Abstract
Purpose
The oncogenic transcription factor signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) promotes gene transcription involved in cancer, and its activation by IL-6 is found in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Four triazolothiadizine STAT3 pathway inhibitors were evaluated to prioritize a single compound for in vivo examination.
Methods
Metabolic stability in mouse liver microsome incubation was used to evaluate four triazolothiadizine analogues, and UPCDC-10205 was administered to mice IV as single or multiple doses to evaluate toxicity. Single-dose pharmacokinetics (PK), bioavailability and metabolism were studied after IV 4 mg/kg, PO 4 mg/kg, or PO 30 mg/kg suspension in 1% carboxymethyl cellulose. Mice were euthanized between 5 min to 24 h after dosing, and plasma and tissues were analyzed by LC–MS. Non-compartmental PK parameters were determined.
Results
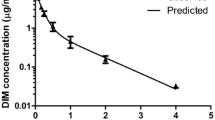
Of the four triazolothiadizine analogues evaluated, UPCDC-10205 was metabolically most stable. The maximum soluble dose of 4 mg/kg in 10% Solutol™ was not toxic to mice after single and multiple doses. PK analysis showed extensive tissue distribution and rapid plasma clearance. Bioavailability was ~5%. A direct glucuronide conjugate was identified as the major metabolite which was recapitulated in vitro.
Conclusions
Rapid clearance of UPCDC-10205 was thought to be the result of phase II metabolism despite its favorable stability in a phase I in vitro metabolic stability assay. The direct glucuronidation explains why microsomal stability (reflective of phase I metabolism) did not translate to in vivo metabolic stability. UPCDC-10205 did not demonstrate appropriate exposure to support efficacy studies in the current formulation.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CMC:
-
Carboxymethyl cellulose
- LC–MS/MS:
-
Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
- PK:
-
Pharmacokinetics
- UGT:
-
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase
- HCS:
-
High-content screening
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- C max :
-
Maximum peak concentration
- T max :
-
Time of maximum concentration
References
Geiger JL, Grandis JR, Bauman JE (2016) The STAT3 pathway as a therapeutic target in head and neck cancer: barriers and innovations. Oral Oncol 56:84–92. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2015.11.022
Argiris A (2015) EGFR inhibition for recurrent or metastatic HNSCC. Lancet Oncol 16(5):488–489. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(15)70178-6
Argiris A, Karamouzis MV, Raben D, Ferris RL (2008) Head and neck cancer. Lancet (London, England) 371(9625):1695–1709. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(08)60728-x
Frank DA (2007) STAT3 as a central mediator of neoplastic cellular transformation. Cancer Lett 251(2):199–210. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2006.10.017
Wang X, Crowe PJ, Goldstein D, Yang JL (2012) STAT3 inhibition, a novel approach to enhancing targeted therapy in human cancers (review). Int J Oncol 41(4):1181–1191. doi:10.3892/ijo.2012.1568
Sriuranpong V, Park JI, Amornphimoltham P, Patel V, Nelkin BD, Gutkind JS (2003) Epidermal growth factor receptor-independent constitutive activation of STAT3 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is mediated by the autocrine/paracrine stimulation of the interleukin 6/gp130 cytokine system. Cancer Res 63(11):2948–2956
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A, Yu H, Lee H, Herrmann A, Buettner R, Jove R, Spitzner M, Ebner R, Wolff HA, Ghadimi BM, Wienands J (2015) Grade M (2015) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 65(1):5–29
Sacco AG, Cohen EE, Waring MJ, Arrowsmith J, Leach AR, Leeson PD, Mandrell S, Owen RM, Pairaudeau G, Pennie WD, Pickett SD, Wang J, Wallace O, Weir A, Argiris A, Oh DY, Lee SH, Han SW, Kim MJ, Kim TM, Kim TY, Heo DS, Yuasa M, Yanagihara Y, Bang YJ (2015) Current treatment options for recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 33(29):3305–3313
Sen M, Joyce S, Panahandeh M, Li C, Thomas SM, Maxwell J, Wang L, Gooding WE, Johnson DE, Grandis JR (2012) Targeting STAT3 abrogates EGFR inhibitor resistance in cancer. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 18(18):4986–4996. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-12-0792
Aggarwal BB, Kunnumakkara AB, Harikumar KB, Gupta SR, Tharakan ST, Koca C, Dey S, Sung B (2009) Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3, inflammation, and cancer: how intimate is the relationship? Ann N Y Acad Sci 1171:59–76. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04911.x
Johnston PA, Grandis JR (2011) STAT3 signaling: anticancer strategies and challenges. Mol Interv 11(1):18–26
Niu G, Wright KL, Huang M, Song L, Haura E, Turkson J, Zhang S, Wang T, Sinibaldi D, Coppola D, Heller R, Ellis LM, Karras J, Bromberg J, Pardoll D, Jove R, Yu H (2002) Constitutive Stat3 activity up-regulates VEGF expression and tumor angiogenesis. Oncogene 21(13):2000–2008. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205260
Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G, Zhao Y, Pestell RG, Albanese C, Darnell JE Jr (1999) STAT3 as an oncogene. Cell 98(3):295–303
Avalle L, Pensa S, Regis G, Novelli F, Poli V (2012) STAT1 and STAT3 in tumorigenesis: a matter of balance. Jakstat 1(2):65–72. doi:10.4161/jkst.20045
Johnston PA, Sen M, Hua Y, Camarco D, Shun TY, Lazo JS, Grandis JR (2014) High-content pSTAT3/1 imaging assays to screen for selective inhibitors of STAT3 pathway activation in head and neck cancer cell lines. Assay Drug Dev Technol 12(1):55–79. doi:10.1089/adt.2013.524
Johnston PA, Sen M, Hua Y, Camarco DP, Shun TY, Lazo JS, Wilson GM, Resnick LO, LaPorte MG, Wipf P, Huryn DM, Grandis JR (2015) HCS campaign to identify selective inhibitors of IL-6-induced STAT3 pathway activation in head and neck cancer cell lines. Assay Drug Dev Technol 13(7):356–376. doi:10.1089/adt.2015.663
LaPorte MG, Wang Z, Colombo R, Garzan A, Peshkov VA, Liang M, Johnston PA, Schurdak ME, Sen M, Camarco DP, Hua Y, Pollock NI, Lazo JS, Grandis JR, Wipf P, Huryn DM (2016) Optimization of pyrazole-containing 1,2,4-triazolo-[3,4-b]thiadiazines, a new class of STAT3 pathway inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26(15):3581–3585. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.06.017
Hill JR (2004) In vitro drug metabolism using liver microsomes. Current protocols in pharmacology/editorial board, SJ Enna Chapter 7:Unit7 8. doi:10.1002/0471141755.ph0708s23
Seo KA, Kim HJ, Jeong ES, Abdalla N, Choi CS, Kim DH, Shin JG, Safdari Y, Khalili M, Farajnia S, Asgharzadeh M, Yazdani Y, Sadeghi M, Wang SW, Sun YM, Johnston PA, Sen M, Hua Y, Camarco D, Shun TY, Lazo JS, Grandis JR (2014) In vitro assay of six UDP-glucuronosyltransferase isoforms in human liver microsomes, using cocktails of probe substrates and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Drug Metab Dispos 42(11):1803–1810
Davies B, Morris T (1993) Physiological parameters in laboratory animals and humans. Pharm Res 10(7):1093–1095
Ghibellini G, Leslie EM, Brouwer KL (2006) Methods to evaluate biliary excretion of drugs in humans: an updated review. Mol Pharm 3(3):198–211. doi:10.1021/mp060011k
Pond SM, Tozer TN (1984) First-pass elimination. Basic concepts and clinical consequences. Clin Pharmacokinet 9(1):1–25. doi:10.2165/00003088-198409010-00001
Gleeson MP, Hersey A, Montanari D, Overington J (2011) Probing the links between in vitro potency, ADMET and physicochemical parameters. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 10(3):197–208. doi:10.1038/nrd3367
Doelle HW, Rokem S, Berovic M (2009) Biotechnology: fundamentals in biotechnology, vol XII. Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems. Eolss Publishers Co. Ltd., Oxford, United Kingdom
Pelkonen O, Turpeinen M, Uusitalo J, Rautio A, Raunio H (2005) Prediction of drug metabolism and interactions on the basis of in vitro investigations. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 96(3):167–175. doi:10.1111/j.1742-7843.2005.pto960305.x
Cayen MN (2010) Early drug development: strategies and routes to first-in-human trials. Wiley, Hoboken
Kaivosaari S, Finel M, Koskinen M (2011) N-glucuronidation of drugs and other xenobiotics by human and animal UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. Xenobiotica 41(8):652–669. doi:10.3109/00498254.2011.563327
Chiu SH, Huskey SW (1998) Species differences in N-glucuronidation. Drug Metab Dispos 26(9):838–847
Izukawa T, Nakajima M, Fujiwara R, Yamanaka H, Fukami T, Takamiya M, Aoki Y, Ikushiro S, Sakaki T, Yokoi T (2009) Quantitative analysis of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 1A and UGT2B expression levels in human livers. Drug Metab Dispos 37(8):1759–1768. doi:10.1124/dmd.109.027227
Harbourt DE, Fallon JK, Ito S, Baba T, Ritter JK, Glish GL, Smith PC (2012) Quantification of human uridine-diphosphate glucuronosyl transferase 1A isoforms in liver, intestine, and kidney using nanobore liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 84(1):98–105
Fisher MB, Paine MF, Strelevitz TJ, Wrighton SA (2001) The role of hepatic and extrahepatic UDP-glucuronosyltransferases in human drug metabolism. Drug Metab Rev 33(3–4):273–297. doi:10.1081/dmr-120000653
Yan Z, Caldwell GW, Gauthier D, Leo GC, Mei J, Ho CY, Jones WJ, Masucci JA, Tuman RW, Galemmo RA Jr, Johnson DL (2006) N-glucuronidation of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor 6,7-(dimethoxy-2,4-dihydroindeno[1,2-C]pyrazol-3-yl)-(3-fluoro-phenyl)-amine by human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. Drug Metab Dispos 34(5):748–755. doi:10.1124/dmd.106.009274
Vourvahis M, Gleave M, Nedderman AN, Hyland R, Gardner I, Howard M, Kempshall S, Collins C, LaBadie R (2010) Excretion and metabolism of lersivirine (5-{[3,5-diethyl-1-(2-hydroxyethyl)(3,5-14C2)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]oxy}benzene-1,3-dic arbonitrile), a next-generation non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, after administration of [14C]Lersivirine to healthy volunteers. Drug Metab Dispos 38(5):789–800. doi:10.1124/dmd.109.031252
Peterson EA, Boezio AA, Andrews PS, Boezio CM, Bush TL, Cheng AC, Choquette D, Coats JR, Colletti AE, Copeland KW, DuPont M, Graceffa R, Grubinska B, Kim JL, Lewis RT, Liu J, Mullady EL, Potashman MH, Romero K, Shaffer PL, Stanton MK, Stellwagen JC, Teffera Y, Yi S, Cai T, La DS (2012) Discovery and optimization of potent and selective imidazopyridine and imidazopyridazine mTOR inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22(15):4967–4974. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.06.033
Dressen D, Garofalo AW, Hawkinson J, Hom D, Jagodzinski J, Marugg JL, Neitzel ML, Pleiss MA, Szoke B, Tung JS, Wone DW, Wu J, Zhang H (2007) Preparation and optimization of a series of 3-carboxamido-5-phenacylaminopyrazole bradykinin B1 receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 50(21):5161–5167. doi:10.1021/jm051292n
Ye XM, Konradi AW, Smith J, Aubele DL, Garofalo AW, Marugg J, Neitzel ML, Semko CM, Sham HL, Sun M, Truong AP, Wu J, Zhang H, Goldbach E, Sauer JM, Brigham EF, Bova M, Basi GS (2010) Discovery of a novel sulfonamide-pyrazolopiperidine series as potent and efficacious gamma-secretase inhibitors (Part II). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20(12):3502–3506. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.04.148
Acknowledgements
This Project has been funded, in part, with Federal Funds from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, under Contract No. HSN261200800001E. The content of this publication does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the Department of Health and Human Services, nor does mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations imply endorsement by the US Government. This work was supported by the NExT-CBC Project ID #1015, S08-221 Task Order 6 ‘‘STAT3 Pathway Inhibitor HCS’’ (Grandis, PI), NCI Chemical Biology Consortium, Pittsburgh Specialized Application Center (PSAC; Lazo and Johnston co-PIs), and University of Pittsburgh Chemical Diversity Center (Huryn, PI). The Project was also supported, in part, by funds from the American Cancer Society (Grandis) and a Head and Neck Spore P50 award (Grandis, CA097190). This Project was funded in the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, under Chemical Biology Consortium Contract No. HSN261200800001E. We are grateful for scientific contributions from Peter Wipf, Matthew LaPorte, Atefeh Garzan, Mary Liang, Vsevolod A. Peshkov, and Zhuzhu Wang. This Project used the UPCI Animal Facility (AF) and Clinical Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Facility (CPPF) and was supported in part by Award P30CA047904.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiesel, B.F., Parise, R.A., Guo, J. et al. Toxicity, pharmacokinetics and metabolism of a novel inhibitor of IL-6-induced STAT3 activation. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 78, 1225–1235 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-016-3181-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-016-3181-9