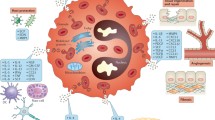
Abstract
Intestinal eosinophils are largely considered to be one of the central immune effector cells during helminth infection and disorders such as eosinophilic oesophagitis and food allergies. Given the abundance of these cells present in the gastrointestinal tract at homeostasis, emerging studies now reveal novel roles for eosinophils in the development and regulation of immunity, and during tissue repair. In addition, the identification of distinct eosinophil subsets indicates that we must consider the heterogeneity of these cells and how they differentially participate in mucosal immunity at steady state and during disease. Here, we summarise the literature on intestinal eosinophils, and how they contribute to mucosal homeostasis through immune regulation and interactions with the microbiome. We then explore the divergent roles of eosinophils in the context of eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders and during helminth infection, whereby we discuss key observations and differences that have emerged from animal models and human studies. Lastly, we consider the possible interactions of eosinophils with the enteric nervous system, and how this represents an exciting area for future research which may inform future therapeutic targets.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rothenberg ME (2004) Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGID). J Allergy Clin Immunol 113(1):11–28 quiz 29
Salzer HJF, Rolling T, Vinnemeier CD, Tannich E, Schmiedel S, Addo MM, Cramer JP (2017) Helminthic infections in returning travelers and migrants with eosinophilia: diagnostic value of medical history, eosinophil count and IgE. Travel Med Infect Dis 20:49–55
Amoani B, Adu B, Frempong MT, Sarkodie-Addo T, Nuvor SV, Wilson MD, Gyan B (2019) Levels of serum eosinophil cationic protein are associated with hookworm infection and intensity in endemic communities in Ghana. PLoS One 14(9):e0222382
Xenakis JJ, Howard ED, Smith KM, Olbrich CL, Huang Y, Anketell D, Maldonado S, Cornwell EW, Spencer LA (2018) Resident intestinal eosinophils constitutively express antigen presentation markers and include two phenotypically distinct subsets of eosinophils. Immunology 154(2):298–308
Chojnacki A, Wojcik K, Petri B, Aulakh G, Jacobsen EA, LeSuer WE, Colarusso P, Patel KD (2019) Intravital imaging allows real-time characterization of tissue resident eosinophils. Commun Biol 2:181
Shah K, Ignacio A, McCoy KD, Harris NL (2020) The emerging roles of eosinophils in mucosal homeostasis. Mucosal Immunol 13(4):574–583
Ohnmacht C, Pullner A, van Rooijen N, Voehringer D (2007) Analysis of eosinophil turnover in vivo reveals their active recruitment to and prolonged survival in the peritoneal cavity. J Immunol 179(7):4766–4774
Carlens J, Wahl B, Ballmaier M, Bulfone-Paus S, Förster R, Pabst O (2009) Common γ-chain-dependent signals confer selective survival of eosinophils in the murine small intestine. J Immunol 183(9):5600–5607
Mishra A, Hogan SP, Lee JJ, Foster PS, Rothenberg ME (1999) Fundamental signals that regulate eosinophil homing to the gastrointestinal tract. J Clin Invest 103(12):1719–1727
Hirasawa R, Shimizu R, Takahashi S, Osawa M, Takayanagi S, Kato Y, Onodera M, Minegishi N, Yamamoto M, Fukao K, Taniguchi H, Nakauchi H, Iwama A (2002) Essential and instructive roles of GATA factors in eosinophil development. J Exp Med 195(11):1379–1386
Yu C, Cantor AB, Yang H, Browne C, Wells RA, Fujiwara Y, Orkin SH (2002) Targeted deletion of a high-affinity GATA-binding site in the GATA-1 promoter leads to selective loss of the eosinophil lineage in vivo. J Exp Med 195(11):1387–1395
Nei Y, Obata-Ninomiya K, Tsutsui H, Ishiwata K, Miyasaka M, Matsumoto K, Nakae S, Kanuka H, Inase N, Karasuyama H (2013) GATA-1 regulates the generation and function of basophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110(46):18620–18625
Lee JJ, Dimina D, Macias MP, Ochkur SI, McGarry M, O'Neill KR, Protheroe C, Pero R, Nguyen T, Cormier SA, Lenkiewicz E, Colbert D, Rinaldi L, Ackerman SJ, Irvin CG, Lee NA (2004) Defining a link with asthma in mice congenitally deficient in eosinophils. Science 305(5691):1773–1776
Jacobsen EA, LeSuer WE, Willetts L, Zellner KR, Mazzolini K, Antonios N, Beck B, Protheroe C, Ochkur SI, Colbert D, Lacy P, Moqbel R, Appleton J, Lee NA, Lee JJ (2014) Eosinophil activities modulate the immune/inflammatory character of allergic respiratory responses in mice. Allergy 69(3):315–327
Doyle AD, Jacobsen EA, Ochkur SI, Willetts L, Shim K, Neely J, Kloeber J, LeSuer WE, Pero RS, Lacy P, Moqbel R, Lee NA, Lee JJ (2013) Homologous recombination into the eosinophil peroxidase locus generates a strain of mice expressing Cre recombinase exclusively in eosinophils. J Leukoc Biol 94(1):17–24
Koutri E, Patereli A, Noni M, Gutiérrez-Junquera C, González-Lois C, Oliva S, Giordano C, Stefanaki K, Papadopoulou A (2020) Distribution of eosinophils in the gastrointestinal tract of children with no organic disease. Ann Gastroenterol 33(5):508–515
Matsushita T et al (2015) The number and distribution of eosinophils in the adult human gastrointestinal tract: a study and comparison of racial and environmental factors. Am J Surg Pathol 39:4
Ferrer-Font L, Mehta P, Harmos P, Schmidt AJ, Chappell S, Price KM, Hermans IF, Ronchese F, le Gros G, Mayer JU (2020) High-dimensional analysis of intestinal immune cells during helminth infection. eLife 9:e51678
Chu VT et al (2014) Eosinophils promote generation and maintenance of immunoglobulin-A-expressing plasma cells and contribute to gut immune homeostasis. Immunity 40(4):582–593
Straumann A, Kristl J, Conus S, Vassina E, Spichtin HP, Beglinger C, Simon HU (2005) Cytokine expression in healthy and inflamed mucosa: probing the role of eosinophils in the digestive tract. Inflamm Bowel Dis 11(8):720–726
Jung Y, Wen T, Mingler MK, Caldwell JM, Wang YH, Chaplin DD, Lee EH, Jang MH, Woo SY, Seoh JY, Miyasaka M, Rothenberg ME (2015) IL-1β in eosinophil-mediated small intestinal homeostasis and IgA production. Mucosal Immunol 8(4):930–942
Singh G, Brass A, Knight CG, Cruickshank SM (2019) Gut eosinophils and their impact on the mucus-resident microbiota. Immunology 158(3):194–205
Forman R, Bramhall M, Logunova L, Svensson-Frej M, Cruickshank SM, Else KJ (2016) Eosinophils may play regionally disparate roles in influencing IgA+ plasma cell numbers during large and small intestinal inflammation. BMC Immunol 17(1):12
FitzPatrick RD et al (2020) Littermate-controlled experiments reveal eosinophils are not essential for maintaining steady-state IgA and demonstrate the influence of rearing conditions on antibody phenotypes in eosinophil-deficient mice. Front Immunol 11:2528
Beller A, Kruglov A, Durek P, Goetze V, Werner K, Heinz GA, Ninnemann J, Lehmann K, Maier R, Hoffmann U, Riedel R, Heiking K, Zimmermann J, Siegmund B, Mashreghi MF, Radbruch A, Chang HD (2020) Specific microbiota enhances intestinal IgA levels by inducing TGF-β in T follicular helper cells of Peyer’s patches in mice. Eur J Immunol 50(6):783–794
Sugawara R, Lee EJ, Jang MS, Jeun EJ, Hong CP, Kim JH, Park A, Yun CH, Hong SW, Kim YM, Seoh JY, Jung YJ, Surh CD, Miyasaka M, Yang BG, Jang MH (2016) Small intestinal eosinophils regulate Th17 cells by producing IL-1 receptor antagonist. J Exp Med 213(4):555–567
Jiménez-Saiz R et al (2020) Microbial regulation of enteric eosinophils and its impact on tissue remodeling and Th2 immunity. Front Immunol 11:155
Yousefi S, Gold JA, Andina N, Lee JJ, Kelly AM, Kozlowski E, Schmid I, Straumann A, Reichenbach J, Gleich GJ, Simon HU (2008) Catapult-like release of mitochondrial DNA by eosinophils contributes to antibacterial defense. Nat Med 14(9):949–953
Arnold IC, Artola-Borán M, Tallón de Lara P, Kyburz A, Taube C, Ottemann K, van den Broek M, Yousefi S, Simon HU, Müller A (2018) Eosinophils suppress Th1 responses and restrict bacterially induced gastrointestinal inflammation. J Exp Med 215(8):2055–2072
Buonomo EL, Cowardin CA, Wilson MG, Saleh MM, Pramoonjago P, Petri WA Jr (2016) Microbiota-regulated IL-25 Increases eosinophil number to provide protection during Clostridium difficile infection. Cell Rep 16(2):432–443
Yoon J et al (2019) Eosinophil activation by toll-like receptor 4 ligands regulates macrophage polarization. Front Cell Dev Biol 7:329
Theiler A, Bärnthaler T, Platzer W, Richtig G, Peinhaupt M, Rittchen S, Kargl J, Ulven T, Marsh LM, Marsche G, Schuligoi R, Sturm EM, Heinemann A (2019) Butyrate ameliorates allergic airway inflammation by limiting eosinophil trafficking and survival. J Allergy Clin Immunol 144(3):764–776
Vieira ELM, Leonel AJ, Sad AP, Beltrão NRM, Costa TF, Ferreira TMR, Gomes-Santos AC, Faria AMC, Peluzio MCG, Cara DC, Alvarez-Leite JI (2012) Oral administration of sodium butyrate attenuates inflammation and mucosal lesion in experimental acute ulcerative colitis. J Nutr Biochem 23(5):430–436
Muzes G et al (2012) Changes of the cytokine profile in inflammatory bowel diseases. World J Gastroenterol 18(41):5848–5861
Valatas V, Vakas M, Kolios G (2013) The value of experimental models of colitis in predicting efficacy of biological therapies for inflammatory bowel diseases. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 305(11):G763–G785
Lampinen M, Backman M, Winqvist O, Rorsman F, Rönnblom A, Sangfelt P, Carlson M (2008) Different regulation of eosinophil activity in Crohn’s disease compared with ulcerative colitis. J Leukoc Biol 84(6):1392–1399
Click B, Anderson AM, Koutroubakis IE, Rivers CR, Babichenko D, Machicado JD, Hartman DJ, Hashash JG, Dunn MA, Schwartz M, Swoger J, Barrie A, Wenzel SE, Regueiro M, Binion DG (2017) Peripheral eosinophilia in patients with inflammatory bowel disease defines an aggressive disease phenotype. Am J Gastroenterol 112(12):1849–1858
Mir A, Minguez M, Tatay J, Pascual I, Pena A, Sanchiz V, Almela P, Mora F, Benages A (2002) Elevated serum eotaxin levels in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol 97(6):1452–1457
Ahrens R, Waddell A, Seidu L, Blanchard C, Carey R, Forbes E, Lampinen M, Wilson T, Cohen E, Stringer K, Ballard E, Munitz A, Xu H, Lee N, Lee JJ, Rothenberg ME, Denson L, Hogan SP (2008) Intestinal macrophage/epithelial cell-derived CCL11/eotaxin-1 mediates eosinophil recruitment and function in pediatric ulcerative colitis. J Immunol 181(10):7390–7399
Xu X, Rivkind A, Pikarsky A, Pappo O, Bischoff SC, Levi-Schaffer F (2004) Mast cells and eosinophils have a potential profibrogenic role in Crohn disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 39(5):440–447
Masterson JC, Capocelli KE, Hosford L, Biette K, McNamee E, de Zoeten EF, Harris R, Fernando SD, Jedlicka P, Protheroe C, Lee JJ, Furuta GT (2015) Eosinophils and IL-33 perpetuate chronic inflammation and fibrosis in a pediatric population with stricturing Crohn’s ileitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 21(10):2429–2440
De Salvo C et al (2016) IL-33 Drives eosinophil infiltration and pathogenic type 2 helper T-cell immune responses leading to chronic experimental ileitis. Am J Pathol 186(4):885–898
Alhmoud T, Gremida A, Colom Steele D, Fallahi I, Tuqan W, Nandy N, Ismail M, Aburajab Altamimi B, Xiong MJ, Kerwin A, Martin D (2020) Outcomes of inflammatory bowel disease in patients with eosinophil-predominant colonic inflammation. BMJ Open Gastro 7(1):e000373
Masterson JC, McNamee EN, Fillon SA, Hosford L, Harris R, Fernando SD, Jedlicka P, Iwamoto R, Jacobsen E, Protheroe C, Eltzschig HK, Colgan SP, Arita M, Lee JJ, Furuta GT (2015) Eosinophil-mediated signalling attenuates inflammatory responses in experimental colitis. Gut 64(8):1236–1247
Karmele EP et al (2019) Anti-IL-13Ralpha2 therapy promotes recovery in a murine model of inflammatory bowel disease. Mucosal Immunol 12(5):1174–1186
O’Shea KM, Aceves SS, Dellon ES, Gupta SK, Spergel JM, Furuta GT, Rothenberg ME (2018) Pathophysiology of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 154(2):333–345
Blanchard C et al (2011) A striking local esophageal cytokine expression profile in eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 127(1):208-17–217 e1-7
Pope SM, Fulkerson PC, Blanchard C, Akei HS, Nikolaidis NM, Zimmermann N, Molkentin JD, Rothenberg ME (2005) Identification of a cooperative mechanism involving interleukin-13 and eotaxin-2 in experimental allergic lung inflammation. J Biol Chem 280(14):13952–13961
Rayapudi M, Mavi P, Zhu X, Pandey AK, Abonia JP, Rothenberg ME, Mishra A (2010) Indoor insect allergens are potent inducers of experimental eosinophilic esophagitis in mice. J Leukoc Biol 88(2):337–346
Mishra A, Rothenberg ME (2003) Intratracheal IL-13 induces eosinophilic esophagitis by an IL-5, eotaxin-1, and STAT6-dependent mechanism. Gastroenterology 125(5):1419–1427
Rieder F et al (2014) T-helper 2 cytokines, transforming growth factor beta1, and eosinophil products induce fibrogenesis and alter muscle motility in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 146(5):1266–1277 e1-9
Han H, Roan F, Ziegler SF (2017) The atopic march: current insights into skin barrier dysfunction and epithelial cell-derived cytokines. Immunol Rev 278(1):116–130
Noti M, Wojno EDT, Kim BS, Siracusa MC, Giacomin PR, Nair MG, Benitez AJ, Ruymann KR, Muir AB, Hill DA, Chikwava KR, Moghaddam AE, Sattentau QJ, Alex A, Zhou C, Yearley JH, Menard-Katcher P, Kubo M, Obata-Ninomiya K, Karasuyama H, Comeau MR, Brown-Whitehorn T, de Waal Malefyt R, Sleiman PM, Hakonarson H, Cianferoni A, Falk GW, Wang ML, Spergel JM, Artis D (2013) Thymic stromal lymphopoietin-elicited basophil responses promote eosinophilic esophagitis. Nat Med 19(8):1005–1013
Dunn JLM, Shoda T, Caldwell JM, Wen T, Aceves SS, Collins MH, Dellon ES, Falk GW, Leung J, Martin LJ, Menard-Katcher P, Rudman-Spergel AK, Spergel JM, Wechsler JB, Yang GY, Furuta GT, Rothenberg ME, Consortium of Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disease Researchers (CEGIR) (2020) Esophageal type 2 cytokine expression heterogeneity in eosinophilic esophagitis in a multisite cohort. J Allergy Clin Immunol 145(6):1629–1640 e4
Judd LM, Heine RG, Menheniott TR, Buzzelli J, O'Brien-Simpson N, Pavlic D, O'Connor L, al Gazali K, Hamilton O, Scurr M, Collison AM, Mattes J, Allen KJ, Giraud AS (2016) Elevated IL-33 expression is associated with pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis, and exogenous IL-33 promotes eosinophilic esophagitis development in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 310(1):G13–G25
Rokkas T, Niv Y, Malfertheiner P (2020) A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials on the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis in adults and children. J Clin Gastroenterol Publish Ahead of Print
Pesek RD, Gupta SK (2020) Future therapies for eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 124(3):219–226
Hirano I, Dellon ES, Hamilton JD, Collins MH, Peterson K, Chehade M, Schoepfer AM, Safroneeva E, Rothenberg ME, Falk GW, Assouline-Dayan Y, Zhao Q, Chen Z, Swanson BN, Pirozzi G, Mannent L, Graham NMH, Akinlade B, Stahl N, Yancopoulos GD, Radin A (2020) Efficacy of dupilumab in a phase 2 randomized trial of adults with active eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 158(1):111–122 e10
Kuang FL et al (2018) Benralizumab (anti-IL5Rα) depletes gut tissue eosinophilia and improves symptoms in hypereosinophilic syndrome with gastrointestinal involvement. J Allergy Clin Immunol 141(2, Supplement):AB196
Kia L, Hirano I (2015) Distinguishing GERD from eosinophilic oesophagitis: concepts and controversies. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 12(7):379–386
Li-Kim-Moy JP, Tobias V, Day AS, Leach S, Lemberg DA (2011) Esophageal subepithelial fibrosis and hyalinization are features of eosinophilic esophagitis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 52(2):147–153
Cheng E, Zhang X, Huo X, Yu C, Zhang Q, Wang DH, Spechler SJ, Souza RF (2013) Omeprazole blocks eotaxin-3 expression by oesophageal squamous cells from patients with eosinophilic oesophagitis and GORD. Gut 62(6):824–832
Zhong C, Duan L, Wang K, Xu Z, Ge Y, Yang C, Han Y (2013) Esophageal intraluminal baseline impedance is associated with severity of acid reflux and epithelial structural abnormalities in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Gastroenterol 48(5):601–610
Marietta EV, Geno DM, Smyrk TC, Becker A, Alexander JA, Camilleri M, Murray JA, Katzka DA (2017) Presence of intraepithelial food antigen in patients with active eosinophilic oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 45(3):427–433
van Rhijn BD, Weijenborg PW, Verheij J, van den Bergh Weerman MA, Verseijden C, van den Wijngaard RMJGJ, de Jonge WJ, Smout AJPM, Bredenoord AJ (2014) Proton pump inhibitors partially restore mucosal integrity in patients with proton pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia but not eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 12(11):1815–1823 e2
Sunkara T, Rawla P, Yarlagadda KS, Gaduputi V (2019) Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: diagnosis and clinical perspectives. Clin Exp Gastroenterol 12:239–253
Hogan SP, Mishra A, Brandt EB, Foster PS, Rothenberg ME (2000) A critical role for eotaxin in experimental oral antigen-induced eosinophilic gastrointestinal allergy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(12):6681–6686
Song DJ, Shim MH, Lee N, Yoo Y, Choung JT (2017) CCR3 monoclonal antibody inhibits eosinophilic inflammation and mucosal injury in a mouse model of eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Allergy, Asthma Immunol Res 9(4):360–367
Oyoshi MK, Oettgen HC, Chatila TA, Geha RS, Bryce PJ (2014) Food allergy: insights into etiology, prevention, and treatment provided by murine models. J Allergy Clin Immunol 133(2):309–317
Schwab D, Müller S, Aigner T, Neureiter D, Kirchner T, Hahn EG, Raithel M (2003) Functional and morphologic characterization of eosinophils in the lower intestinal mucosa of patients with food allergy. Am J Gastroenterol 98(7):1525–1534
Chu DK, Jimenez-Saiz R, Verschoor CP, Walker TD, Goncharova S, Llop-Guevara A, Shen P, Gordon ME, Barra NG, Bassett JD, Kong J, Fattouh R, McCoy KD, Bowdish DM, Erjefält JS, Pabst O, Humbles AA, Kolbeck R, Waserman S, Jordana M (2014) Indigenous enteric eosinophils control DCs to initiate a primary Th2 immune response in vivo. J Exp Med 211(8):1657–1672
Sturrock RF, Kimani R, Cottrell BJ, Butterworth AE, Seitz HM, Siongok TK, Houba V (1983) Observations on possible immunity to reinfection among Kenyan schoolchildren after treatment for Schistosoma mansoni. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 77(3):363–371
Croese J, Wood MJ, Melrose W, Speare R (2006) Allergy controls the population density of Necator americanus in the small intestine. Gastroenterology 131(2):402–409
Masure D, Vlaminck J, Wang T, Chiers K, van den Broeck W, Vercruysse J, Geldhof P (2013) A role for eosinophils in the intestinal immunity against infective Ascaris suum larvae. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 7(3):e2138
Buys J, Wever R, van Stigt R, Ruitenberg EJ (1981) The killing of newborn larvae of Trichinella spiralis by eosinophil peroxidase in vitro. Eur J Immunol 11(10):843–845
O’Connell AE et al (2011) Major basic protein from eosinophils and myeloperoxidase from neutrophils are required for protective immunity to Strongyloides stercoralis in mice. Infect Immun 79(7):2770–2778
Munoz-Caro T et al (2015) Leucocyte-derived extracellular trap formation significantly contributes to Haemonchus contortus larval entrapment. Parasit Vectors 8:607
Ehrens A, Lenz B, Neumann AL, Giarrizzo S, Reichwald JJ, Frohberger SJ, Stamminger W, Buerfent BC, Fercoq F, Martin C, Kulke D, Hoerauf A, Hübner MP (2021) Microfilariae trigger eosinophil extracellular DNA traps in a dectin-1-dependent manner. Cell Rep 34(2):108621
Padigel UM, Lee JJ, Nolan TJ, Schad GA, Abraham D (2006) Eosinophils can function as antigen-presenting cells to induce primary and secondary immune responses to Strongyloides stercoralis. Infect Immun 74(6):3232–3238
Huang L, Appleton JA (2016) Eosinophils in helminth infection: defenders and dupes. Trends Parasitol 32(10):798–807
Behm CA, Ovington KS (2000) The role of eosinophils in parasitic helminth infections: insights from genetically modified mice. Parasitol Today 16(5):202–209
de Andres B, Rakasz E, Hagen M, McCormik ML, Mueller AL, Elliot D, Metwali A, Sandor M, Britigan BE, Weinstock JV, Lynch RG (1997) Lack of Fc-epsilon receptors on murine eosinophils: implications for the functional significance of elevated IgE and eosinophils in parasitic infections. Blood 89(10):3826–3836
Hamann KJ et al (1990) in vitro killing of microfilariae of Brugia pahangi and Brugia malayi by eosinophil granule proteins. J Immunol 144(8):3166–3173
Gebreselassie NG, Moorhead AR, Fabre V, Gagliardo LF, Lee NA, Lee JJ, Appleton JA (2012) Eosinophils preserve parasitic nematode larvae by regulating local immunity. J Immunol 188(1):417–425
Cadman ET, Thysse KA, Bearder S, Cheung AYN, Johnston AC, Lee JJ, Lawrence RA (2014) Eosinophils are important for protection, immunoregulation and pathology during infection with nematode microfilariae. PLoS Pathog 10(3):e1003988
Huang L, Gebreselassie NG, Gagliardo LF, Ruyechan MC, Lee NA, Lee JJ, Appleton JA (2014) Eosinophil-derived IL-10 supports chronic nematode infection. J Immunol 193(8):4178–4187
Huang L, Gebreselassie NG, Gagliardo LF, Ruyechan MC, Luber KL, Lee NA, Lee JJ, Appleton JA (2015) Eosinophils mediate protective immunity against secondary nematode infection. J Immunol 194(1):283–290
Knott ML, Matthaei KI, Giacomin PR, Wang H, Foster PS, Dent LA (2007) Impaired resistance in early secondary Nippostrongylus brasiliensis infections in mice with defective eosinophilopoeisis. Int J Parasitol 37(12):1367–1378
Daly CM, Mayrhofer G, Dent LA (1999) Trapping and immobilization of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis larvae at the site of inoculation in primary infections of interleukin-5 transgenic mice. Infect Immun 67(10):5315–5323
Foster EL, Simpson EL, Fredrikson LJ, Lee JJ, Lee NA, Fryer AD, Jacoby DB (2011) Eosinophils increase neuron branching in human and murine skin and in vitro. PLoS One 6(7):e22029
Jacoby DB, Gleich GJ, Fryer AD (1993) Human eosinophil major basic protein is an endogenous allosteric antagonist at the inhibitory muscarinic M2 receptor. J Clin Invest 91(4):1314–1318
Costello RW et al (1997) Localization of eosinophils to airway nerves and effect on neuronal M2 muscarinic receptor function. Am J Phys Lung Cell Mol Phys 273(1):L93–L103
Wallon C, Persborn M, Jönsson M, Wang A, Phan V, Lampinen M, Vicario M, Santos J, Sherman PM, Carlson M, Ericson A–C, Mckay DM, Söderholm JD (2011) Eosinophils express muscarinic receptors and corticotropin-releasing factor to disrupt the mucosal barrier in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 140(5):1597–1607
Metwali A et al (1994) Eosinophils within the healthy or inflamed human intestine produce substance P and vasoactive intestinal peptide. J Neuroimmunol 52(1):69–78
Saluja R, Saini R, Mitra K, Bajpai VK, Dikshit M (2010) Ultrastructural immunogold localization of nitric oxide synthase isoforms in rat and human eosinophils. Cell Tissue Res 340(2):381–388
Olbrich CL, Bivas-Benita M, Xenakis JJ, Maldonado S, Cornwell E, Fink J, Yuan Q, Gill N, Mansfield R, Dockstader K, Spencer LA (2020) Remote allergen exposure elicits eosinophil infiltration into allergen nonexposed mucosal organs and primes for allergic inflammation. Mucosal Immunol 13(5):777–787
Arisawa T, Arisawa S, Yokoi T, Kuroda M, Hirata I, Nakano H (2007) Endoscopic and histological features of the large intestine in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Clin Biochem Nutr 40(1):24–30
Filbey KJ, Camberis M, Chandler J, Turner R, Kettle AJ, Eichenberger RM, Giacomin P, le Gros G (2019) Intestinal helminth infection promotes IL-5- and CD4(+) T cell-dependent immunity in the lung against migrating parasites. Mucosal Immunol 12(2):352–362
Gazzinelli-Guimaraes PH, de Queiroz Prado R, Ricciardi A, Bonne-Année S, Sciurba J, Karmele EP, Fujiwara RT, Nutman TB (2019) Allergen presensitization drives an eosinophil-dependent arrest in lung-specific helminth development. J Clin Invest 129(9):3686–3701
Mesnil C, Raulier S, Paulissen G, Xiao X, Birrell MA, Pirottin D, Janss T, Starkl P, Ramery E, Henket M, Schleich FN, Radermecker M, Thielemans K, Gillet L, Thiry M, Belvisi MG, Louis R, Desmet C, Marichal T, Bureau F (2016) Lung-resident eosinophils represent a distinct regulatory eosinophil subset. J Clin Invest 126(9):3279–3295
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
This article is a contribution to the Special issue on: Eosinophils - Guest Editor: Hans-Uwe Simon
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
. Coakley, G., . Wang, H. & . Harris, N.L. Intestinal eosinophils: multifaceted roles in tissue homeostasis and disease. Semin Immunopathol 43, 307–317 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-021-00851-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-021-00851-2