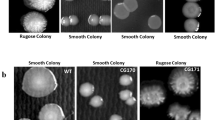
Abstract
Vibrio parahaemolyticus is a seafood opportunistic pathogen. There are evidences suggesting that virulence skills, including hemolytic activity and biofilm formation, are regulated by the luxM/luxS-dependent quorum-sensing system in V. parahaemolyticus, and their regulatory mechanism is not well understood. To better understand the virulence regulatory mechanism of V. parahaemolyticus, the luxM deletion (△luxM) and luxS deletion (△luxS) mutants were constructed and their impacts on growth, hemolysin activity, and biofilm were investigated. Results show that both luxM and luxS are involved in the adaptation to environmental conditions in early adaptive-log phase growth of V. parahaemolyticus. Thermostable direct hemolysin gene (tdh) was negatively regulated by luxM and positively regulated by luxS. The biofilm formation was negatively regulated by both luxS and luxM. This study provides an insight into some aspects of V. parahaemolyticus virulence regulation by luxM/luxS-dependent quorum-sensing system.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banik SK, Fenley AT, Kulkarni RV (2009) A model for signal transduction during quorum sensing in Vibrio harveyi. Phys Biol 6(4):046008. https://doi.org/10.1088/1478-3975/6/4/046008
Brachmann CB, Davies A, Cost GJ, Caputo E, Li J, Hieter P, Boeke JD (1998) Designer deletion strains derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C: a useful set of strains and plasmids for PCR-mediated gene disruption and other applications. Yeast 14(2):115–132
Carius L, Carius AB, McIntosh M, Grammel H (2013) Quorum sensing influences growth and photosynthetic membrane production in high-cell-density cultivations of Rhodospirillum rubrum. BMC Microbiol 13:189. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-13-189
Daniels NA, MacKinnon L, Bishop R, Altekruse S, Ray B, Hammond RM, Thompson S, Wilson S, Bean NH, Griffin PM, Slutsker L (2000) Vibrio parahaemolyticus infections in the United States, 1973–1998. J Infect Dis 181(5):1661–1666. https://doi.org/10.1086/315459
Davies DG, Parsek MR, Pearson JP, Iglewski BH, Costerton JW, Greenberg EP (1998) The involvement of cell-to-cell signals in the development of a bacterial biofilm. Science 280(5361):295–298
Defoirdt T, Bossier P, Sorgeloos P, Verstraete W (2005) The impact of mutations in the quorum sensing systems of Aeromonas hydrophila, Vibrio anguillarum and Vibrio harveyi on their virulence towards gnotobiotically cultured Artemia franciscana. Environ Microbiol 7(8):1239–1247. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00807.x
Fabbri A, Falzano L, Frank C, Donelli G, Matarrese P, Raimondi F, Fasano A, Fiorentini C (1999) Vibrio parahaemolyticus thermostable direct hemolysin modulates cytoskeletal organization and calcium homeostasis in intestinal cultured cells. Infect Immun 67(3):1139–1148
Fang Z, Wang S, Du X, Shi P, Huang Z (2014) Phosphatidate phosphatase-1 is functionally conserved in lipid synthesis and storage from human to yeast. Acta Biol Hung 65(4):481–492. https://doi.org/10.1556/ABiol.65.2014.4.11
Faruque SM, Biswas K, Udden SM, Ahmad QS, Sack DA, Nair GB, Mekalanos JJ (2006) Transmissibility of cholera: in vivo-formed biofilms and their relationship to infectivity and persistence in the environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(16):6350–6355. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0601277103
Ham H, Orth K (2012) The role of type III secretion system 2 in Vibrio parahaemolyticus pathogenicity. J Microbiol 50(5):719–725. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-012-2550-2
Hammer BK, Bassler BL (2003) Quorum sensing controls biofilm formation in Vibrio cholerae. Mol Microbiol 50(1):101–104
Henke JM, Bassler BL (2004) Quorum sensing regulates type III secretion in Vibrio harveyi and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Bacteriol 186(12):3794–3805. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.186.12.3794-3805.2004
Hiyoshi H, Kodama T, Iida T, Honda T (2010) Contribution of Vibrio parahaemolyticus virulence factors to cytotoxicity, enterotoxicity, and lethality in mice. Infect Immun 78(4):1772–1780. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.01051-09
Hongping W, Jilun Z, Ting J, Yixi B, Xiaoming Z (2011) Insufficiency of the Kanagawa hemolytic test for detecting pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Shanghai, China. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 69(1):7–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2010.08.016
Huang Y, Chen Y, Sun H, Lan D (2016) Stability of reference gene expression after porcine Sapelovirus infection in porcine intestinal epithelial cells. Viral Immunol 29(6):343–349. https://doi.org/10.1089/vim.2015.0130
Huq A, Whitehouse CA, Grim CJ, Alam M, Colwell RR (2008) Biofilms in water, its role and impact in human disease transmission. Curr Opin Biotechnol 19(3):244–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2008.04.005
Jensen RV, Depasquale SM, Harbolick EA, Hong T, Kernell AL, Kruchko DH, Modise T, Smith CE, McCarter LL, Stevens AM (2013) Complete genome sequence of prepandemic Vibrio parahaemolyticus BB22OP. Genome Announc. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00002-12
Klug B, Rodler C, Koller M, Wimmer G, Kessler HH, Grube M, Santigli E (2011) Oral biofilm analysis of palatal expanders by fluorescence in-situ hybridization and confocal laser scanning microscopy. J Visual Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/2967
Leon-Sicairos N, Angulo-Zamudio UA, de la Garza M, Velazquez-Roman J, Flores-Villasenor HM, Canizalez-Roman A (2015) Strategies of Vibrio parahaemolyticus to acquire nutritional iron during host colonization. Front Microbiol 6:702. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00702
Liao Y, Li Y, Wu S, Mou J, Xu Z, Cui R, Klena JD, Shi X, Lu Y, Qiu Y, Lin Y, Xie X, Ma H, Li Z, Yu H, Varma JK, Ran L, Hu Q, Cheng J (2015) Risk factors for Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection in a Southern Coastal region of China. Foodborne Pathog Dis 12(11):881–886. https://doi.org/10.1089/fpd.2015.1988
Liu Z, Stirling FR, Zhu J (2007) Temporal quorum-sensing induction regulates Vibrio cholerae biofilm architecture. Infect Immun 75(1):122–126. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.01190-06
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lynch MJ, Swift S, Kirke DF, Keevil CW, Dodd CE, Williams P (2002) The regulation of biofilm development by quorum sensing in Aeromonas hydrophila. Environ Microbiol 4(1):18–28
Makino K, Oshima K, Kurokawa K, Yokoyama K, Uda T, Tagomori K, Iijima Y, Najima M, Nakano M, Yamashita A, Kubota Y, Kimura S, Yasunaga T, Honda T, Shinagawa H, Hattori M, Iida T (2003) Genome sequence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus: a pathogenic mechanism distinct from that of V. cholerae. Lancet 361(9359):743–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12659-1
Miller MB, Bassler BL (2001) Quorum sensing in bacteria. Ann Rev Microbiol 55:165–199. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.55.1.165
Nackerdien ZE, Keynan A, Bassler BL, Lederberg J, Thaler DS (2008) Quorum sensing influences Vibrio harveyi growth rates in a manner not fully accounted for by the marker effect of bioluminescence. PLoS ONE 3(2):e1671. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001671
Nishibuchi M, Kaper JB (1995) Thermostable direct hemolysin gene of Vibrio parahaemolyticus: a virulence gene acquired by a marine bacterium. Infect Immun 63(6):2093–2099
Raghunath P (2014) Roles of thermostable direct hemolysin (TDH) and TDH-related hemolysin (TRH) in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Front Microbiol 5:805. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00805
Shakibazadeh S, Saad CR, Christianus A, Kamarudin MS, Sijam K, Shamsudin MN, Neela VK (2008) Evaluation of in vitro vibrio static activity of Shewanella algae isolated from healthy Penaeus monodon. Afr J Biotechnol 7(21):3952–3961
Sperandio V, Mellies JL, Nguyen W, Shin S, Kaper JB (1999) Quorum sensing controls expression of the type III secretion gene transcription and protein secretion in enterohemorrhagic and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(26):15196–15201
Vezzulli L, Pezzati E, Stauder M, Stagnaro L, Venier P, Pruzzo C (2015) Aquatic ecology of the oyster pathogens Vibrio splendidus and Vibrio aestuarianus. Environ Microbiol 17(4):1065–1080. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12484
Wai SN, Mizunoe Y, Takade A, Kawabata SI, Yoshida SI (1998) Vibrio cholerae O1 strain TSI-4 produces the exopolysaccharide materials that determine colony morphology, stress resistance, and biofilm formation. Appl Environ Microbiol 64(10):3648–3655
Wang L, Ling Y, Jiang H, Qiu Y, Qiu J, Chen H, Yang R, Zhou D (2013) AphA is required for biofilm formation, motility, and virulence in pandemic Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Int J Food Microbiol 160(3):245–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2012.11.004
Wen Y, Kim IH, Son JS, Lee BH, Kim KS (2012) Iron and quorum sensing coordinately regulate the expression of vulnibactin biosynthesis in Vibrio vulnificus. J Biol Chem 287(32):26727–26739. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.374165
Xavier KB, Bassler BL (2003) LuxS quorum sensing: more than just a numbers game. Curr Opin Microbiol 6(2):191–197
Yanagihara I, Nakahira K, Yamane T, Kaieda S, Mayanagi K, Hamada D, Fukui T, Ohnishi K, Kajiyama S, Shimizu T, Sato M, Ikegami T, Ikeguchi M, Honda T, Hashimoto H (2010) Structure and functional characterization of Vibrio parahaemolyticus thermostable direct hemolysin. J Biol Chem 285(21):16267–16274. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.074526
Zhang L, Orth K (2013) Virulence determinants for Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection. Curr Opin Microbiol 16(1):70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2013.02.002
Zhou D, Yan X, Qu F, Wang L, Zhang Y, Hou J, Hu Y, Li J, Xin S, Qiu J, Yang R, Mao P (2013) Quorum sensing modulates transcription of cpsQ-mfpABC and mfpABC in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Int J Food Microbiol 166(3):458–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.07.008
Zhu J, Miller MB, Vance RE, Dziejman M, Bassler BL, Mekalanos JJ (2002) Quorum-sensing regulators control virulence gene expression in Vibrio cholerae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(5):3129–3134. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.052694299
Zhu J, Zhao A, Feng L, Gao H (2016) Quorum sensing signals affect spoilage of refrigerated large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) by Shewanella baltica. Int J Food Microbiol 217:146–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2015.10.020
Acknowledgements
This work was sponsored by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31371746) and the higher educational cultivation program for major scientific research projects of Guangdong Ocean University (Nos. GDOU2013050205, 2014050203) and the scientific research program of administration of quality and technology supervision of Guangdong province (No. 2015ZZ02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, M., Fang, Z., Sun, L. et al. Regulation of Thermostable Direct Hemolysin and Biofilm Formation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus by Quorum-Sensing Genes luxM and luxS. Curr Microbiol 75, 1190–1197 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-018-1508-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-018-1508-y