Abstract
The phospholipase B homolog Plb1 and the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) pathway are required by fission yeast, also known as to Schizosaccharomyces pombe, to grow under KCl-stress conditions. Here, we report the relative contributions of Plb1 and the cAMP/PKA pathway during the hypertonic stress response. We show that the plb1∆, cyr1∆, and pka1∆ single mutants are sensitive to high concentrations of KCl but insensitive to sorbitol-induced osmotic stress. In contrast, the plb1∆ cyr1∆ and plb1∆ pka1∆ double mutants are hypersensitive to KCl and sorbitol. The cyr1∆ pka1∆ double mutants showed the same phenotype of each single mutant. Growth inhibition due to hypertonic stress in the plb1∆, plb1∆ cyr1∆, and plb1∆ pka1∆ strains was partially rescued by cgs1 deletion—cgs1∆ has constitutively active Pka1—or by the deletion of transcription factor Rst2, which is negatively regulated by Pka1. Pka1-GFP localized in the nucleus and cytoplasm in plb1∆, whereas it is localized only in the cytoplasm in cyr1∆, indicating that Plb1 does not regulate Pka1 localization. Glucose limitation downregulates the PKA pathway, and it was accordingly observed that glucose limitation in plb1∆ further increased the strain’s sensitivity to KCl. Growth inhibition by KCl in plb1∆ under glucose-limited conditions was significantly rescued by cgs1∆ and slightly rescued by rst2∆. These findings indicate that, in fission yeast, Plb1 and the glucose-sensing cAMP/PKA pathway play a synergistic role in responding to hypertonic stress.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansell GB, Hawthorne JN (1964) Catabolism. In: Ansell GB, Hawthorne JN (eds) Phospholipids. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 152–174
Asadi F, Michalski D, Karagiannis J (2016) A genetic screen for fission yeast gene deletion mutants exhibiting hypersensitivity to latrunculin A. G3 (bethesda) 6:3399–3408. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.116.032664
Bahler J, Wu JQ, Longtine MS, Shah NG, McKenzie A 3rd, Steever AB, Wach A, Philippsen P, Pringle JR (1998) Heterologous modules for efficient and versatile PCR-based gene targeting in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Yeast 14:943–951. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0061(199807)14:10%3c943::AID-YEA292%3e3.0.CO;2-Y
Byrne SM, Hoffman CS (1993) Six git genes encode a glucose-induced adenylate cyclase activation pathway in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Cell Sci 105:1095–1100. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.105.4.1095
Cohen A, Kupiec M, Weisman R (2014) Glucose activates TORC2-Gad8 protein via positive regulation of the cAMP/cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) pathway and negative regulation of the Pmk1 protein-mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Biol Chem 289:21727–21737. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.573824
DeVoti J, Seydoux G, Beach D, McLeod M (1991) Interaction between ran1+ protein kinase and cAMP dependent protein kinase as negative regulators of fission yeast meiosis. EMBO J 10:3759–3768. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04945.x
Ekwall K, Thon G (2017) Spore analysis and tetrad dissection of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2017:pdb prot091710. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.prot091710
Fraile R, Sanchez-Mir L, Hidalgo E (2020) A new adaptation strategy to glucose starvation: modulation of the gluconate shunt and pentose phosphate pathway by the transcriptional repressor Rsv1. FEBS J 287:874–877. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.15131
Gupta DR, Paul SK, Oowatari Y, Matsuo Y, Kawamukai M (2011a) Complex formation, phosphorylation, and localization of protein kinase A of Schizosaccharomyces pombe upon glucose starvation. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 75:1456–1465. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.110125
Gupta DR, Paul SK, Oowatari Y, Matsuo Y, Kawamukai M (2011b) Multistep regulation of protein kinase A in its localization, phosphorylation and binding with a regulatory subunit in fission yeast. Curr Genet 57:353–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-011-0354-2
Halova L, Du W, Kirkham S, Smith DL, Petersen J (2013) Phosphorylation of the TOR ATP binding domain by AGC kinase constitutes a novel mode of TOR inhibition. J Cell Biol 203:595–604. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201305103
Higuchi T, Watanabe Y, Yamamoto M (2002) Protein kinase A regulates sexual development and gluconeogenesis through phosphorylation of the Zn finger transcriptional activator Rst2p in fission yeast. Mol Cell Biol 22:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.22.1.1-11.2002
Hoffman CS (2005) Glucose sensing via the protein kinase A pathway in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Biochem Soc Trans 33:257–260. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST0330257
Hoffman CS, Winston F (1990) Isolation and characterization of mutants constitutive for expression of the fbp1 gene of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Genetics 124:807–816. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/124.4.807
Ikai N, Nakazawa N, Hayashi T, Yanagida M (2011) The reverse, but coordinated, roles of Tor2 (TORC1) and Tor1 (TORC2) kinases for growth, cell cycle and separase-mediated mitosis in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Open Biol 1:110007. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsob.110007
Inamura SI, Tanabe T, Kawamukai M, Matsuo Y (2021) Expression of Mug14 is regulated by the transcription factor Rst2 through the cAMP-dependent protein kinase pathway in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Curr Genet 67:807–821. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-021-01194-z
Kawamukai M, Ferguson K, Wigler M, Young D (1991) Genetic and biochemical analysis of the adenylyl cyclase of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Cell Regul 2:155–164. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.2.2.155
Krawchuk MD, Wahls WP (1999) High-efficiency gene targeting in Schizosaccharomyces pombe using a modular, PCR-based approach with long tracts of flanking homology. Yeast 15:1419–1427. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0061(19990930)15:13%3c1419::AID-YEA466%3e3.0.CO;2-Q
Maeda T, Watanabe Y, Kunitomo H, Yamamoto M (1994) Cloning of the pka1 gene encoding the catalytic subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Biol Chem 269:9632–9637. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(17)36928-4
Matsuo Y, Kawamukai M (2017) cAMP-dependent protein kinase involves calcium tolerance through the regulation of Prz1 in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 81:231–241. https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2016.1246171
Matsuo Y, Tanaka K, Nakagawa T, Matsuda H, Kawamukai M (2004) Genetic analysis of chs1+ and chs2+ encoding chitin synthases from Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68:1489–1499. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.68.1489
Matsuo Y, Fisher E, Patton-Vogt J, Marcus S (2007) Functional characterization of the fission yeast phosphatidylserine synthase gene, pps1, reveals novel cellular functions for phosphatidylserine. Eukaryot Cell 6:2092–2101. https://doi.org/10.1128/EC.00300-07
Matsuo Y, McInnis B, Marcus S (2008) Regulation of the subcellular localization of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in response to physiological stresses and sexual differentiation in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Eukaryot Cell 7:1450–1459. https://doi.org/10.1128/EC.00168-08
McInnis B, Mitchell J, Marcus S (2010) Phosphorylation of the protein kinase A catalytic subunit is induced by cyclic AMP deficiency and physiological stresses in the fission yeast, Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 399:665–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.07.139
Murray JM, Watson AT, Carr AM (2016) Transformation of Schizosaccharomyces pombe: Lithium acetate/dimethyl sulfoxide procedure. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2016:pdb prot090969. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.prot090969
Nunez A, Franco A, Madrid M, Soto T, Vicente J, Gacto M, Cansado J (2009) Role for RACK1 orthologue Cpc2 in the modulation of stress response in fission yeast. Mol Biol Cell 20:3996–4009. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E09-05-0388
Petersen J, Russell P (2016) Growth and the environment of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2016:pdb top079764. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.top079764
Roux AE, Quissac A, Chartrand P, Ferbeyre G, Rokeach LA (2006) Regulation of chronological aging in Schizosaccharomyces pombe by the protein kinases Pka1 and Sck2. Aging Cell 5:345–357. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-9726.2006.00225.x
Saitoh S, Mori A, Uehara L, Masuda F, Soejima S, Yanagida M (2015) Mechanisms of expression and translocation of major fission yeast glucose transporters regulated by CaMKK/phosphatases, nuclear shuttling, and TOR. Mol Biol Cell 26:373–386. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E14-11-1503
Sanchez-Mir L, Salat-Canela C, Paulo E, Carmona M, Ayte J, Oliva B, Hidalgo E (2018) Phospho-mimicking Atf1 mutants bypass the transcription activating function of the MAP kinase Sty1 of fission yeast. Curr Genet 64:97–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-017-0730-7
Shieh JC, Wilkinson MG, Buck V, Morgan BA, Makino K, Millar JB (1997) The Mcs4 response regulator coordinately controls the stress-activated Wak1-Wis1-Sty1 MAP kinase pathway and fission yeast cell cycle. Genes Dev 11:1008–1022. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.11.8.1008
Shieh JC, Wilkinson MG, Millar JB (1998) The Win1 mitotic regulator is a component of the fission yeast stress-activated Sty1 MAPK pathway. Mol Biol Cell 9:311–322. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.9.2.311
Shiozaki K, Russell P (1996) Conjugation, meiosis, and the osmotic stress response are regulated by Spc1 kinase through Atf1 transcription factor in fission yeast. Genes Dev 10:2276–2288. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.10.18.2276
Stiefel J, Wang L, Kelly DA, Janoo RT, Seitz J, Whitehall SK, Hoffman CS (2004) Suppressors of an adenylate cyclase deletion in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Eukaryot Cell 3:610–619. https://doi.org/10.1128/EC.3.3.610-619.2004
Sugimoto A, Iino Y, Maeda T, Watanabe Y, Yamamoto M (1991) Schizosaccharomyces pombe ste11+ encodes a transcription factor with an HMG motif that is a critical regulator of sexual development. Genes Dev 5:1990–1999. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.5.11.1990
Takenaka K, Tanabe T, Kawamukai M, Matsuo Y (2018) Overexpression of the transcription factor Rst2 in Schizosaccharomyces pombe indicates growth defect, mitotic defects, and microtubule disorder. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 82:247–257. https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2017.1415126
Tanabe T, Yamaga M, Kawamukai M, Matsuo Y (2019) Mal3 is a multi-copy suppressor of the sensitivity to microtubule-depolymerizing drugs and chromosome mis-segregation in a fission yeast pka1 mutant. PLoS ONE 14:e0214803. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0214803
Tanabe T, Kawamukai M, Matsuo Y (2020) Glucose limitation and pka1 deletion rescue aberrant mitotic spindle formation induced by Mal3 overexpression in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 84:1667–1680. https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2020.1763157
Welton RM, Hoffman CS (2000) Glucose monitoring in fission yeast via the Gpa2 galpha, the git5 Gbeta and the git3 putative glucose receptor. Genetics 156:513–521. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/156.2.513
Wilkinson MG, Samuels M, Takeda T, Toone WM, Shieh JC, Toda T, Millar JB, Jones N (1996) The Atf1 transcription factor is a target for the Sty1 stress-activated MAP kinase pathway in fission yeast. Genes Dev 10:2289–2301. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.10.18.2289
Wu SY, McLeod M (1995) The sak1+ gene of Schizosaccharomyces pombe encodes an RFX family DNA-binding protein that positively regulates cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase-mediated exit from the mitotic cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol 15:1479–1488. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.15.3.1479
Yang P, Du H, Hoffman CS, Marcus S (2003) The phospholipase B homolog Plb1 is a mediator of osmotic stress response and of nutrient-dependent repression of sexual differentiation in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Genet Genomics 269:116–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-003-0820-8
Zuin A, Carmona M, Morales-Ivorra I, Gabrielli N, Vivancos AP, Ayte J, Hidalgo E (2010) Lifespan extension by calorie restriction relies on the Sty1 MAP kinase stress pathway. EMBO J 29:981–991. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2009.407
Acknowledgements
The authors also thank all the members of the laboratory for helpful support and scientific advice. We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for English language editing.
Funding
The authors thank the faculty of Life and Environmental Sciences in Shimane University for help in financial support for publication. This work was supported by a JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP18K05438 (to YM) and JP19K222831 (to MK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YM planned this study, designed the experiments, carried out the experiments, made the yeast strains, and analyzed the data; SM planned this study; MK analyzed the data and provided advice. YM wrote the original draft. YM and MK reviewed and edited the original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest with the content of this article.
Additional information
Communicated by M. Polymenis.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Stevan Marcus—Deceased January 2018.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
Schematic diagram of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase pathway in S. pombe. Supplementary file1 (PPTX 54 KB)
Fig. S2
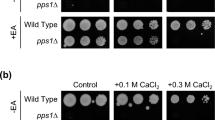
The plb1∆ strain normally grows in the presence of CaCl2 or NaCl. Wild-type (PR109), plb1∆ (YMP603), cyr1∆ (YMP28), plb1∆ cyr1∆ (YMP628), pka1∆ (YMP36), plb1∆ pka1∆ (YMP629), and cyr1∆ pka1∆ (YMP60) cells were spotted onto the YES, YES+0.1 M CaCl2, YES+0.3 M CaCl2, and YES+0.2 M NaCl plates and incubated at 30˚C for 3 to 5 days (YES for 3 days, YES+0.1 M CaCl2 for 4 days and the others for 5 days). Supplementary file2 (PPTX 220 KB)
Fig. S3
The GFP-Plb1 plasmid is functional. Wild-type (PR109) or plb1∆ (YMP603) cells harboring pREP41GFP (vector) or pREP41GFP-plb1 were cultured for 1 day on EMMU at 30˚C to induce expression from the nmt1 promoter. Cells were spotted onto EMMU in the presence or absence of KCl. The plates were incubated for 4 to 7 days at 30˚C (no stress for 4 days and KCl for 7 days). Supplementary file3 (PPTX 83 KB)
Fig. S4
Pka1-GFP localizes in the cytoplasm under KCl stress condition. Pka1-GFP (YMP19), plb1∆ Pka1-GFP (YMP893), cyr1∆ Pka1-GFP (YMP48), and cgs1∆ Pka1-GFP (YMP56) cells were cultured for 24 hours in the presence of 1.2 M KCl, stained by DAPI, and observed by fluorescent microscopy. Supplementary file4 (PPTX 107 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Matsuo, Y., Marcus, S. & Kawamukai, M. Synergistic roles of the phospholipase B homolog Plb1 and the cAMP-dependent protein kinase Pka1 in the hypertonic stress response of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Curr Genet 68, 661–674 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-022-01253-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-022-01253-z