Abstract
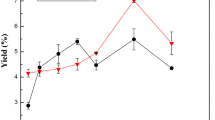
Different pretreatment methods were applied on Rhinobatos cemiculus skin, and their effect on the physicochemical properties of the extracted gelatin was investigated. Prior to extracting gelatin, the skin was pretreated using three methods: bleaching (RCG-BT), ultrasound (RCG-UST) and microwave (RCG-MT). The properties of the resulting gelatins were compared to those of the untreated-skin gelatin (RCG-WT). The pretreatment of R. cemiculus skin was found to differently affect the isoelectric point (pHi), color, structure, thermal stability as well as foam/emulsion-forming capacities of the derived gelatins. In fact, the SDS-PAGE profile revealed the presence of the three gelatin characteristic chains (β and α1/α2) as predominant components in all gelatins with a slight decrease in bands intensity for gelatin exposed to microwave radiation. Based on FTIR analysis, gelatin characteristic bands were found in all gelatins with a slight shift for RCG-MT proving its structural re-arrangements confirmed by X-ray diffraction. Furthermore, among the applied pretreatments on RCG, ultrasound and bleaching were found to be the best techniques giving the most thermally stable gelatins. Additionally, functional properties related to gelatin derived from ultrasound pretreated skin were found to exhibit the highest foam expansion and emulsion activity.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dai H, Ou S, Huang Y, Liu Z, Huang H (2018) Enhanced swelling and multiple-responsive properties of gelatin/sodium alginate hydrogels by the addition of carboxymethyl cellulose isolated from pineapple peel. Cellulose 25:593–606
Kaewruang P, Benjakul S, Prodpran T (2013) Molecular and functional properties of gelatin from the skin of unicorn leatherjacket as affected by extracting temperatures. Food Chem 138:1431–1437
Schrieber R, Gareis H (2007) Gelatine handbook: theory and industrial practice. John Wiley & Sons
Lv L-C, Huang Q-Y, Ding W, Xiao X-H, Zhang H-Y, Xiong L-X (2019) Fish gelatin: the novel potential applications. J Funct Foods 63:103581
Deng L, Kang X, Liu Y, Feng F, Zhang H (2017) Effects of surfactants on the formation of gelatin nanofibres for controlled release of curcumin. Food Chem 231:70–77
Kim S-K, Ngo D-H, Vo T-S (2012) Marine fish-derived bioactive peptides as potential antihypertensive agents. In: Advances in food and nutrition research. Elsevier, pp 249–260
Noma T, Takasugi S, Shioyama M, Yamaji T, Itou H, Suzuki Y, Sakuraba K, Sawaki K (2017) Effects of dietary gelatin hydrolysates on bone mineral density in magnesium-deficient rats. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 18:385
Zhang Z, Zhao M, Wang J, Ding Y, Dai X, Li Y (2011) Oral administration of skin gelatin isolated from chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) enhances wound healing in diabetic rats. Mar Drugs 9:696–711
Alemán A, Martínez-Alvarez O (2013) Marine collagen as a source of bioactive molecules: a review. Nat Prod J 3:105–114
Hosseini SF, Gómez-Guillén MC (2018) A state-of-the-art review on the elaboration of fish gelatin as bioactive packaging: special emphasis on nanotechnology-based approaches. Trends Food Sci Technol 79:125–135
Benjakul S, Oungbho K, Visessanguan W, Thiansilakul Y, Roytrakul S (2009) Characteristics of gelatin from the skins of bigeye snapper, Priacanthus tayenus and Priacanthus macracanthus. Food Chem 116(9):445–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.02.063
Jridi M, Nasri R, Lassoued I, Souissi N, Mbarek A, Barkia A, Nasri M (2013) Chemical and biophysical properties of gelatins extracted from alkali-pretreated skin of cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) using pepsin. Food Res Int 54:1680–1687
Yang H, Wang Y, Zhou P, Regenstein JM (2008) Effects of alkaline and acid pretreatment on the physical properties and nanostructures of the gelatin from channel catfish skins. Food Hydrocoll 22:1541–1550
Kittiphattanabawon P, Benjakul S, Visessanguan W, Shahidi F (2010) Comparative study on characteristics of gelatin from the skins of brownbanded bamboo shark and blacktip shark as affected by extraction conditions. Food Hydrocoll 24:164–171
Monsur HA, Jaswir I, Salleh HM, Alkahtani HA (2014) Effects of pretreatment on properties of gelatin from perch (Lates niloticus) skin. Int J Food Prop 17:1224–1236
Ali AMM, Kishimura H, Benjakul S (2018) Physicochemical and molecular properties of gelatin from skin of golden carp (Probarbus Jullieni) as influenced by acid pretreatment and prior-ultrasonication. Food Hydrocoll 82:164–172
Khiari Z, Rico D, Martin-Diana AB, Barry-Ryan C (2017) Valorization of fish by-products: rheological, textural and microstructural properties of mackerel skin gelatins. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 19:180–191
Tkaczewska J, Morawska M, Kulawik P, Zając M (2018) Characterization of carp (Cyprinus carpio) skin gelatin extracted using different pretreatments method. Food Hydrocoll 81:169–179
Ahmad T, Ismail A, Ahmad S, Khalil K, Leo T, Awad E, Imlan J, Sazili A (2018) Effects of ultrasound assisted extraction in conjugation with aid of actinidin on the molecular and physicochemical properties of bovine hide gelatin. Molecules 23:730
Arzeni C, Martínez K, Zema P, Arias A, Pérez O, Pilosof A (2012) Comparative study of high intensity ultrasound effects on food proteins functionality. J Food Eng 108:463–472
Soria AC, Villamiel M (2010) Effect of ultrasound on the technological properties and bioactivity of food: a review. Trends Food Sci Technol 21:323–331
George N, Zynudheen A, Anu J, Binsi P, Joshy C (2015) Effect of pretreatment conditions and bleaching on physico-chemical and functional properties of gelatin prepared from cuttlefish skin. Indian J Fish 62(2):62–69
Singh P, Benjakul S (2017) Extraction and characterisation of gelatin from the skin of striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) and studies on its colour improvement. Afr J Biotech 16:1–9
Thanonkaew A, Benjakul S, Visessanguan W, Decker EA (2008) The effect of antioxidants on the quality changes of cuttlefish (Sepia pharaonis) muscle during frozen storage. LWT Food Sci Technol 41:161–169
Kori R, Rama S, Kidwai Z (2018) Colour improvement and extraction of gelatin from the skin of striped catfish. Int J Biochem Biotechnol 7(1):782–790
Cassol L, Rodrigues E, Noreña CPZ (2019) Extracting phenolic compounds from Hibiscus sabdariffa L. calyx using microwave assisted extraction. Ind Crops Prod 133:168–177
Hu W, Zhao Y, Yang Y, Zhang H, Ding C, Hu C, Zhou L, Zhang Z, Yuan S, Chen Y (2019) Microwave-assisted extraction, physicochemical characterization and bioactivity of polysaccharides from Camptotheca acuminata fruits. Int J Biol Macromol 133:127–136
Tsukui A, Júnior HS, Oigman S, De Souza R, Bizzo H, Rezende C (2014) Microwave-assisted extraction of green coffee oil and quantification of diterpenes by HPLC. Food Chem 164:266–271
Binsi P, Nayak N, Sarkar P, Joshy C, Ninan G, Ravishankar C (2017) Gelation and thermal characteristics of microwave extracted fish gelatin–natural gum composite gels. J Food Sci Technol 54:518–530
Park J-H, Choe J-H, Kim H-W, Hwang K-E, Song D-H, Yeo E-J, Kim H-Y, Choi Y-S, Lee S-H, Kim C-J (2013) Effects of various extraction methods on quality characteristics of duck feet gelatin. Korean J Food Sci Anim Resour 33:162–169
Gómez-Guillén MC, Turnay J, Fernández-Dıaz M, Ulmo N, Lizarbe MA, Montero P (2002) Structural and physical properties of gelatin extracted from different marine species: a comparative study. Food Hydrocoll 16:25–34
Karim AA, Bhat R (2009) Fish gelatin: properties, challenges, and prospects as an alternative to mammalian gelatins. Food Hydrocoll 23(5):563–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2008.07.002
Horwitz W (2000) Official methods of analysis of AOAC International. AOAC International, Gaithersburg, Md.
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685. https://doi.org/10.1038/227680a0
Pearce KN, Kinsella JE (1978) Emulsifying properties of proteins: evaluation of a turbidimetric technique. J Agric Food Chem 26:716–723
Shahidi F, Han X-Q, Synowiecki J (1995) Production and characteristics of protein hydrolysates from capelin (Mallotus villosus). Food Chem 53:285–293
Giménez B, Gómez-Guillén MC, Montero P (2005) Storage of dried fish skins on quality characteristics of extracted gelatin. Food Hydrocoll 19:958–963
Johnston-Banks FA (1990) Gelatine. In: Harris P (ed) Food gels. Springer Netherlands, pp. 233–289. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-0755-3_7
Zhou P, Regenstein JM (2005) Effects of alkaline and acid pretreatments on Alaska pollock skin gelatin extraction. J Food Sci 70:c392–c396
Cheow C, Norizah M, Kyaw Z, Howell N (2007) Preparation and characterisation of gelatins from the skins of sin croaker (Johnius dussumieri) and shortfin scad (Decapterus macrosoma). Food Chem 101:386–391
Jongjareonrak A, Benjakul S, Visessanguan W, Tanaka M (2006) Skin gelatin from bigeye snapper and brownstripe red snapper: chemical compositions and effect of microbial transglutaminase on gel properties. Food Hydrocoll 20(12):1216–1222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2006.01.006
Arnesen JA, Gildberg A (2007) Extraction and characterisation of gelatine from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) skin. Bioresour Technol 98(1):53–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.11.021
Rostagno MA, Prado JM (2013) Natural product extraction: principles and applications. Royal Society of Chemistry
Jiang X, Chang M, Wang X, Jin Q, Wang X (2014) Effect of ultrasound treatment on oil recovery from soybean gum by using phospholipase C. J Clean Prod 69:237–242
Nagarajan M, Benjakul S, Prodpran T, Songtipya P, Kishimura H (2012) Characteristics and functional properties of gelatin from splendid squid (Loligo formosana) skin as affected by extraction temperatures. Food Hydrocoll 29:389–397
Courts A (1961) Structural changes in collagen. 2. Enhanced solubility of bovine collagen: reactions with hydrogen peroxide and some properties of soluble eucollagen. Biochem J 81:356
Donnelly TH, McGinnis RS (1977) Gelatin manufacture-peroxide liquefaction process
Poppe H (1997) Some reflections on speed and efficiency of modern chromatographic methods. J Chromatogr A 778:3–21
Muyonga JH, Cole CG, Duodu KG (2004) Extraction and physico-chemical characterisation of Nile perch (Lates niloticus) skin and bone gelatin. Food Hydrocoll 18(4):581–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2003.08.009
Kong J, Yu S (2007) Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic analysis of protein secondary structures. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 39:549–559
Bandekar J (1992) Amide modes and protein conformation. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Protein Struct Mol Enzymol 1120:123–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-4838(92)90261-B
Jackson M, Watson PH, Halliday WC, Mantsch HH (1995) Beware of connective tissue proteins: Assignment and implications of collagen absorptions in infrared spectra of human tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Mol Basis Dis 1270:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/0925-4439(94)00056-V
Nur Hanani ZA, Beatty E, Roos YH, Morris MA, Kerry JP (2013) Development and characterization of biodegradable composite films based on gelatin derived from beef, pork and fish sources. Foods 2:1–17
Tongnuanchan P, Benjakul S, Prodpran T (2012) Properties and antioxidant activity of fish skin gelatin film incorporated with citrus essential oils. Food Chem 134:1571–1579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.03.094
Uriarte-Montoya MH, Santacruz-Ortega H, Cinco-Moroyoqui FJ, Rouzaud-Sández O, Plascencia-Jatomea M, Ezquerra-Brauer JM (2011) Giant squid skin gelatin: chemical composition and biophysical characterization. Food Res Int 44:3243–3249
Gómez-Guillén M, Pérez-Mateos M, Gómez-Estaca J, López-Caballero E, Giménez B, Montero P (2009) Fish gelatin: a renewable material for developing active biodegradable films. Trends Food Sci Technol 20:3–16
Tümerkan ET, Cansu Ü, Boran G, Mac Regenstein J, Özoğul F (2019) Physiochemical and functional properties of gelatin obtained from tuna, frog and chicken skins. Food Chem 287:273–279
Badii F, Howell NK (2006) Fish gelatin: Structure, gelling properties and interaction with egg albumen proteins. Food Hydrocoll 20:630–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2005.06.006
Mad-Ali S, Benjakul S, Prodpran T, Maqsood S (2017) Characteristics and gelling properties of gelatin from goat skin as affected by drying methods. J Food Sci Technol 54:1646–1654
Hazirah MN, Isa M, Sarbon N (2016) Effect of xanthan gum on the physical and mechanical properties of gelatin-carboxymethyl cellulose film blends. Food Packag Shelf Life 9:55–63
Yu Z-L, Zeng W-C, Zhang W-H, Liao X-P, Shi B (2016) Effect of ultrasonic pretreatment on kinetics of gelatin hydrolysis by collagenase and its mechanism. Ultrason Sonochem 29:495–501
Aewsiri T, Benjakul S, Visessanguan W (2009) Functional properties of gelatin from cuttlefish (Sepia pharaonis) skin as affected by bleaching using hydrogen peroxide. Food Chem 115:243–249
Li D, Mu C, Zhang Q, Zhou Y, Lin W (2010) Effects of microwave irradiation on collagen denaturation. J Food Biochem 34:1319–1331
Kchaou H, Benbettaieb N, Jridi M, Nasri M, Debeaufort F (2019) Influence of Maillard reaction and temperature on functional, structure and bioactive properties of fish gelatin films. Food Hydrocoll 97:105196
Pirestani S, Nasirpour A, Keramat J, Desobry S, Jasniewski J (2018) Structural properties of canola protein isolate-gum Arabic Maillard conjugate in an aqueous model system. Food Hydrocoll 79:228–234
Krokida MK, Maroulis ZB (2001) Structural properties of dehydrated products during rehydration. Int J Food Sci Technol 36:529–538
Zhou B, Zhang M, Fang Z, Liu Y (2015) Effects of ultrasound and microwave pretreatments on the ultrafiltration desalination of salted duck egg white protein. Food Bioprod Process 96:306–313
Requena JR, Dimitrova MN, Legname G, Teijeira S, Prusiner SB, Levine RL (2004) Oxidation of methionine residues in the prion protein by hydrogen peroxide. Arch Biochem Biophys 432:188–195
Mulinacci F, Poirier E, Capelle MA, Gurny R, Arvinte T (2013) Influence of methionine oxidation on the aggregation of recombinant human growth hormone. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 85:42–52
Benbettaïeb N, Karbowiak T, Brachais C-H, Debeaufort F (2016) Impact of electron beam irradiation on fish gelatin film properties. Food Chem 195:11–18
Barreto P, Pires A, Soldi V (2003) Thermal degradation of edible films based on milk proteins and gelatin in inert atmosphere. Polym Degrad Stab 79:147–152
Muthyala S, Bhonde RR, Nair PD (2010) Cytocompatibility studies of mouse pancreatic islets on gelatin-PVP semi IPN scaffolds in vitro: potential implication towards pancreatic tissue engineering. Islets 2:357–366
Oszmiański J, Wojdyło A (2007) Effects of various clarification treatments on phenolic compounds and color of apple juice. Eur Food Res Technol 224:755–762
Sinthusamran S, Benjakul S, Kishimura H (2014) Characteristics and gel properties of gelatin from skin of seabass (Lates calcarifer) as influenced by extraction conditions. Food Chem 152:276–284
Jridi M, Lassoued I, Kammoun A, Nasri R, Nasri M, Souissi N (2015) Screening of factors influencing the extraction of gelatin from the skin of cuttlefish using supersaturated design. Food Bioprod Process 94:525–535
Zayas JF (1997) Functionality of proteins in food, pp 6–67
Townsend A, Nakai S (1983) Relationships between hydrophobicity and foaming characteristics of food proteins. J Food Sci 48:588–594
Damodaran S (1997) Food proteins and their applications, pp 57–110
van der Ven C, Gruppen H, de Bont DB, Voragen AG (2002) Correlations between biochemical characteristics and foam-forming and-stabilizing ability of whey and casein hydrolysates. J Agric Food Chem 50:2938–2946
Liu D, Liang L, Regenstein JM, Zhou P (2012) Extraction and characterisation of pepsin-solubilised collagen from fins, scales, skins, bones and swim bladders of bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis). Food Chem 133:1441–1448
Abdelmalek BE, Gómez-Estaca J, Sila A, Martinez-Alvarez O, Gómez-Guillén MC, Chaabouni-Ellouz S, Ayadi MA, Bougatef A (2016) Characteristics and functional properties of gelatin extracted from squid (Loligo vulgaris) skin. LWT Food Sci Technol 65:924–931
Yamauchi K, Shimizu M, Kamiya T (1980) Emulsifying properties of whey protein. J Food Sci 45:1237–1242. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.1980.tb06529.x
Sikorski ZE (2001) Functional properties of proteins in food systems. Chemical and functional properties of food proteins, pp 113–135
Sow LC, Yang H (2015) Effects of salt and sugar addition on the physicochemical properties and nanostructure of fish gelatin. Food Hydrocoll 45:72–82
Acknowledgements
This research work was conducted in the framework of PHC-Utique Program, (partenariat Hubert Curien « Utique » du Ministère de l’Europe et des Affaires Etrangères français et du Ministère de l’Enseignement et de la Recherche Scientifique tunisien) financed by CMCU (Comité mixte de coopération universitaire), grant N°: 19G0815.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boughriba, S., Nasri, R., Li, S. et al. Effect of pretreatment-assisted extraction on the physicochemical and structural properties of Rhinobatos cemiculus skin gelatin. Polym. Bull. 80, 445–468 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-04038-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-021-04038-5