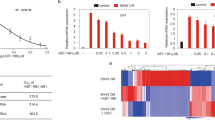
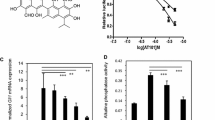
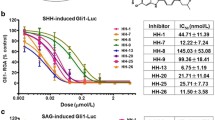
Abstract
Abnormally activated Hedgehog (Hh) pathway has been linked to multiple types of cancers including medulloblastoma (MB). Current Hh-targeted drug development projects mainly focus on antagonizing the upstream oncoprotein Smoothened (Smo). However, the effectiveness of Smo inhibitors is compromised by primary and acquired resistance, which is caused by mutations of Smo or other downstream components. Here, we conducted a cellular screening of small-molecule compounds and identified ABT-737 as a selective Hh inhibitor resulting in active suppression of human Hh-dependent MB cells. Mechanistically, ABT-737 suppressed Hh signals far-downstream of Smo and Sufu at Gli transcriptional effector level. In line with this, ABT-737 potentially inhibited wild-type and drug-resistant mutant Smo. More importantly, ABT-737 also delayed the growth of drug-refractory Hh-dependent MB xenografts derived from genetically engineered mouse model in vivo. These findings identify ABT-737 as a therapeutical substance for cancers with excessive Hh signaling activity, especially for those with primary or acquired resistance to Smo inhibitors in clinic.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the authors on reasonable request.
References
Jiang J, Hui CC. Hedgehog signaling in development and cancer. Dev Cell. 2008;15(6):801–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2008.11.010.
Wu F, et al. Hedgehog signaling: From basic biology to cancer therapy. Cell Chem Biol. 2017;24(3):252–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2017.02.010.
Raleigh DR, Reiter JF. Misactivation of Hedgehog signaling causes inherited and sporadic cancers. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(2):465–75. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci120850.
Reifenberger J, et al. Missense mutations in SMOH in sporadic basal cell carcinomas of the skin and primitive neuroectodermal tumors of the central nervous system. Cancer Res. 1998;58(9):1798–803.
Pugh TJ, et al. Medulloblastoma exome sequencing uncovers subtype-specific somatic mutations. Nature. 2012;488(7409):106–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11329.
Taylor MD, et al. Mutations in SUFU predispose to medulloblastoma. Nat Genet. 2002;31(3):306–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng916.
Kool M, et al. Genome sequencing of SHH medulloblastoma predicts genotype-related response to smoothened inhibition. Cancer Cell. 2014;25(3):393–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2014.02.004.
Wang W, et al. Constitutive GLI1 expression in chondrosarcoma is regulated by major vault protein via mTOR/S6K1 signaling cascade. Cell Death Differ. 2021;28(7):2221–37. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-021-00749-4.
Tosello V, et al. Cross-talk between GLI transcription factors and FOXC1 promotes T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia dissemination. Leukemia. 2021;35(4):984–1000. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-020-0999-2.
Yang J, et al. PGE2-JNK signaling axis non-canonically promotes Gli activation by protecting Gli2 from ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(7):707. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-03995-z.
Steele NG, et al. Inhibition of hedgehog signaling alters fibroblast composition in pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27(7):2023–37. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-20-3715.
Petty AJ, et al. Hedgehog signaling promotes tumor-associated macrophage polarization to suppress intratumoral CD8+ T cell recruitment. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(12):5151–62. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci128644.
Hinshaw DC, et al. Hedgehog signaling regulates metabolism and polarization of mammary tumor-associated macrophages. Cancer Res. 2021;81(21):5425–37. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-20-1723.
Sekulic A, et al. Efficacy and safety of vismodegib in advanced basal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(23):2171–9. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1113713.
Lear JT, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of sonidegib in patients with locally advanced and metastatic basal cell carcinoma: 30-month analysis of the randomized phase 2 BOLT study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32(3):372–81. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.14542.
Cortes JE, et al. Randomized comparison of low dose cytarabine with or without glasdegib in patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia or high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia. 2019;33(2):379–89. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-018-0312-9.
Sharpe HJ, et al. Genomic analysis of smoothened inhibitor resistance in basal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2015;27(3):327–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2015.02.001.
Atwood SX, et al. Smoothened variants explain the majority of drug resistance in basal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2015;27(3):342–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2015.02.002.
Zhao X, et al. RAS/MAPK activation drives resistance to smo inhibition, metastasis, and tumor evolution in Shh pathway-dependent tumors. Cancer Res. 2015;75(17):3623–35. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-14-2999-t.
Wang J, et al. ABT-199 inhibits Hedgehog pathway by acting as a competitive inhibitor of oxysterol, rather as a BH3 mimetic. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021;42(6):1005–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-020-00504-4.
Mo J, et al. Inhibition of the FACT complex targets aberrant hedgehog signaling and overcomes resistance to smoothened antagonists. Cancer Res. 2021;81(11):3105–20. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-20-3186.
Tang Y, et al. Epigenetic targeting of Hedgehog pathway transcriptional output through BET bromodomain inhibition. Nat Med. 2014;20(7):732–40. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3613.
Wu CC, et al. mTORC1-mediated inhibition of 4EBP1 is essential for hedgehog signaling-driven translation and medulloblastoma. Dev Cell. 2017;43(6):673-688.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2017.10.011.
Beauchamp EM, et al. Arsenic trioxide inhibits human cancer cell growth and tumor development in mice by blocking Hedgehog/GLI pathway. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(1):148–60. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI42874.
Petros AM, et al. Discovery of a potent inhibitor of the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-xL from NMR and parallel synthesis. J Med Chem. 2006;49(2):656–63. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm0507532.
Kim J, et al. Itraconazole, a commonly used antifungal that inhibits Hedgehog pathway activity and cancer growth. Cancer Cell. 2010;17(4):388–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2010.02.027.
Hatton BA, et al. The Smo/Smo model: hedgehog-induced medulloblastoma with 90% incidence and leptomeningeal spread. Cancer Res. 2008;68(6):1768–76. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5092.
Buonamici S, et al. Interfering with resistance to smoothened antagonists by inhibition of the PI3K pathway in medulloblastoma. Sci Translational Med. 2010;2(51):5170. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3001599.
Wang J, et al. AT-101 inhibits hedgehog pathway activity and cancer growth. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015;76(3):461–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-015-2812-x.
Taipale J, et al. Effects of oncogenic mutations in Smoothened and Patched can be reversed by cyclopamine. Nature. 2000;406(6799):1005–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/35023008.
Chen JK, et al. Small molecule modulation of Smoothened activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(22):14071–6. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.182542899.
Triscott J, et al. Personalizing the treatment of pediatric medulloblastoma: Polo-like kinase 1 as a molecular target in high-risk children. Cancer Res. 2013;73(22):6734–44. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-12-4331.
Di Magno L, et al. Phenformin inhibits hedgehog-dependent tumor growth through a complex I-Independent Redox/Corepressor module. Cell Rep. 2020;30(6):1735–17527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.01.024.
Parchure A, Vyas N, Mayor S. Wnt and hedgehog: secretion of lipid-modified morphogens. Trends Cell Biol. 2018;28(2):157–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2017.10.003.
Coquenlorge S, et al. GLI2 Modulated by SUFU and SPOP induces intestinal stem cell niche signals in development and tumorigenesis. Cell Rep. 2019;27(10):3006–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.05.016.
Regl G, et al. Human GLI2 and GLI1 are part of a positive feedback mechanism in basal cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 2002;21(36):5529–39. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205748.
Dijkgraaf GJ, et al. Small molecule inhibition of GDC-0449 refractory smoothened mutants and downstream mechanisms of drug resistance. Cancer Res. 2011;71(2):435–44. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-10-2876.
Rodriguez-Blanco J, et al. A CK1α Activator Penetrates the Brain and Shows Efficacy Against Drug-resistant Metastatic Medulloblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25(4):1379–88. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-18-1319.
Robarge KD, et al. GDC-0449-a potent inhibitor of the hedgehog pathway. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009;19(19):5576–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.08.049.
Liu G, et al. Discovery of novel macrocyclic hedgehog pathway inhibitors acting by suppressing the Gli-mediated transcription. J Med Chem. 2017;60(19):8218–45. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01185.
Wu X, et al. Extra-mitochondrial prosurvival BCL-2 proteins regulate gene transcription by inhibiting the SUFU tumour suppressor. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19(10):1226–36. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3616.
Levesley J, et al. RASSF1A and the BH3-only mimetic ABT-737 promote apoptosis in pediatric medulloblastoma cell lines. Neuro Oncol. 2011;13(12):1265–76. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nor129.
Pazzaglia L, et al. Genetic and molecular alterations in rhabdomyosarcoma mRNA overexpression of MCL1 and MAP2K4 genes. Histol Histopathol. 2009;24(1):61–7. https://doi.org/10.14670/hh-24.61.
Graab U, Hahn H, Fulda S. Identification of a novel synthetic lethality of combined inhibition of hedgehog and PI3K signaling in rhabdomyosarcoma. Oncotarget. 2015;6(11):8722–35. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.2726.
Meister MT, et al. Concomitant targeting of Hedgehog signaling and MCL-1 synergistically induces cell death in Hedgehog-driven cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2019;465:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2019.08.012.
Funding
This work was financially supported by grants from Chinese Natural Science Foundation (No. 81573452, 81773767).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by WH. The first draft of the manuscript was written by JW and WH and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
All animal studies were approved by and conformed to the policies and regulations of the Animal Care and Use Committee of Shanghai University, China (Date Jul. 8, 2019 /No.2019–0020).
Consent for publication
All authors gave final approval of the version to be published.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, W., Liu, H., Tan, W. et al. ABT-737 suppresses aberrant Hedgehog pathway and overcomes resistance to smoothened antagonists by blocking Gli. Med Oncol 39, 188 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-022-01794-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-022-01794-w