Abstract
Purpose
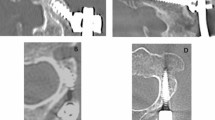
Pedicle morphology is important for intraoperative surgical anatomy and to define pedicle screw design and parameters. However, differences of pedicle size according to ethnicity and gender are not well studied. The purpose of this study is to investigate morphological characteristics of the pedicle in Japanese patients for determining adequate screw size and optimal surgical planning.
Methods
We investigated thoracic and lumbar pedicle morphology in Japanese patients using computed tomography (CT) measurements and analyzed the standard size of pedicles on upper thoracic to lumbar spine CT images in 227 Japanese patients.
Results
Gender had a larger impact on the shape and size of pedicles than racial differences. In the distribution of pedicle width, we calculated the ratio of values less than 4.5 mm, that in females resulted to be over 30% for the Th3−Th9 segment, and particularly high, above 60% at Th4 and Th5.
Conclusion
Our measurement analysis showed that pedicle morphological parameters in Japanese patients showed tendency to be smaller to those found in other studies, and particularly in female patients, they were statistically significantly smaller. Adequate transpedicular instrumentation for Japanese patients will require smaller size pedicle-related devices that will match our anatomical findings to achieve safe device placement. In addition, serving ethnically non-homogenous patient population can require further to spinal morphometric for precise device selection.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Anonymized data on pedicle measurements can be provided upon reasonable requests from the corresponding author.
References
Albano J, Lentz J, Stockton R, DePalma V, Markowitz M, Ganz M, Katsigiorgis G, Grewal K (2019) Demographic analysis of lumbar pedicle diameters in a diverse population. Asian Spine J 13:410–416
Aoude AA, Fortin M, Figueiredo R, Jarzem P, Ouellet J, Weber MH (2015) Methods to determine pedicle screw placement accuracy in spine surgery: a systematic review. Eur Spine J 24:990–1004
Attar A, Ugur HC, Uz A, Tekdemir I, Egemen N, Genc Y (2001) Lumbar pedicle: surgical anatomic evaluation and relationships. Eur Spine J 10:10–15
Bernard TN, Seibert CE (1992) Pedicle diameter determined by computed tomography. Its relevance to pedicle screw fixation in the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 17:160–163
Berry JL, Moran JM, Berg WS, Steffee AD (1987) A morphometric study of human lumbar and selected thoracic vertebrae. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 12:362–367
Brasiliense LBC, Theodore N, Lazaro BCR, Sayed ZA, Deniz FE, Sonntag VKH, Crawford NR (2010) Quantitative analysis of misplaced pedicle screws in the thoracic spine: how much pullout strength is lost? Presented at the 2009 joint spine section meeting. J Neurosurg Spine 12:503–508
Cheung KM, Ruan D, Chan FL, Fang D (1994) Computed tomographic osteometry of Asian lumbar pedicles. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 19:1495–1498
Ebraheim NA, Xu R, Ahmad M, Yeasting RA (1997) Projection of the thoracic pedicle and its morphometric analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 22:233–238
Hailong Y, Wei L, Zhensheng M, Hongxun S (2007) Computer analysis of the safety of using three different pedicular screw insertion points in the lumbar spine in the Chinese population. Eur Spine J 16:619–623
Hou S, Hu R, Shi Y (1993) Pedicle morphology of the lower thoracic and lumbar spine in a Chinese population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 18:1850–1855
Kim NH, Lee HM, Chung IH, Kim HJ, Kim SJ (1994) Morphometric study of the pedicles of thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in Koreans. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 19:1390–1394
Konishiike T (1994) Youtui-tuikyuukonno kaibougakuteki keisoku(Japanese). Chubu-seisai-shi 37:606–612
Kretzer RM, Chaput C, Sciubba DM, Garonzik IM, Jallo GI, McAfee PC, Cunningham BW, Tortolani PJ (2011) A computed tomography-based morphometric study of thoracic pedicle anatomy in a random United States trauma population. J Neurosurg Spine 14:235–243
Makino T, Kaito T, Fujiwara H, Yonenobu K (2012) Analysis of lumbar pedicle morphology in degenerative spines using multiplanar reconstruction computed tomography: what can be the reliable index for optimal pedicle screw diameter? Eur Spine J 21:1516–1521
Mitra SR, Datir SP, Jadhav SO (2002) Morphometric study of the lumbar pedicle in the Indian population as related to pedicular screw fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 27:453–459
Nojiri K, Matsumoto M, Chiba K, Toyama Y (2005) Morphometric analysis of the thoracic and lumbar spine in Japanese on the use of pedicle screws. Surg Radiol Anat 27:123–128
Nojiri K, Matsumoto M, Chiba K, Toyama Y, Momoshima S (2005) Comparative assessment of pedicle morphology of the lumbar spine in various degenerative diseases. Surg Radiol Anat 27:317–321
Obernauer J, Kavakebi P, Quirbach S, Thomé C (2014) Pedicle-based non-fusion stabilization devices: a critical review and appraisal of current evidence. Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg 41:131–142
Olsewski JM, Simmons EH, Kallen FC, Mendel FC, Severin CM, Berens DL (1990) Morphometry of the lumbar spine: anatomical perspectives related to transpedicular fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 72:541–549
Panjabi MM, Goel V, Oxland T, Takata K, Duranceau J, Krag M, Price M (1992) Human lumbar vertebrae. Quantitative three-dimensional anatomy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 17:299–306
Robertson PA, Novotny JE, Grobler LJ, Agbai JU (1998) Reliability of axial landmarks for pedicle screw placement in the lower lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 23:60–66
Robertson PA, Stewart NR (2000) The radiologic anatomy of the lumbar and lumbosacral pedicles. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 25:709–715
Scoles PV, Linton AE, Latimer B, Levy ME, Digiovanni BF (1988) Vertebral body and posterior element morphology: the normal spine in middle life. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 13:1082–1086
Sugisaki K, An HS, Espinoza Orías AA, Rhim R, Andersson GB, Inoue N (2009) In vivo three-dimensional morphometric analysis of the lumbar pedicle isthmus. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34:2599–2604
Tan SH, Teo EC, Chua HC (2002) Quantitative three-dimensional anatomy of lumbar vertebrae in Singaporean Asians. Eur Spine J 11:152–158
Ugur HC, Attar A, Uz A, Tekdemir I, Egemen N, Genç Y (2001) Thoracic pedicle: surgical anatomic evaluation and relations. J Spinal Disord 14:39–45
Yoshida G, Sato K, Kanemura T, Iwase T, Togawa D, Matsuyama Y (2016) Accuracy of percutaneous lumbosacral pedicle screw placement using the oblique fluoroscopic view based on computed tomography evaluations. Asian Spine J 10:630–638
Zheng C, Huang Q, Hu Y, Wang X, Chen W (2009) Computed tomographic morphometry of thoracic pedicles: safety pedicle parameter measurement of the Chinese immature thoracic spine. Int Orthop 33:1663–1668
Zindrick MR, Wiltse LL, Doornik A, Widell EH, Knight GW, Patwardhan AG, Thomas JC, Rothman SL, Fields BT (1987) Analysis of the morphometric characteristics of the thoracic and lumbar pedicles. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 12:160–166
Funding
This research was supported by The Jikei University Research Fund for Graduate Students.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KM project development, data collection and management, data analysis, and manuscript writing. HO project development and manuscript editing. DK project development. ST project development and manuscript editing. KK protocol/project development and manuscript writing/editing. YM project development and manuscript editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the article content was composed in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Consent to participate
Patients’ consent was waived for usages of pool data.
Consent for publication
All co-authors have approved the manuscript and agreed with submission.
Ethical approval
All patients’ information is anonymized before being included in the study. We have obtained the approval required by the Ethical commission of our university, as # 32–232(10313).
Informed consent
All patients’ information is anonymized before being included in the study and the study information and contact address are published in the website of our university.
Research involving human and animal participants
Patients’ consent was waived for usages of pool data and the study information and contact address are published in the website of our university.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morita, K., Ohashi, H., Kawamura, D. et al. Thoracic and lumbar spine pedicle morphology in Japanese patients. Surg Radiol Anat 43, 833–842 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-021-02707-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-021-02707-8