Abstract
Purpose
We evaluated the population pharmacokinetics (PPK) and exposure–response relationship of imatinib mesylate in Iranian patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML).This study was designed to assess steady state (SS) imatinib trough concentrations (Cmin) and pharmacokinetics parameters of imatinib in patients with CML in chronic phase after at least 12-month treatment.
Methods
Plasma concentrations from a randomized controlled trial consist of 61 patients who received oral imatinib at doses ranged between 300 and 800 mg in various dosing interval, which were quantified using a validated reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic method with UV detection method on different occasions at SS and evaluated using PPK model.
Results
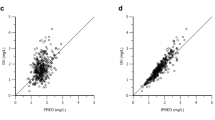
A one-compartment model with zero-order absorption and a lag time was sufficient in describing the concentration–time profile. Inter-individual variability (IIV) was modeled for all parameters. Oral clearance (CL/F) and the volume of distribution (V/F) were estimated to 10.8 L/h with 30 % IIV and 265 L with 53 % IIV, respectively. Inter-occasion variability (IOV) was included in CL/F (17 %) and V/F (22 %).The proportional residual error of the model was 8 %.
Conclusions
Simulation analysis from individual parameters shows exposure to imatinib is highly variable among patients. Imatinib trough plasma levels <1,257 ng/mL were associated with lower rates of major molecular response. Because of the wide IIV compared with IOV with imatinib in our study, trough levels may play a role in investigating instances of suboptimal response.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buchdunger E, Zimmermann J, Mett H, Meyer T, Muller M, Druker BJ, Lydon NB (1996) Inhibition of the Abl protein-tyrosine kinase in vitro and in vivo by a 2-phenylaminopyrimidine derivative. Cancer Res 56(1):100–104
Druker BJ, Talpaz M, Resta DJ, Peng B, Buchdunger E, Ford JM, Lydon NB, Kantarjian H, Capdeville R, Ohno-Jones S, Sawyers CL (2001) Efficacy and safety of a specific inhibitor of the BCR–ABL tyrosine kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 344(14):1031–1037
Wang Y, Chia YL, Nedelman J, Schran H, Mahon FX, Molimard M (2009) A therapeutic drug monitoring algorithm for refining the imatinib trough level obtained at different sampling times. Ther Drug Monit 31(5):579–584
Peng B, Lloyd P, Schran H (2005) Clinical pharmacokinetics of imatinib. Clin Pharmacokinet 44(9):879–894
Gandia P, Arellano C, Lafont T, Huguet F, Malard L, Chatelut E (2012) Should therapeutic drug monitoring of the unbound fraction of imatinib and its main active metabolite N-desmethyl-imatinib be developed? Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 71(2):531–536. doi:10.1007/s00280-012-2035-3
Picard S, Titier K, Etienne G, Teilhet E, Ducint D, Bernard MA, Lassalle R, Marit G, Reiffers J, Begaud B, Moore N, Molimard M, Mahon FX (2007) Trough imatinib plasma levels are associated with both cytogenetic and molecular responses to standard-dose imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 109(8):3496–3499. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-07-036012
Larson RA, Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O’Brien SG, Riviere GJ, Krahnke T, Gathmann I, Wang Y (2008) Imatinib pharmacokinetics and its correlation with response and safety in chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: a subanalysis of the IRIS study. Blood 111(8):4022–4028. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-10-116475
Awidi A, Ayed AO, Bsoul N, Magablah A, Mefleh R, Dweiri M, Ramahi M, Arafat E, Bishtawi M, Marie L (2010) Relationship of serum imatinib trough level and response in CML patients: long term follow-up. Leuk Res 34(12):1573–1575. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2010.07.014
Gotta V, Widmer N, Montemurro M, Leyvraz S, Haouala A, Decosterd LA, Csajka C, Buclin T (2012) Therapeutic drug monitoring of imatinib: Bayesian and alternative methods to predict trough levels. Clin Pharmacokinet 51(3):187–201. doi:10.2165/11596990-000000000-00000
Sheiner LB, Beal S, Rosenberg B, Marathe VV (1979) Forecasting individual pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 26(3):294–305
Samara E, Granneman R (1997) Role of population pharmacokinetics in drug development. A pharmaceutical industry perspective. Clin Pharmacokinet 32(4):294–312
Williams PJ, Ette EI (2000) The role of population pharmacokinetics in drug development in light of the Food and Drug Administration’s ‘Guidance for Industry: population pharmacokinetics’. Clin Pharmacokinet 39(6):385–395
Petain A, Kattygnarath D, Azard J, Chatelut E, Delbaldo C, Geoerger B, Barrois M, Seronie-Vivien S, LeCesne A, Vassal G (2008) Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacogenetics of imatinib in children and adults. Clin Cancer Res 14(21):7102–7109. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0950
Schmidli H, Peng B, Riviere GJ, Capdeville R, Hensley M, Gathmann I, Bolton AE, Racine-Poon A (2005) Population pharmacokinetics of imatinib mesylate in patients with chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukaemia: results of a phase III study. Br J Clin Pharmacol 60(1):35–44
Faber E, Friedecky D, Micova K, Rozmanova S, Divoka M, Jarosova M, Indrak K, Adam T (2012) Imatinib trough plasma levels do not correlate with the response to therapy in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in routine clinical setting. Ann Hematol 91(6):923–929. doi:10.1007/s00277-011-1394-x
Golabchifar AA, Rouini MR, Shafaghi B, Rezaee S, Foroumadi A, Khoshayand MR (2011) Optimization of the simultaneous determination of imatinib and its major metabolite, CGP74588, in human plasma by a rapid HPLC method using D-optimal experimental design. Talanta 85(5):2320–2329. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2011.07.093
Ette EI, Sun H, Ludden TM (1998) Balanced designs in longitudinal population pharmacokinetic studies. J Clin Pharmacol 38(5):417–423
Hughes T, Deininger M, Hochhaus A, Branford S, Radich J, Kaeda J, Baccarani M, Cortes J, Cross NC, Druker BJ, Gabert J, Grimwade D, Hehlmann R, Kamel-Reid S, Lipton JH, Longtine J, Martinelli G, Saglio G, Soverini S, Stock W, Goldman JM (2006) Monitoring CML patients responding to treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: review and recommendations for harmonizing current methodology for detecting BCR–ABL transcripts and kinase domain mutations and for expressing results. Blood 108(1):28–37. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-01-0092
Hughes TP, Kaeda J, Branford S, Rudzki Z, Hochhaus A, Hensley ML, Gathmann I, Bolton AE, van Hoomissen IC, Goldman JM, Radich JP (2003) Frequency of major molecular responses to imatinib or interferon alfa plus cytarabine in newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 349(15):1423–1432. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa030513349/15/1423
Holford NH (1999) Target concentration intervention: beyond Y2K. Br J Clin Pharmacol 48(1):9–13
Menon-Andersen D, Mondick JT, Jayaraman B, Thompson PA, Blaney SM, Bernstein M, Bond M, Champagne M, Fossler MJ, Barrett JS (2008) Population pharmacokinetics of imatinib mesylate and its metabolite in children and young adults. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. doi:10.1007/s00280-008-0730-x
Acknowledgments
This study was part of a PhD thesis supported by Tehran University of Medical Sciences (TUMS).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golabchifar, AA., Rezaee, S., Ghavamzadeh, A. et al. Population pharmacokinetics of imatinib in Iranian patients with chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 74, 85–93 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2473-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2473-1