Abstract
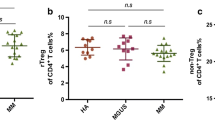
The exact role of regulatory T cells (Tregs) in multiple myeloma (MM) has not been yet determined. Data regarding alterations of Tregs during therapy with novel agents (NA), i.e., bortezomib and lenalidomide are conflicted and limited. We evaluated prospectively alterations of Tregs and searched for correlations with disease characteristics, response, and outcome in 29 patients with active MM treated with either bortezomib-dexamethasone (BD; 11 patients) or lenalidomide-dexamethasone (LenDex, 18 patients). Additionally, we recorded changes of lymphocytes subsets and cytokines related to Tregs function and MM biology, i.e., interleukin (IL) 6, 2, 17, and TGF-β. Compared with controls, patients had significantly higher median levels of Tregs%, IL-6, and IL-17 (p < 0.001). Median CD4 T and B cells frequencies were significantly lower, whereas CD8 T and natural killers were increased compared to controls. In BD group, no significant alterations of Tregs% were observed. Patients treated with LenDex, displayed a significant reduction of Tregs% (p < 0.001) especially those who achieved at least very good partial response (≥vgPR) (p = 0.04). Lymphocyte subsets or cytokines did not significantly change during therapy. In summary, Tregs% are higher in patients with active MM compared with controls, and they significantly decrease after treatment with LenDex but not with BD; After therapy with LenDex, Tregs reduction between baseline and major response correlated with achievement of ≥vgPR suggesting a possible predictive role, that may contribute to therapeutic strategy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rajkumar SV (2013) Multiple myeloma: 2013 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am J Hematol 88:226–235
Morgan GJ, Walker BA, Davies FE (2012) The genetic architecture of multiple myeloma. Nat Rev Cancer 12:335–348
Pratt G, Goodyear O, Moss P (2007) Immunodeficiency and immunotherapy in multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 138:563–579
Dosani T, Carlsten M, Maric I, Landgren O (2015) The cellular immune system in myelomagenesis: NK cells and T cells in the development of MM and their uses in immunotherapies. Blood Cancer J 5:e321
Fehervari Z, Sakaguchi S (2004) Development and function of CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells. Curr Opin Immunol 16:203–208
Workman CJ, Szymcak-Workman AL, Collison LW, Pilai MR, DAA V (2009) The development and function of regulatory T cells. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:2603–2622
Raja Muthu KR, Hajek R. Regulatory cells and multiple myeloma (2012) https://www.intechopen.com /doi.org /https://doi.org/10.5772/31207
Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S (2003) Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science 299:1057–1061
Fontenot JD, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY (2003) Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25 regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol 4:330–336
Curiel TJ (2008) Regulatory T cells and treatment of cancer. Curr Opin Immunol 20:241–246
Wang HY, Wang RF (2007) Regulatory T cells and cancer. Curr Opin Immunol 19:217–223
Merico F, Bergui L, Gregoretti MG, Ghia P, Aimo G, Lindley IJD, Caligaris-Cappio F (1993) Cytokines involved in the progression of multiple myeloma. Clin Exp Immunol 92:27–31
La Cava A (2008) Tregs are regulated by cytokines: implications for autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev 8:83–87
Βraga WMT, Atanackovic D, Colleoni GWB (2012) The role of regulatory T cells and TH17 cells in multiple myeloma. Clin Dev Immunol 2012:293479
Bettelli E, Carrier Y, Gao W, Korn T, Strom TB, Oukka M, Weiner HL, Kuchroo VK (2006) Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature 441:235–238
Noonan K, Marchionni L, Anderson J, Pardoll D, Roodman GD, Borrello I (2010) A novel role of IL-17-producing lymphocytes in mediating lytic bone disease in multiple myeloma. Blood 116:3554–3563
Seddiki N, Santner-Nanan B, Martinson J, Zaunders J, Sasson S, Landay A, Solomon M, Selby W, Alexander SI, Nanan R, Kelleher A, Fazekas de St Groth B (2006) Expression of interleukin IL-2 and IL-7 receptors discriminates between human regulatory and activated T cells. J Exp Med 203:1693–1700
Liu W, Putnam AL, Xu-Yu Z, Szot GL, Lee MR, Zhu S, Gottlieb PA, Kapranov P, Gingeras TR, Fazekas de St Groth B, Clayberger C, Soper DM, Ziegler SF, Bluestone JA (2006) CD127 expression inversely correlates with FoxP3 and suppressive function of human CD4(+) Treg cells. J Exp Med 203:1701–1711
Durie BG, Harousseau JL, Miguel JS, Bladé J, Barlogie B, Anderson K, Gertz M, Dimopoulos M, Westin J, Sonneveld P, Ludwig H, Gahrton G, Beksac M, Crowley J, Belch A, Boccadaro M, Cavo M, Turesson I, Joshua D, Vesole D, Kyle R, Alexanian R, Tricot G, Attal M, Merlini G, Powles R, Richardson P, Shimizu K, Tosi P, Morgan G, Rajkumar SV (2006) International uniform criteria for multiple. Leukemia 20:1467–1473
Feyler S, von Lilienfeld-Toal M, Jarmin S, Lee Marles L, Rawstron A, Ashcroft AJ, Owen RG, Selby PJ, Cook G (2009) CD4(+)CD25(+)FoxP3(+) regulatory-T cells are increased whilst CD3(+)CD4(−)CD8(−)αβTCR(+) double negative T cells are decreased in the peripheral blood of patients with multiple myeloma which correlates with disease burden. Br J Haematol 144:686–689
Beyler M, Kochanek M, Giese T, Endl E, Weihrauch MR, Knolle PA, Classen S, Schultze JL (2006) In vivo peripheral expansion of naive CD4+CD25highFoxP3+ regulatory T cells in patients with multiple myeloma. Blood 107:3940–3949
Prabhala RH, Neri P, Bae JE, Tassone P, Shammas MA, Allam CK, Daley JF, Chauhan D, Blanchard E, Thatte HS, Anderson KC, Munshi NC (2006) Dysfunctional T regulatory cells in multiple myeloma. Blood 07:301–304
Gupta R, Ganeshan P, Hakim M, Verma R, Sharma A, Kumar L (2011) Significantly reduced regulatory T cell population in patients with untreated multiple myeloma. Leuk Res 35:874–878
Galustian C, Meyer B, Labarthe MC, Dredge K, Klaschka D, Henry J, Todryk S, Chen R, Muller G, Stirling D, Schafer P, Bartlett JB, Dalgleish AG (2009) The anti-cancer agents lenalidomide and pomalidomide inhibit the proliferation and function of T regulatory cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother 58:1033–1045
Muthu Raja KR, Kovarova L, Hajek R (2012) Induction by lenalidomide and dexamethasone combination increases regulatory cells of patients with previously untreated multiple myeloma. Leuk Lymphoma 53:1406–1408
Blanco B, Pérez-Simón JA, Sánchez-Abarca LI, Caballero-Velazquez T, Gutierrez-Cossío S, Hernández-Campo P, Díez-Campelo M, Herrero-Sanchez C, Rodriguez-Serrano C, Santamaría C, Sánchez-Guijo FM, Del Cañizo C, San Miguel JF (2009) Treatment with bortezomib of human CD4+ T cells preserves natural regulatory T cells and allows the emergence of a distinct suppressor T-cell population. Haematologica 94:975–983
Atanackovic D, Cao Y, Luetkens T, Panse J, Faltz C, Arfsten J, Bartels K, Wolschke C, Eiermann T, Zander AR, Fehse B, Bokemeyer C, Kroger N (2008) CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ T regulatory cells reconstitute and accumulate in the bone marrow of patients with multiple myeloma following allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica 93:423–430
Rezvani K, Mielke S, Ahmadzadeh M, Kilical Y, Savani BN, Zeilah J, Keyvanfar K, Montero A, Hensel N, Kurlander R, Barrett AJ (2006) High donor FOXP3-positive regulatory T-cell (Treg) content is associated with a low risk of GVHD following HLA-matched allogeneic SCT. Blood 108:1291–1297
Giannopoulos K, Kameniska W, Dmoszynska A (2012) The frequency of T regulatory cells modulates the survival of multiple myeloma patients: detailed characterization of immune status in multiple myeloma. Βr J Cancer 106:546–552
Muthu Raja KR, Kovarova L, Kaisarova P, Bartonova J, Hajek R, Michalek J (2011) Regulatory T cells predicts progression in previously untreated myeloma patients and treatment by cyclophosphamide, thalidomide plus dexamethasone reduces regulatory T cells. Blood 118:2870
Gandhi AK, Kang J, Capone L, Parton A, Wu L, Zhang LH, Mendy D, Lopez-Girona A, Tran T, Sapinoso L, Fang W, Xu S, Hampton G, Bartlett JB, Schafer P (2010) Dexamethasone synergizes with lenalidomide to inhibit multiple myeloma tumor growth, but reduces lenalidomide-induced immunomodulation of T and NK cell function. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 10:155–167
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hadjiaggelidou, C., Mandala, E., Terpos, E. et al. Evaluation of regulatory T cells (Tregs) alterations in patients with multiple myeloma treated with bortezomib or lenalidomide plus dexamethasone: correlations with treatment outcome. Ann Hematol 98, 1457–1466 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-019-03657-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-019-03657-3