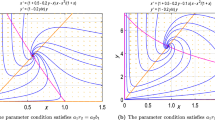
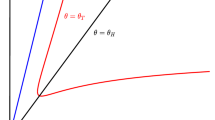
Abstract
A characteristic of ecosystems is the existence of manifold of independencies which are highly complex. Various mathematical models have made considerable contributions in gaining a better understanding of the predator–prey interactions. The main components of any predator–prey models are, firstly, how the different population classes grow and secondly, how the prey and predator interacts. In this paper, the two populations’ growth rates obey the logistic law and the carrying capacity of the predator depends on the available number of prey are considered. Our aim is to clarify the relationship between models and Holling types functional and numerical responses in order to gain insights into predator interferences and to answer an important question how competition is carried out. We consider a predator–prey model and a two-predator one-prey model to explain the idea. The novel approach is explained for the mechanism measurement of predator interference through depending on numerical response. Our approach gives good correspondence between an important real data and computer simulations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Hasan Y, Alebraheem J (2015) Functional and numerical response in prey–predator system. AIP Conf Proc 1651:3. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4914425
Alebraheem J (2016) Fluctuations in interactions of prey predator systems. Sci Int 28:2357–2362
Alebraheem J (2018) Relationship between the paradox of enrichment and the dynamics of persistence and extinction in prey–predator systems. Symmetry 10:532
Alebraheem J (2021) Dynamics of a predator–prey model with the effect of oscillation of immigration of the prey. Diversity 13(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13010023
Alebraheem J, Abu-Hassan Y (2011) The effects of capture efficiency on the coexistence of a predator in a two predators–one prey model. J Appl Sci 11:3717–3724
Alebraheem J, Abu-Hassan Y (2012b) Persistence of predators in a two predators–one prey model with non-periodic solution. J Appl Sci 6:943–956
Alebraheem J, Abu-Hassan Y (2013) Efficient biomass conversion and its effect on the existence of predators in a predator–prey system. Res J Appl Sci 8:286–295
Alebraheem J, Abu-Hassan Y (2014) Dynamics of a two predator–one prey system. Comput Appl Math 33:767–780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-013-0093-8
Alebraheem J, Abu-Hassan Y (2012a) Simulation of complex dynamical behaviour in prey predator model. In: Proceedings of the 2012a International Conference on Statistics in Science, Business and Engineering, Langkawi, Malaysia, 10–12 Sep 2012a. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSSBE.2012.6396618
Ali N, Jazar M (2013) Global dynamics of a modified Leslie-Gower predator–prey model with Crowley–Martin functional responses. J Appl Math Comput 43:271–293
Beddington JR (1975) Mutual interference between parasites or predators and its effect on searching efficiency. J Anim Ecol 44:331–341. https://doi.org/10.2307/3866
Chase RD, Abrams PA, Grover J, Diehl S, Holt RD, Richards S, Case T, Wilson W, Nisbet R, Chesson P (2002) The influence between predation and competition a review and synthesis. Ecol Lett 5:302–315
Crowley PH, Martin EK (1989) Functional responses and interference within and between year classes of a dragonfly population. J North Am Benthol Soc 8:211–221
DeAngelis DL, Goldsten RA, O’Neill RV (1975) A model for trophic interaction. Ecology 56:881–892. https://doi.org/10.2307/1936298
Freedman I (1980) Deterministic mathematical models in population ecology. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York
Gakkhar S, Naji RK (2003) Seasonally perturbed prey–predator system with predator-dependent functional response. Chaos Solitons Fractals 18(5):1075–1083
Gakkhar S, Singh B, Naji RK (2007) Dynamical behavior of two predators competing over a single prey. Biosystems 90(3):808–817
Haberman R (1998) Mathematical models mechanical vibrations, population dynamics, and traffic flow. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia
Holling CS (1959) Some characteristics of simple types of predation and parasitism. Can Entomol 91(7):385–398
Hunsicker ME, Cianelli L, Bailey KM, Buckel JA et al (2011) Functional responses and scaling in predator–prey interactions of marine fishes: contemporary issues and emerging concepts. Ecol Lett 14:1288–1299
Jana A, Roy SK (2022) Holling-Tanner prey-predator model with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response including delay. Int J Model Simul 42(1):86–100. https://doi.org/10.1080/02286203.2020.1839168
Kendall BE (2001) Nonlinear dynamics and chaos, eLS 13: 255–263
Leslie PH (1948) Some further notes on the use of matrices in population mathematics. Biometrika 325:213–245
Leslie PH, Gower JC (1960) The properties of a stochastic model for the predator–prey type of interaction between two species. Biometrika 47:219–234
Lotka AJ (1925) Elements of physical biology. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, Maryland USA
Ma Z, Wang S (2018) A delay-induced predator–prey model with Holling type functional response and habitat complexity. Nonlinear Dyn 93:1519. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4274-2
May RM (1972) Limit cycles in predator–prey communities. Science 177:900–902
Maynard-Smith J (1978) Models in ecology. CUP Archive, London
Molla H, Sabiar Rahman M, Sarwardi S (2018) Dynamics of a predator–prey model with holling type II functional response incorporating a prey refuge depending on both the species. Int J Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 20(1):89–104. https://doi.org/10.1515/ijnsns-2017-0224
Mortoja Golam SK, Panja P, Mondal SK (2018) Dynamics of a predator–prey model with stage-structure on both species and anti-predator behavior. Inf Med Unlocked 10:50–57
Mortoja Golam SK, Panja P, Mondal SK (2019) Dynamics of a predator–prey model with nonlinear incidence rate, Crowley-Martin type functional response and disease in prey population. Ecol Gen Genom 10:100035
Murray JD (2002) Mathematical biology. Springer, Berlin
O’Donoghue M, Boutin S, Krebs CJ, Zuleta G, Murray DL, Hofer EJ (1998) Functional responses of coyotes and lynx to the snowshoe hare cycle. Ecology 79(4):1193–1208
Pal S, Majhi S, Mandal S, Pal N (2019) Role of fear in a predator–prey model with Beddington–DeAngelis functional response. Z Naturforschung A 74(7):581–595. https://doi.org/10.1515/zna-2018-0449
Panja P (2021) Dynamics of a predator–prey model with crowley–martin functional response, refuge on predator and harvesting of super-predator. J Biol Syst 29(3):631–646
Pastor J (2008) Mathematical ecology of populations and ecosystems. Wiley, USA
Perko L (1996) Differential equations and dynamical Systems, 3rd edn. Springer, USA
Qiu H, Huo Y, Ma T (2022) Dynamical analysis of a stochastic hybrid predator-prey model with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response and Lévy jumps[J]. AIMS Math 7(8):14492–14512. https://doi.org/10.3934/math.2022799
Rockwood LL (2006) Introduction to population ecology. Blackwell Publishing Ltd, Malden
Sahoo B, Poria S (2019) Dynamics of predator–prey system with fading memory. Appl Math Comput 347:319–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2018.11.013
Shao Y, Kong W (2022) A predator–prey model with beddington–deangelis functional response and multiple delays in deterministic and stochastic environments. Mathematics 10(18):3378. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10183378
Skalski GT, Gilliam JF (2001) Functional responses with predator interference: viable alternatives to the Holling type II model. Ecology 82:3083–3092
Solomon ME (1949) The natural control of animal populations. J Anim Ecol 18:1–35
Upadhyay R, Iyengar SRK (2007) Effect of seasonality on the dynamics of 2 and 3 species prey-predator systems. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 6(3):509–530
Upadhyay R, Raw S, Rai V (2010) Dynamical complexities in a tri-trophic hybrid food chain model with holling type II and crowley-martin functional responses. Nonlinear Anal Model Control 15(3):361–375
Volterra V (1926) Variazione e fluttuazini del numero d’individui in specie animali conviventi. Mem R Accad Naz Dei Lincei 2:31–113
Xiao Z, Xie X, Xue Y (2018) Stability and bifurcation in a Holling type II predator–prey model with Allee effect and time delay. Adv Differ Equ. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13662-018-1742-4
Yang P (2019) Hopf bifurcation of an age-structured prey-predator model with Holing type II functional response incorporating a prey refuge. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 49:368–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nonrwa.2019.03.014
Ye Y, Liu H, Wei Y et al (2019) Dynamic study of a predator-prey model with Allee effect and Holling type-I functional response. Adv Differ Equ. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13662-019-2311-1
Zhu X, Ding W (2019) Global stability of periodic solutions of predator-prey system with holling type III functional response. J Appl Anal Comput 9(4):1606–1615. https://doi.org/10.11948/2156-907X.20190121
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alebraheem, J., Abu-Hassan, Y. A novel mechanism measurement of predator interference in predator–prey models. J. Math. Biol. 86, 84 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-023-01914-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-023-01914-8