Abstract
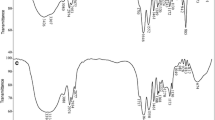
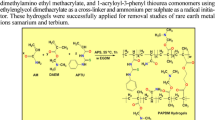
Synthesis, characterization, and study of the cation adsorption properties of four hydrogels are presented. The hydrogels were synthesized via radical copolymerization of a 1:1 mixture of 2-hydroxyethyl-methacrylate and 2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid, with different initiators and cross-linking reagents. HM1 hydrogel was obtained by adding only ammonium persulfate; HM2 hydrogel was synthesized using a redox initiator solution containing ammonium persulfate and sodium metabisulfite at room temperature. For HM3 hydrogel the initiator benzoyl peroxide and the cross-linking reagent ethylene glycol dimethacrylate were used. Finally, for HM4 hydrogel the polymerization was carried out using ammonium persulfate as initiator and poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether as cross-linking reagent. The sorption properties were analyzed by pH, contact time, maximum sorption capacity, and selectivity studies. The HM2 and HM3 hydrogels exhibited good ion sorption properties. These copolymers were capable of interacting and removing Cd(II), Cu(II), Pb(II), Ni(II), and Zn(II) ions from synthetic solutions and with real samples from mining wastewaters. The results obtained from the studies of maximum sorption capacity at different concentrations showed that the HM2 hydrogel was capable of adsorbing 226 mg/g Cd(II), 241 mg/g Pb(II), 166 mg/g Cu(II), 161 mg/g Zn(II), and 110 mg/g Ni(II) and the HM3 hydrogel was capable of adsorbing 184 mg/g Ni(II), 172 mg/g Cd(II), 126 mg/g Zn(II), 90 mg/g Pb(II), and 39 mg/g Cu(II). The experimental data were correlated with the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models. Thermodynamic parameters such as enthalpy (ΔH°), Gibbs free energy (ΔG°), and entropy (ΔS°) changes were obtained. The sorption kinetics were analyzed using Lagergren pseudo-second-order equation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luan Y, Lu A, Chen J, Fu H, Xu L (2016) A label-free aptamer-based fluorescent assay for cadmium detection. Appl Sci 6:432(1)–432(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/app6120432
Kim HN, Ren WX, Kim JS, Yoon J (2012) Fluorescent and colorimetric sensors for detection of lead, cadmium, and mercury ions. Chem Soc Rev 41:3210–3244. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1cs15245a
Çavuş S, Yaşar G, Kaya Y, Gönder ZB, Gürdağ G, Vergili I (2016) Synthesis and characterization of gel beads based on ethyleneglycoldimethacrylate and 2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propane sulfonic acid: removal of Fe(II), Cu(II), Zn(II), and Ni(II) from metal finishing wastewater. Process Saf Environ 103:227–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2016.07.011
Turhanen PA, Vepsäläinen JJ, Peräniemi S (2015) Advanced material and approach for metal ions removal from aqueous solutions. Sci Rep 5:8992(1)–8992(8). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep08992
Zainol Z, Nicol MJ (2009) Comparative study of chelating ion exchange resins for the recovery of nickel and cobalt from laterite leach tailings. Hydrometallurgy 96:283–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2008.11.005
Salama TM, Ali IO, Gumaa HA, Lateef MA, Bakr MF (2016) Novel synthesis of nay zeolite from rice husk silica: modification with ZnO and ZnS for antibacterial application. Chem Sci J 7:118(1)–118(9). https://doi.org/10.4172/2150-3494.1000118
Taha AA, Moustafa AHE, Abdel-Rahman HH, AbdEl-Hameed MMA (2018) Comparative biosorption study of Hg(II) using raw and chemically activated almond shell. Adsorpt Sci Technol 36:521–548. https://doi.org/10.1177/0263617417705473
Rivas BL, Pereira ED, Palencia M, Sánchez J (2011) Water-soluble functional polymers in conjunction with membranes to remove pollutant ions from aqueous solutions. Progr Polym Sci 36:294–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2010.11.001
Rehman S, Siddiq M, Al-Lohedan H, Aktas N, Sahiner M, Demirci S, Sahiner N (2016) Fast removal of high quantities of toxic arsenate via cationic p(APTMACl) microgels. J Environ Manag 166:217–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.10.026
Tang SCN, Lo IMC, Mak MSH (2012) Comparative Study of the adsorption selectivity of Cr(VI) onto cationic hydrogels with different functional groups. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:1713–1722. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0977-4
Khan M, Lo IMC (2017) Removal of ionizable aromatic pollutants from contaminated water using nano γ-Fe2O3 based magnetic cationic hydrogel: sorptive performance, magnetic separation and reusability. J Hazard Mater 322:195–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.01.051
Shi J, Li H, Lu H, Zhao X (2015) Use of carboxyl functional magnetite nanoparticles as potential sorbents for the removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. J Chem Eng Data 60:2035–2041. https://doi.org/10.1021/je5011196
Pereira FV, Gurgel LVA, Gil LF (2010) Removal of Zn2+ from aqueous single metal solutions and electroplating wastewater with wood sawdust and sugarcane bagasse modified with EDTA dianhydride (EDTAD). J Hazard Mater 176:856–863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.11.115
Fang R, He W, Xue H, Chen W (2016) Synthesis and characterization of a high capacity cationic hydrogel adsorbent and its application in the removal of Acid Black 1 from aqueous solution. React Funct Polym 102:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2016.02.013
Ozay O, Ekici S, Baran Y, Aktas N, Sahiner N (2009) Removal of toxic metal ions with magnetic hydrogels. Water Res 43:4403–4411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.06.058
Zhu Y, Zheng Y, Wang F, Wang A (2016) Monolithic supermacroporous hydrogel prepared from high internal phase emulsions (HIPEs) for fast removal of Cu2+ and Pb2+. Chem Eng J 284:422–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.08.157
Toledo L, Urbano BF (2016) Poly(2-hydroxyethyl-methacrylate)-based porous hydrogel: Influence of surfactant and SiO2 nanoparticles on the morphology, swelling and thermal properties. Eur Polym J 81:316–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2016.06.021
Dobić SN, Filipović JM, Tomić SL (2012) Synthesis and characterization of poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate/itaconic acid/poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate) hydrogels. Chem Eng J 179:372–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.10.083
Gupta VK, Tyagi I, Agarwal S, Sadegh H, Shahryari-ghoshekandi R, Yari M, Yousefi-nejat O (2015) Experimental study of surfaces of hydrogel polymers HEMA, HEMA-EEMA-MA, and PVA as adsorbent for removal of azo dyes from liquid phase. J Mol Liq 206:129–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.02.015
Podkościelna B, Bartnicki A, Gawdzik B (2012) New crosslinked hydrogels derivatives of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate: synthesis, modifications and properties. Express Polym Lett 6:759–771. https://doi.org/10.3144/expresspolymlett.2012.81
Moradi O, Aghaie M, Zare K, Monajjemi M, Aghaie H (2009) The study of adsorption characteristics Cu2+ and Pb2+ ions onto PHEMA and P(MMA-HEMA) surfaces from aqueous single solution. J Hazard Mater 170:673–679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.012
Su E, Okay O (2018) Hybrid cross-linked poly(2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid) hydrogels with tunable viscoelastic, mechanical and self-healing properties. React Funct Polym 123:70–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2017.12.009
Boonkaew B, Barber PM, Rengpipat S, Supaphol P, Kempf M, He J, John VT, Cuttle L (2014) Production with gamma irradiation creates silver nanoparticles and radical polymerization. J Pharm Sci 103:3244–3253. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.24095
Yang C, Liu Z, Chen C, Shi K, Zhang L, Ju X-J, Wang W, Xie R, Chu LY (2017) Reduced graphene oxide-containing smart hydrogels with excellent electro-response and mechanical properties for soft actuators. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:15758–15767. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b01710
Jones A, Vaughan JD (2005) Hydrogel dressings in the management of a variety of wound types: a review. J Orthop Nurs 9:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1361-3111(05)80001-9
Nalampang K, Panjakha R, Molloy R, Tighe BJ (2013) Structural effects in photopolymerized sodium AMPS hydrogels crosslinked with poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate for use as burn dressings. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 24:1291–1304. https://doi.org/10.1080/09205063.2012.755601
Çavuş S, Çakal E (2017) Poly(2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propane sulfonic acid-co-1-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) hydrogel and its use in the removal of Cd(II), Pb(II) and Cu(II). Acta Phys Pol A 132:505–508. https://doi.org/10.12693/APhysPolA.132.505
Çavuş S, Gürdağ G (2008) Competitive heavy metal removal by poly(2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propane sulfonic acid-co-itaconic acid). Polym Adv Technol 19:1209–1217. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.1113
Lee KE, Morad N, Teng TT, Poh BT (2012) Kinetics and in situ rheological behavior of acrylamide redox polymerization. J Dispers Sci Technol 33:387–395. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2011.567176
Elgueta E, Sánchez J, Dax D, Xu C, Willför S, Rivas BL, González M (2016) Functionalized galactoglucomannan-based hydrogels for the removal of metal cations from aqueous solutions. J Appl Polym Sci 133:44093(1)–44093(8). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.44093
Wan Ngah WS, Endud CS, Mayanar R (2002) Removal of copper(II) ions from aqueous solution onto chitosan and cross-linked chitosan beads. React Funct Polym 50:181–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1381-5148(01)00113-4
Çavuş S, Gürdaǧ G (2009) Noncompetitive removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by poly[2-(acrylamido)-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonicacid-co-itaconic acid] hydrogel. Ind Eng Chem Res 48:2652–2658. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie801449k
Rivas BL, Maureira A, Guzmán C, Mondaca MA (2009) Poly(2-acrylamido glycolic acid-co-2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propane sulfonic acid): synthesis, characterization, and retention properties for environmentally impacting metal ions. J Appl Polym Sci 111:78–86. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.29019
Kono H, Ogasawara K, Kusumoto R, Oshima K, Hashimoto H, Shimizu Y (2016) Cationic cellulose hydrogels cross-linked by poly(ethylene glycol): preparation, molecular dynamics, and adsorption of anionic dyes. Carbohydr Polym 152:170–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.07.011
Cuizano NA, Reyes ÚF, Domínguez S, Llanos BP, Navarro AE (2010) Relevancia del pH en la adsorción de iones metálicos mediante algas pardas. Revista de la Sociedad Química del Perú 76:123–130
Rivas BL, Maureira A (2008) Water-soluble polyelectrolytes containing sulfonic acid groups with metal ion binding ability by using the liquid phase polymer based retention technique. Macromol Symp 270:143–152. https://doi.org/10.1002/masy.200851017
Lin L-C, Thirumavalavan M, Wang Y-T, Lee J-F (2010) Effect of preparation conditions on the adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution by mesoporous silica materials prepared using organic template (HDTMAB). J Chem Eng Data 55:3667–3673. https://doi.org/10.1021/je1002253
Bohli T, Villaescusa I, Ouederni A (2014) Comparative study of bivalent cationic metals adsorption Pb(II), Cd(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II) on olive stones chemically activated carbon. J Chem Eng Process Technol 4:4(1)–4(7). https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7048.1000158
Urbano BF, Rivas BL (2013) Synthesis, characterization, and sorption properties of water-insoluble poly(2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propane sulfonic acid)-montmorillonite composite. Polym Bull 70:1143–1162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-012-0894-8
Chen X (2015) Modeling of experimental adsorption isotherm data. Information 6:14–22. https://doi.org/10.3390/info6010014
Okeola FO, Odebunmi EO (2010) Comparison of Freundlich and Langmuir isoterms for adsorption of Methylene Blue by agrowaste derived activated carbon. Adv Environ Biol 4:329–335
McKay G, Otterburn MS, Sweeney AG (1981) The removal of colour from effluent using various adsorbents. III: silica rate process. Water Res 14:14–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90037-8
Özer A, Pirinççi HB (2006) The adsorption of Cd(II) ions on sulphuric acid-treated wheat bran. J Hazard Mater 137:849–855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.03.009
Malik PK (2004) Dye removal from wastewater using activated carbon developed from sawdust: adsorption equilibrium and kinetics. J Hazard Mater 113:81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.05.022
Desta M (2013) Batch sorption experiments: Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm studies for the adsorption of textile metal ions onto teff straw (Eragrostistef) agricultural waste. J Thermodyn. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/375830
Bazrafshan E, Zarei AA, Mostafapour FK (2016) Biosorption of cadmium from aqueous solutions by Trichoderma fungus: kinetic, thermodynamic, and equilibrium study. Desalin Water Treat 57:14598–14608. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1065764
Robati D (2013) Pseudo-second-order kinetic equations for modeling adsorption systems for removal of lead ions using multi-walled carbon nanotube. JNSC 3:55(1)–55(6). https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-8865-3-55DO
Wan Ngah WS, Fatinathan S (2010) Adsorption characterization of Pb(II) and Cu(II) ions onto chitosan-tripolyphosphate beads: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J Environ Manag 91:958–969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.12.003
Peng S, Meng H, Ouyang Y, Chang J (2014) Nanoporous magnetic cellulose-chitosan composite microspheres: preparation, characterization, and application for Cu(II) adsorption. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:2106–2113. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie402855t
Urbano BF, Paredes J, Rivas BL, Kusku O, Kabay N, Bryjak M (2014) Water-insoluble copolymer based on N-methyl-d-glucamine and quaternary ammonium groups with capability to remove arsenic. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 33:1187–1193. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.11905
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the PAI (Grant No. 781301006), FONDECYT (Grant No. 1150510), CIPA, CONICYT Regional, GORE BIO BIO, R17A10003, and the scholarship given to Aritz Mancisidor by the Global Training Internationalization Programme from the Basque Government, Spain. The authors thank the Center for Water Resources for Agriculture and Mining, University of Concepción, Chile, for supplying real water sample.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elgueta, E., Rivas, B.L., Mancisidor, A. et al. Hydrogels derived from 2-hydroxyethyl-methacrylate and 2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid, with ability to remove metal cations from wastewater. Polym. Bull. 76, 6503–6528 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02697-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02697-z