion to use work disability-related outcome measures in the trials of biologic agents. Reports from clinical trials of biologic agents appear to be based on a traditional 'biomedical model' [29] view that work disability is a direct consequence of severe disease activity and damage. Previous studies document that mean levels of clinical variables in RA patients who were work-disabled in Finland indicated better clinical status than RA patients who were working in the US, and this difference was explained by different social policies regarding work disability [19]. In QUEST-RA, disease activity and disability levels were as high in working people in low-GDP countries as in work-disabled people in high-GDP countries. Thus, the QUEST-RA data extend evidence that macroeconomic variables influence an individual's work status to a greater degree than an individual's disease activity. The majority of patients with RA are women, a low proportion of whom are employed in certain countries at disease onset. In the present study, women continued working with higher scores of disease activity and functional disability compared with men (Figure 2). Cultural and socioeconomic differences between societies affect work disability as an outcome measure. In the RA population, losses in household productivity may be a more important matter than disability at paid work; household productivity is affected many-fold compared with paid productivity [30].
The HAQ functional disability score as the most significant identifier of work disability was confirmed in the QUEST-RA database including different countries and cultures in addition to what has been observed in Western countries [31, 32]. In addition to disease activity and damage, variables such as age, sex, education, occupation, duration of disease, functional status, family, physical demand, and time control issues at work have an impact on work status [1, 33]. In one study, if scores were known for physical function, occupation, age, and duration of disease, other clinical status measures, including joint counts, radiographs, and laboratory tests, did not add to the explanation of a patient's work or disability status [34].
Limitations
This study has several limitations. First, cross-sectional QUEST-RA data cannot provide detailed analysis of all work disability-related issues such as specified instruments concerning work disability/participation but rather provide an overview across various countries. The short 4-page patient questionnaire did not include a question about workload, for example, to analyze in this multinational setting whether, as has been suggested [35], work disability is a consequence of mismatch between an individual's functional capacity (HAQ) and work requirements. Second, some of the patients have a long disease duration and might not fully remember their work history. Therefore, recall bias may be one of the limitations of this study. Third, a limited number of patients were included per country. Nonetheless, results were quite similar among clinics within each country [20]. Fourth, it is possible that only RA patients with poor clinical status visit clinics in low-GDP countries and that patients with better status in high-GDP countries seek medical care. While this possibility cannot be excluded, the study was designed to incorporate a cross-section of patients seen in various countries. Nevertheless, the QUEST-RA results illustrate the potential value of collaborative databases, with identical database content and architecture, to provide an opportunity to study associations between disease characteristics, therapies, and outcomes at many sites in many countries with different cultural and socioeconomic environments. Work disability accounts for a major fraction of the costs of RA to both patients and societies. Improved work disability outcomes in RA will require attention to social, economic, and political issues and wider physician and public education in addition to improved medical management of the disease.
Conclusions
Work disability rates remain high among people with RA during this millennium. In low-GDP countries, people remain working with high levels of disability and disease activity. Cultural and economic differences between societies affect work disability as an outcome measure for RA.
Abbreviations
- ACR20:
-
American College of Rheumatology 20% improvement criteria
- DAS28:
-
disease activity score using 28 joint counts
- DMARD:
-
disease-modifying antirheumatic drug
- ESR:
-
erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- FIN-RACo:
-
The Finnish Rheumatoid Arthritis Combination Trial
- GDP:
-
gross domestic product
- HAQ:
-
Health Assessment Questionnaire
- ln:
-
logarithm
- PTGL:
-
patient global estimate of disease activity
- QUEST-RA:
-
Quantitative Standard Monitoring of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- RA:
-
rheumatoid arthritis
- RF:
-
rheumatoid factor
- SJC28:
-
swollen joint count using 28 joints
- TJC28:
-
tender joint count using 28 joints
- USD:
-
US dollars.
References
Yelin E, Meenan R, Nevitt M, Epstein W: Work disability in rheumatoid arthritis: effects of disease, social, and work factors. Ann Intern Med. 1980, 93: 551-556.
Mäkisara GL, Mäkisara P: Prognosis of functional capacity and work capacity in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 1982, 1: 117-125. 10.1007/BF02275601.
Pincus T, Callahan LF, Sale WG, Brooks AL, Payne LE, Vaughn WK: Severe functional declines, work disability, and increased mortality in seventy-five rheumatoid arthritis patients studied over nine years. Arthritis Rheum. 1984, 27: 864-872. 10.1002/art.1780270805.
Sokka T, Krishnan E, Häkkinen A, Hannonen P: Functional disability in rheumatoid arthritis patients compared with a community population in Finland. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48: 59-63. 10.1002/art.10731.
Sokka T: Work disability in early rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003, 21: S71-S74.
Puolakka K, Kautiainen H, Möttönen T, Hannonen P, Korpela M, Hakala M, Järvinen P, Ahonen J, Forsberg S, Leirisalo-Repo M, FIN-RACo Trial Group: Early suppression of disease activity is essential for maintenance of work capacity in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis: five-year experience from the FIN-RACo trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52: 36-41. 10.1002/art.20716.
Verstappen SM, Jacobs JW, Hyrich KL: Effect of anti-tumor necrosis factor on work disability. J Rheumatol. 2007, 34: 2126-2128.
Yelin E, Trupin L, Katz P, Lubeck D, Rush S, Wanke L: Association between etanercept use and employment outcomes among patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48: 3046-3054. 10.1002/art.11285.
Smolen JS, Han C, Heijde van der D, Emery P, Bathon JM, Keystone E, Kalden JR, Schiff M, Bala M, Baker D, Han J, Maini RN, St Clair EW: Infliximab treatment maintains employability in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54: 716-722. 10.1002/art.21661.
Kimel M, Cifaldi M, Chen N, Revicki D: Adalimumab plus methotrexate improved SF-36 scores and reduced the effect of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) on work activity for patients with early RA. J Rheumatol. 2008, 35: 206-215.
Anis A, Zhang W, Emery P, Sun H, Singh A, Freundlich B, Sato R: The effect of etanercept on work productivity in patients with early active rheumatoid arthritis: results from the COMET study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009, 48: 1283-1289. 10.1093/rheumatology/kep239.
Kavanaugh A, Smolen JS, Emery P, Purcaru O, Keystone E, Richard L, Strand V, van Vollenhoven RF: Effect of certolizumab pegol with methotrexate on home and work place productivity and social activities in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 61: 1592-1600. 10.1002/art.24828.
Wolfe F, Allaire S, Michaud K: The prevalence and incidence of work disability in rheumatoid arthritis, and the effect of anti-tumor necrosis factor on work disability. J Rheumatol. 2007, 34: 2211-2217.
Allaire S, Wolfe F, Niu J, Zhang Y, Zhang B, LaValley M: Evaluation of the effect of anti-tumor necrosis factor agent use on rheumatoid arthritis work disability: the jury is still out. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 59: 1082-1089. 10.1002/art.23923.
Laas K, Peltomaa R, Kautiainen H, Puolakka K, Leirisalo-Repo M: Pharmacoeconomic study of patients with chronic inflammatory joint disease before and during infliximab treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006, 65: 924-928. 10.1136/ard.2005.041574.
Augustsson J, Neovius M, Cullinane-Carli C, Eksborg S, van Vollenhoven RF: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tumour necrosis factor antagonists increase their participation in the workforce: potential for significant long-term indirect cost gains (data from a population-based registry). Ann Rheum Dis. 2010, 69: 126-131. 10.1136/ard.2009.108035.
Sokka T, Envalds M, Pincus T: Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a global perspective on the use of antirheumatic drugs. Mod Rheumatol. 2008, 18: 228-239. 10.1007/s10165-008-0056-x.
Eberhardt K: Very early intervention is crucial to improve work outcome in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2009, 36: 1104-1106. 10.3899/jrheum.090174.
Chung CP, Sokka T, Arbogast P, Pincus T: Work disability in early rheumatoid arthritis: higher rates but better clinical status in Finland compared with the US. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006, 65: 1653-1657. 10.1136/ard.2005.048439.
Sokka T, Kautiainen H, Toloza S, Makinen H, Verstappen SMM, Hetland ML, Naranjo A, Baecklund E, Herborn G, Rau R, Cazzato M, Gossec L, Skakic V, Gogus F, Sierakowski S, Bresnihan B, Taylor P, McClinton C, Pincus T, for the QUEST-RA Group: QUEST-RA: quantitative clinical assessment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis seen in standard rheumatology care in 15 countries. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007, 66: 1491-1496. 10.1136/ard.2006.069252.
Sokka T, Hetland ML, Makinen H, Kautiainen H, Horslev-Petersen K, Luukkainen RK, Combe B, Badsha H, Drosos AA, Devlin J, Ferraccioli G, Morelli A, Hoekstra M, Majdan M, Sadkiewicz S, Belmonte M, Holmqvist AC, Choy E, Burmester GR, Tunc R, Dimic A, Nedovic J, Stankovic A, Bergman M, Toloza S, Pincus T: Remission and rheumatoid arthritis: data on patients receiving usual care in twenty-four countries. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58: 2642-2651. 10.1002/art.23794.
Pincus T, Brooks RH, Callahan LF: A proposed standard protocol to evaluate rheumatoid arthritis (SPERA) that includes measures of inflammatory activity, joint damage, and longterm outcomes. J Rheumatol. 1999, 26: 473-480.
Fries JF, Spitz P, Kraines RG, Holman HR: Measurement of patient outcome in arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1980, 23: 137-145. 10.1002/art.1780230202.
Pincus T, Swearingen C, Wolfe F: Toward a multidimensional health assessment questionnaire (MDHAQ): assessment of advanced activities of daily living and psychological status in the patient friendly health assessment questionnaire format. Arthritis Rheum. 1999, 42: 2220-2230. 10.1002/1529-0131(199910)42:10<2220::AID-ANR26>3.0.CO;2-5.
International Monetary Fund: World Economic Outlook Databases. [http://www.imf.org/external/ns/cs.aspx?id=28]
Prevoo MLL, van't Hof MA, Kuper HH, van Leeuwen MA, Putte van de LBA, van Riel PLCM: Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts: Development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995, 38: 44-48. 10.1002/art.1780380107.
Sokka T, Kautiainen H, Pincus T, Toloza S, da Rocha Castelar Pinheiro G, Lazovskis J, Hetland ML, Peets T, Immonen K, Maillefert JF, Drosos AA, Alten R, Pohl C, Rojkovich B, Bresnihan B, Minnock P, Cazzato M, Bombardieri S, Rexhepi S, Rexhepi M, Andersone D, Stropuviene S, Huisman M, Sierakowski S, Karateev D, Skakic V, Baecklund E, Henrohn D, Gogus F, Badsha H, et al: Disparities in rheumatoid arthritis disease activity according to gross domestic product in 25 countries in the QUEST-RA database. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009, 68: 1666-1672. 10.1136/ard.2009.109983.
Möttönen T, Hannonen P, Korpela M, Nissilä M, Kautiainen H, Ilonen J, Laasonen L, Kaipiainen-Seppänen O, Franzen P, Helve T, Koski J, Gripenberg-Gahmberg M, Myllykangas-Luosujärvi R, Leirisalo-Repo M: Delay to institution of therapy and induction of remission using single-drug or combination-disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy in early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46: 894-898. 10.1002/art.10135.
Engel GL: The need for a new medical model: a challenge for biomedicine. Science. 1977, 196: 129-136. 10.1126/science.847460.
Verstappen SM, Boonen A, Verkleij H, Bijlsma JW, Buskens E, Jacobs JW: Productivity costs among patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the influence of methods and sources to value loss of productivity. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005, 64: 1754-1760. 10.1136/ard.2004.033977.
Sokka T, Pincus T: Markers for work disability in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2001, 28: 1718-1722.
Odegard S, Finset A, Kvien TK, Mowinckel P, Uhlig T: Work disability in rheumatoid arthritis is predicted by physical and psychological health status: a 7-year study from the Oslo RA register. Scand J Rheumatol. 2005, 34: 441-447. 10.1080/03009740510018633.
Reisine ST, Grady KE, Goodenow C, Fifield J: Work disability among women with rheumatoid arthritis: the relative importance of disease, social, work, and family factors. Arthritis Rheum. 1989, 32: 538-543. 10.1002/anr.1780320505.
Callahan LF, Bloch DA, Pincus T: Identification of work disability in rheumatoid arthritis: Physical, radiographic and laboratory variables do not add explanatory power to demographic and functional variables. J Clin Epidemiol. 1992, 45: 127-138. 10.1016/0895-4356(92)90005-8.
Puolakka K, Kautiainen H, Mottonen T, Hannonen P, Korpela M, Hakala M, Viikari-Juntura E, Solovieva S, Arkela-Kautiainen M, Leirisalo-Repo M: A mismatch between self-reported physical work load and the HAQ: early identification of rheumatoid arthritis patients at risk for loss of work productivity. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2009, 27: 422-429.
Acknowledgements
QUEST-RA Investigators:
Argentina: Sergio Toloza, Santiago Aguero, Sergio Orellana Barrera, Soledad Retamozo, Hospital San Juan Bautista, Catamarca; Paula Alba, Cruz Lascano, Alejandra Babini, Eduardo Albiero, Hospital of Cordoba, Cordoba.
Brazil: Geraldo da Rocha Castelar Pinheiro, Universidade do Estado do Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro; Licia Maria Henrique da Mota, Hospital Universitário de Brasília; Ines Guimaraes da Silveira, Pontifícia Universidade Católica do Rio Grande do Sul (PUCRS), Porto Alegre; FAC Rocha, Universidade Federal do Ceará, Fortaleza; Ieda Maria Magalhães Laurindo, Universidade Estadual de São Paulo, São Paulo.
Canada: Juris Lazovskis, Riverside Professional Center, Sydney, NS.
Denmark: Merete Lund Hetland, Lykke Ørnbjerg, Copenhagen Univ Hospital at Hvidovre and Glostrup, Hvidovre; Kim Hørslev-Petersen, King Christian the Xth Hospital, Gråsten; Troels Mørk Hansen, Lene Surland Knudsen, Copenhagen Univ Hospital at Herlev, Herlev.
Egypt: Hisham Hamoud, Mohamad Sobhy, Ahmad Fahmy, Mohamad Magdy, Hany Aly, Hatem Saeid, Ahmad Nagm, Al-Azhar University, Cairo; Nihal A Fathi, Assiut University Hospital, Assiut; Esam Abda, Zahra Ebraheam, Abo Sohage University Hospital, Sohage.
Estonia: Raili Müller, Reet Kuuse, Marika Tammaru, Riina Kallikorm, Tartu University Hospital, Tartu; Tony Peets, Kati Otsa, Karin Laas, East-Tallinn Central Hospital, Tallinn; Ivo Valter, Center for Clinical and Basic Research, Tallinn.
Finland: Heidi Mäkinen, Jyväskylä Central Hospital, Jyväskylä, and Tampere University Hospital, Tampere; Kai Immonen, Sinikka Forsberg, Jukka Lähteenmäki, North Karelia Central Hospital, Joensuu; Reijo Luukkainen, Satakunta Central Hospital, Rauma.
France: Laure Gossec, Maxime Dougados, University René Descartes, Hôpital Cochin, Paris; Jean Francis Maillefert, Dijon University Hospital, University of Burgundy, and INSERM U887, Dijon; Bernard Combe, Hôpital Lapeyronie, Montpellier; Jean Sibilia, Hôpital Hautepierre, Strasbourg.
Greece: Alexandros A Drosos, Sofia Exarchou, University of Ioannina, Ioannina; H M Moutsopoulos, Afrodite Tsirogianni, School of Medicine, National University of Athens, Athens; Fotini N Skopouli, Maria Mavrommati, Euroclinic Hospital, Athens.
Germany: Gertraud Herborn, Rolf Rau, Siegfrid Wassenberg, Evangelisches Fachkrankenhaus, Ratingen; Rieke Alten, Christof Pohl, Schlosspark-Klinik, Berlin; Gerd R Burmester, Bettina Marsmann, Charite - University Medicine Berlin, Berlin.
Hungary: Pál Géher, Semmelweis University of Medical Sciences, Budapest; Bernadette Rojkovich, Ilona Újfalussy, Polyclinic of the Hospitaller Brothers of St. John of God in Budapest, Budapest.
Ireland: Barry Bresnihan, St. Vincent University Hospital, Dublin; Patricia Minnock, Our Lady's Hospice, Dublin; Eithne Murphy, Claire Sheehy, Edel Quirke, Connolly Hospital, Dublin; Joe Devlin, Shafeeq Alraqi, Waterford Regional Hospital, Waterford.
India: Amita Aggarwal, Department of Immunology, Lucknow; Sapan C Pandya, Vedanta Institiute of Medical Sciences, Ahmedabad; Banwari Sharma, Department of Immunology, Jaipur Hospital.
Italy: Massimiliano Cazzato, Stefano Bombardieri, Santa Chiara Hospital, Pisa; Gianfranco Ferraccioli, Alessia Morelli, Catholic University of Sacred Heart, Rome; Maurizio Cutolo, University of Genova, Genova; Fausto Salaffi, Andrea Stancati, University of Ancona, Ancona.
Japan: Hisashi Yamanaka, Ayako Nakajima, Institute of Rheumatology, Tokyo Women's Medical University, Tokyo; Wataru Fukuda, Department of Rheumatology, Kyoto First Red Cross Hospital, Kyoto; Eisuke Shono, Shono Rheumatism Clinic, Fukuoka.
Kenya: G Omondi Oyoo, Kenyatta Hospital, Nairobi.
Kosovo: Sylejman Rexhepi, Mjellma Rexhepi, Rheumatology Department, Pristine.
Latvia: Daina Andersone, Pauls Stradina Clinical University Hospital, Riga.
Lithuania: Sigita Stropuviene, Jolanta Dadoniene, Institute of Experimental and Clinical Medicine at Vilnius University, Vilnius; Asta Baranauskaite, Kaunas University Hospital, Kaunas.
Morocco: Najia Hajjaj-Hassouni, Karima Benbouazza, Fadoua Allali, Rachid Bahiri, Bouchra Amine, El Ayachi Hospital Mohamed Vth Souissi University, Rabat.
The Netherlands: Johannes WG Jacobs, Suzan MM Verstappen, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht; Margriet Huisman, Femke Bonte-Mineur, Sint Franciscus Gasthuis, Rotterdam; Monique Hoekstra, Medisch Spectrum Twente, Enschede.
Norway: Glenn Haugeberg, Hilde Gjelberg, Eirik Wilberg, Sørlandet Hospital, Kristiansand.
Poland: Stanislaw Sierakowski, Medical University in Bialystok, Bialystok; Maria Majdan, Medical University of Lublin, Lublin; Wojciech Romanowski, Poznan Rheumatology Center in Srem, Srem; Witold Tlustochowicz, Military Institute of Medicine, Warsaw; Danuta Kapolka, Silesian Hospital for Rheumatology and Rehabilitation in Ustron Slaski, Ustroñ Slaski; Stefan Sadkiewicz, Szpital Wojewodzki im. Jana Biziela, Bydgoszcz; Danuta Zarowny-Wierzbinska, Wojewodzki Zespol Reumatologiczny im. dr Jadwigi Titz-Kosko, Sopot.
Romania: Ruxandra Ionescu, Denisa Predeteanu, Spitalul Clinic Sf Maria, Bucharest; Lia Georgescu, Spitalul Cinic Judetean de Urgenta Mures, Targu Mures; Rodica Marieta Chirieac, Codrina Ancuta, Gr. T. Popa University of Medicine and Pharmacy Iasi, Iasi.
Russia: Dmitry Karateev, Elena Luchikhina, Institute of Rheumatology of Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Moscow; Natalia Chichasova, Moscow Medical Academy, Moscow; Vladimir Badokin, Russian Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education, Moscow.
Serbia: Vlado Skakic, Aleksander Dimic, Jovan Nedovic, Aleksandra Stankovic, Rheumatology Institut, Niska Banja.
Spain: Antonio Naranjo, Carlos Rodríguez-Lozano, Hospital de Gran Canaria Dr. Negrin, Las Palmas; Jaime Calvo-Alen, Hospital Sierrallana Ganzo, Torrelavega; Miguel Belmonte, Hospital General de Castellón, Castellón.
Sweden: Eva Baecklund, Dan Henrohn, Uppsala University Hospital, Uppsala; Rolf Oding, Margareth Liveborn, Centrallasarettet, Västerås; Ann-Carin Holmqvist, Hudiksvall Medical Clinic, Hudiksvall.
Turkey: Feride Gogus, Gazi University Medical Faculty, Ankara; Recep Tunc, Meram Medical Faculty, Konya; Selda Celic, Cerrahpasa Medic Faculty, Istanbul.
United Arab Emirates: Humeira Badsha, Dubai Bone and Joint Center, Dubai; Ayman Mofti, American Hospital Dubai, Dubai.
UK: Peter Taylor, Catherine McClinton, Charing Cross Hospital, London; Anthony Woolf, Ginny Chorghade, Royal Cornwall Hospital, Truro; Ernest Choy, Stephen Kelly, Kings College Hospital, London.
USA: Theodore Pincus, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN; Yusuf Yazici, NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases, New York, NY; Martin Bergman, Taylor Hospital, Ridley Park, PA; Jurgen Craig-Müller, CentraCare Clinic, St. Cloud, MN.
Study Center: Tuulikki Sokka, Hannu Kautiainen, Jyväskylä Central Hospital, Jyväskylä, and Medcare Oy, Äänekoski, Finland; Christopher Swearingen, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock, AR, USA; Theodore Pincus, New York University Hospital for Joint Diseases, New York, NY, USA.
Funding sources: Abbott provided an unrestricted grant to establish the study and to cover printing and mailing expenses to participating rheumatologists but did not participate in conducting the study, analyzing data, or writing reports.
TS has received grants from Central Finland Health Care District and Heinola Rheumatism Foundation Hospital (EVO grants).
Ethics committee approvals: the study was carried out in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethics committees or internal review boards of participating institutes approved the study, and informed consent was obtained from the patients.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
One or more authors of this article have received reimbursements, fees, or funding from the following pharmaceutical companies: Abbott (Abbott Park, IL, USA), Allergan, Inc. (Irvine, CA, USA), Amgen (Thousand Oaks, CA, USA), Bristol-Myers Squibb Company (Princeton, NJ, USA), Chelsea Therapeutics, Inc. (Charlotte, NC, USA), GlaxoSmithKline (Uxbridge, Middlesex, UK), Jazz Pharmaceuticals (Palo Alto, CA, USA), Merrimack Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Cambridge, MA, USA), MSD (Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA), Pfizer Inc (New York, NY, USA), Pierre Fabre Medicament (Boulogne Cedex, France), Roche (Basel, Switzerland), sanofi-aventis (Paris, France), Schering-Plough Corporation (Kenilworth, NJ, USA), UCB (Brussels, Belgium), and Wyeth (Madison, NJ, USA).
Authors' contributions
TS, HK, and TP contributed to study design and analyses. The entire QUEST-RA study group contributed to data collection and preparation of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Sokka, T., Kautiainen, H., Pincus, T. et al. Work disability remains a major problem in rheumatoid arthritis in the 2000s: data from 32 countries in the QUEST-RA Study. Arthritis Res Ther 12, R42 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2951
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2951