Abstract
Purpose
The successful use of SMO inhibitors in tumors with activating mutations in hedgehog signaling raised interests in their exploitation against other malignancies. The role of hedgehog signaling in pediatric malignancies remains unclear.
Methods
We investigated the hedgehog signaling and its inhibition in a panel of 18 tumor cell lines derived from six of the most common and highly aggressive pediatric tumor types. None of the cell lines was known to stem from tumors with activating hedgehog mutations. Tetrazolium-based assays (MTT and MTS) and BrdU assays were used to analyze cell viability and proliferation after exposure to SANT1 and GANT61. Expression analysis of hedgehog signaling members and cyclins was performed by quantitative real-time PCR and Western blot.
Results
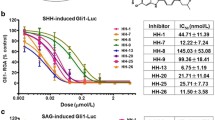
Key members of hedgehog signaling (SHH, PTCH1, SMO, GLI1, GLI2 and SUFU) were expressed in all cell lines. In 50 % of the cell lines viability was significantly increased by SHH exposure. Stimulation was not restricted to distinct tumor types, but related to cell lines with higher mRNA levels of PTCH1, SMO, GLI1 and GLI2. SMO inhibition by SANT1 moderately decreased cell viability with GI50s between 28 and 93 µmol/l. Sensitivity to SANT1 was not related to distinct tumor types. The GLI inhibitor GANT61 inhibited cell viability and proliferation more effectively than SANT1.
Conclusions
Our preclinical data provide evidence that hedgehog signaling is active and can be stimulated by PTCH1 ligands in various pediatric tumors. We suggest further evaluation of GLI inhibitors as inhibitors of hedgehog signaling for the treatment of the investigated tumor types.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hahn H, Wicking C, Zaphiropoulous PG, Gailani MR, Shanley S, Chidambaram A, Vorechovsky I, Holmberg E, Unden AB, Gillies S, Negus K, Smyth I, Pressman C, Leffell DJ, Gerrard B, Goldstein AM, Dean M, Toftgard R, Chenevix-Trench G, Wainwright B, Bale AE (1996) Mutations of the human homolog of Drosophila patched in the nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. Cell 85(6):841–851
Gorlin RJ (1995) Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. Dermatol Clin 13(1):113–125
Athar M, Tang X, Lee JL, Kopelovich L, Kim AL (2006) Hedgehog signalling in skin development and cancer. Exp Dermatol 15(9):667–677
Hui CC, Angers S (2011) Gli proteins in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 27:513–537
Hooper JE, Scott MP (2005) Communicating with Hedgehogs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6(4):306–317
Lum L, Beachy PA (2004) The Hedgehog response network: sensors, switches, and routers. Science 304(5678):1755–1759
Galvin KE, Ye H, Wetmore C (2007) Differential gene induction by genetic and ligand-mediated activation of the Sonic hedgehog pathway in neural stem cells. Dev Biol 308(2):331–342
Regl G, Neill GW, Eichberger T, Kasper M, Ikram MS, Koller J, Hintner H, Quinn AG, Frischauf AM, Aberger F (2002) Human GLI2 and GLI1 are part of a positive feedback mechanism in basal cell carcinoma. Oncogene 21(36):5529–5539
Northcott PA, Korshunov A, Witt H, Hielscher T, Eberhart CG, Mack S, Bouffet E, Clifford SC, Hawkins CE, French P, Rutka JT, Pfister S, Taylor MD (2011) Medulloblastoma comprises four distinct molecular variants. J Clin Oncol 29(11):1408–1414
Kimura H, Stephen D, Joyner A, Curran T (2005) Gli1 is important for medulloblastoma formation in Ptc1 ± mice. Oncogene 24(25):4026–4036
Tostar U, Malm CJ, Meis-Kindblom JM, Kindblom LG, Toftgard R, Unden AB (2006) Deregulation of the hedgehog signalling pathway: a possible role for the PTCH and SUFU genes in human rhabdomyoma and rhabdomyosarcoma development. J Pathol 208(1):17–25
Bridge JA, Liu J, Weibolt V, Baker KS, Perry D, Kruger R, Qualman S, Barr F, Sorensen P, Triche T, Suijkerbuijk R (2000) Novel genomic imbalances in embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma revealed by comparative genomic hybridization and fluorescence in situ hybridization: an intergroup rhabdomyosarcoma study. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 27(4):337–344
Hirotsu M, Setoguchi T, Sasaki H, Matsunoshita Y, Gao H, Nagao H, Kunigou O, Komiya S (2010) Smoothened as a new therapeutic target for human osteosarcoma. Mol Cancer 9:5
Yang L, Xie G, Fan Q, Xie J (2010) Activation of the hedgehog-signaling pathway in human cancer and the clinical implications. Oncogene 29(4):469–481
Sekulic A, Migden MR, Oro AE, Dirix L, Lewis KD, Hainsworth JD, Solomon JA, Yoo S, Arron ST, Friedlander PA, Marmur E, Rudin CM, Chang AL, Low JA, Mackey HM, Yauch RL, Graham RA, Reddy JC, Hauschild A (2012) Efficacy and safety of vismodegib in advanced basal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 366(23):2171–2179
Tang JY, Mackay-Wiggan JM, Aszterbaum M, Yauch RL, Lindgren J, Chang K, Coppola C, Chanana AM, Marji J, Bickers DR, Epstein EH Jr (2012) Inhibiting the hedgehog pathway in patients with the basal-cell nevus syndrome. N Engl J Med 366(23):2180–2188
Von Hoff DD, LoRusso PM, Rudin CM, Reddy JC, Yauch RL, Tibes R, Weiss GJ, Borad MJ, Hann CL, Brahmer JR, Mackey HM, Lum BL, Darbonne WC, Marsters JC Jr, de Sauvage FJ, Low JA (2009) Inhibition of the hedgehog pathway in advanced basal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 361(12):1164–1172
Taylor MD, Northcott PA, Korshunov A, Remke M, Cho YJ, Clifford SC, Eberhart CG, Parsons DW, Rutkowski S, Gajjar A, Ellison DW, Lichter P, Gilbertson RJ, Pomeroy SL, Kool M, Pfister SM (2012) Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: the current consensus. Acta Neuropathol 123(4):465–472
Gajjar A, Stewart CF, Ellison DW, Kaste S, Kun LE, Packer RJ, Goldman S, Chintagumpala M, Wallace D, Takebe N, Boyett JM, Gilbertson RJ, Curran T (2013) Phase I study of vismodegib in children with recurrent or refractory medulloblastoma: a pediatric brain tumor consortium study. Clin Cancer Res 19(22):6305–6312
Robinson GW, Orr BA, Wu G, Gururangan S, Lin T, Qaddoumi I, Packer RJ, Goldman S, Prados MD, Desjardins A, Chintagumpala M, Takebe N, Kaste SC, Rusch M, Allen SJ, Onar-Thomas A, Stewart CF, Fouladi M, Boyett JM, Gilbertson RJ, Curran T, Ellison DW, Gajjar A (2015) Vismodegib exerts targeted efficacy against recurrent sonic hedgehog-subgroup medulloblastoma: results from phase II pediatric brain tumor consortium studies PBTC-025B and PBTC-032. J Clin Oncol 33(24):2646–2654
Yauch RL, Dijkgraaf GJ, Alicke B, Januario T, Ahn CP, Holcomb T, Pujara K, Stinson J, Callahan CA, Tang T, Bazan JF, Kan Z, Seshagiri S, Hann CL, Gould SE, Low JA, Rudin CM, de Sauvage FJ (2009) Smoothened mutation confers resistance to a Hedgehog pathway inhibitor in medulloblastoma. Science 326(5952):572–574
Wang C, Wu H, Evron T, Vardy E, Han GW, Huang XP, Hufeisen SJ, Mangano TJ, Urban DJ, Katritch V, Cherezov V, Caron MG, Roth BL, Stevens RC (2014) Structural basis for smoothened receptor modulation and chemoresistance to anticancer drugs. Nat Commun 5:4355
Spaniol K, Boos J, Lanvers-Kaminsky C (2011) An in vitro evaluation of the polo-like kinase inhibitor GW843682X against paediatric malignancies. Anticancer Drugs 22(6):531–542
Lanvers-Kaminsky C, Bremer A, Dirksen U, Jurgens H, Boos J (2006) Cytotoxicity of treosulfan and busulfan on pediatric tumor cell lines. Anticancer Drugs 17(6):657–662
Beauchamp E, Bulut G, Abaan O, Chen K, Merchant A, Matsui W, Endo Y, Rubin JS, Toretsky J, Uren A (2009) GLI1 is a direct transcriptional target of EWS-FLI1 oncoprotein. J Biol Chem 284(14):9074–9082
Joo J, Christensen L, Warner K, States L, Kang HG, Vo K, Lawlor ER, May WA (2009) GLI1 is a central mediator of EWS/FLI1 signaling in Ewing tumors. PLoS ONE 4(10):e7608
Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Hallahan AR, Pritchard JI, Eberhart CG, Watkins DN, Chen JK, Cooper MK, Taipale J, Olson JM, Beachy PA (2002) Medulloblastoma growth inhibition by hedgehog pathway blockade. Science 297(5586):1559–1561
Pressey JG, Anderson JR, Crossman DK, Lynch JC, Barr FG (2011) Hedgehog pathway activity in pediatric embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma and undifferentiated sarcoma: a report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Pediatr Blood Cancer 57(6):930–938
Bailey JM, Mohr AM, Hollingsworth MA (2009) Sonic hedgehog paracrine signaling regulates metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in pancreatic cancer. Oncogene 28(40):3513–3525
Li X, Wang Z, Ma Q, Xu Q, Liu H, Duan W, Lei J, Ma J, Wang X, Lv S, Han L, Li W, Guo J, Guo K, Zhang D, Wu E, Xie K (2014) Sonic hedgehog paracrine signaling activates stromal cells to promote perineural invasion in pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 20(16):4326–4338
Chen JK, Taipale J, Young KE, Maiti T, Beachy PA (2002) Small molecule modulation of Smoothened activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(22):14071–14076
Lauth M, Bergstrom A, Shimokawa T, Toftgard R (2007) Inhibition of GLI-mediated transcription and tumor cell growth by small-molecule antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(20):8455–8460
Kawabata N, Ijiri K, Ishidou Y, Yamamoto T, Nagao H, Nagano S, Maeda S, Komiya S, Setoguchi T (2011) Pharmacological inhibition of the Hedgehog pathway prevents human rhabdomyosarcoma cell growth. Int J Oncol 39(4):899–906
Mazumdar T, Devecchio J, Agyeman A, Shi T, Houghton JA (2011) Blocking Hedgehog survival signaling at the level of the GLI genes induces DNA damage and extensive cell death in human colon carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 71(17):5904–5914
Wickstrom M, Dyberg C, Shimokawa T, Milosevic J, Baryawno N, Fuskevag OM, Larsson R, Kogner P, Zaphiropoulos PG, Johnsen JI (2013) Targeting the hedgehog signal transduction pathway at the level of GLI inhibits neuroblastoma cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Int J Cancer 132(7):1516–1524
Katoh Y, Katoh M (2009) Hedgehog target genes: mechanisms of carcinogenesis induced by aberrant hedgehog signaling activation. Curr Mol Med 9(7):873–886
Vokes SA, Ji H, McCuine S, Tenzen T, Giles S, Zhong S, Longabaugh WJ, Davidson EH, Wong WH, McMahon AP (2007) Genomic characterization of Gli-activator targets in sonic hedgehog-mediated neural patterning. Development 134(10):1977–1989
Rutter M, Wang J, Huang Z, Kuliszewski M, Post M (2010) Gli2 influences proliferation in the developing lung through regulation of cyclin expression. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 42(5):615–625
Yoon JW, Kita Y, Frank DJ, Majewski RR, Konicek BA, Nobrega MA, Jacob H, Walterhouse D, Iannaccone P (2002) Gene expression profiling leads to identification of GLI1-binding elements in target genes and a role for multiple downstream pathways in GLI1-induced cell transformation. J Biol Chem 277(7):5548–5555
Shahi MH, Afzal M, Sinha S, Eberhart CG, Rey JA, Fan X, Castresana JS (2010) Regulation of sonic hedgehog-GLI1 downstream target genes PTCH1, Cyclin D2, Plakoglobin, PAX6 and NKX2.2 and their epigenetic status in medulloblastoma and astrocytoma. BMC Cancer 10:614
Berlin J, Bendell JC, Hart LL, Firdaus I, Gore I, Hermann RC, Mulcahy MF, Zalupski MM, Mackey HM, Yauch RL, Graham RA, Bray GL, Low JA (2013) A randomized phase II trial of vismodegib versus placebo with FOLFOX or FOLFIRI and bevacizumab in patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 19(1):258–267
Mazumdar T, DeVecchio J, Shi T, Jones J, Agyeman A, Houghton JA (2011) Hedgehog signaling drives cellular survival in human colon carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 71(3):1092–1102
Acknowledgments
The authors thank S. Hoogestraat, S. Schulz and P. Schulze Westhoff for their excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arnhold, V., Boos, J. & Lanvers-Kaminsky, C. Targeting hedgehog signaling pathway in pediatric tumors: in vitro evaluation of SMO and GLI inhibitors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 77, 495–505 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-016-2962-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-016-2962-5