Abstract
Purpose
This study aims to investigate nerve distribution patterns of human lower leg skeletal muscles using a modified Sihler’s staining method.
Methods
Sixteen lower leg from eight fresh adult cadavers were used in this study and all the skeletal muscles were dissected. The muscle specimens were classified according to Lim’s classification. The specimens were then stained by further modified Sihler’s staining technique. Data were analyzed according to research results.
Results
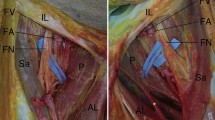
After the staining, we found four patterns of nerve distribution in human lower leg muscles: (1) Type 1: single nerve pattern in which the nerve branches into two either running parallel to each other or radiating in a spray pattern (such as the extensor digitorum longus, extensor hallucis longus, fibularis brevis and flexor hallucis longus). (2) Type 2: double nerve pattern, one being proximal and the other being distal (such as the extensor digitorum longus, flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus). (3) Type 3: multiple branch pattern (such as the tibialis anterior, fibularis longus, gastrocnemius, soleus, tibialis anterior and popliteus).
Conclusion
Our modified Sihler’s staining method is useful for research of large muscles and intramuscular nerves in human. These findings might provide guidance for clinicians for muscle reconstruction surgery.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad I, Akhtar S et al (2013) Hemisoleus muscle flap in the reconstruction of exposed bones in the lower limb. J Wound Care 22(11):638–640
An X, Yue B et al (2012) Intramuscular distribution of the phrenic nerve in human diaphragm as shown by Sihler staining. Muscle Nerve 45(4):522–526
Beretta Piccoli M, Rainoldi A et al (2014) Innervation zone locations in 43 superficial muscles: toward a standardization of electrode positioning. Muscle Nerve 49(3):413–421
Buckland A, Pan WR et al (2009) Neurovascular anatomy of sartorius muscle flaps: implications for local transposition and facial reanimation. Plast Reconstr Surg 123(1):44–54
Elghamry AH (2014) The medial gastrocnemius muscle with an achilles tendon sheath extension flap as a versatile myo-tendon sheath flap for coverage of the upper two-thirds of the tibia and pre-tibial area: a preliminary report. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 67(2):252–256
Fattah AY, Ravichandiran K et al (2013) A three-dimensional study of the musculotendinous and neurovascular architecture of the gracilis muscle: application to functional muscle transfer. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 66(9):1230–1237
Grinsell D, Yue BY (2014) The functional free innervated medial gastrocnemius flap. J Reconstr Microsurg 30(7):451–456
Gulekon N, Peker T et al (2007) Qualitative comparison of anatomical microdissection, Sihler’s staining and computerized reconstruction methods for visualizing intramuscular nerve branches. Surg Radiol Anat 29(5):373–378
Gundlapalli V, Gillespie JW et al (2014) Split hemianterior tibialis turndown muscle flap for coverage of distal leg wounds with preservation of function. Eplasty 14:e12
Gupta R, Nelson SD et al (2001) The innervation of the triangular fibrocartilage complex: nitric acid maceration rediscovered. Plast Reconstr Surg 107(1):135–139
Hankiss J, Schmitz C (2013) The soleus muscle flap. Oper Orthop Traumatol 25(2):145–151
Hierner R, Berger A (2009) Pectoralis major muscle transfer for reconstruction of elbow flexion in posttraumatic brachial plexus lesions. Oper Orthop Traumatol 21(2):126–140
Homma T, Sakai T (1991) Ramification pattern of intermetacarpal branches of the deep branch (ramus profundus) of the ulnar nerve in the human hand. Acta Anat (Basel) 141(2):139–144
Homma T, Sakai T (1992) Thenar and hypothenar muscles and their innervation by the ulnar and median nerves in the human hand. Acta Anat (Basel) 145(1):44–49
Hua J, Kumar VP et al (1999) Split flexor carpi radialis muscle. Plast Reconstr Surg 103(3):930–934
Jiang H, Guo ET et al (1995) One-stage microneurovascular free abductor hallucis muscle transplantation for reanimation of facial paralysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 96(1):78–85
Kim HN, Dong Q et al (2014) Percutaneous lateral ankle ligament reconstruction using a split peroneus longus tendon free graft: technical tip. Foot Ankle Int 35(10):1082–1086
Kishi K, Nakajima H et al (2009) Extended split superior gluteus maximus musculocutaneous flap and reconstruction after resection of perianal and lower gluteal hidradenitis suppurativa. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 62(8):1081–1086
Kosutic D, Biraima AM et al (2013) Posterior and anterior tibialis turn-over muscle flaps with primatrix for salvage of lower extremity after free-flap failure. Microsurgery 33(1):77–78
Li X, Yang ZP et al (2008) Soft tissue reconstruction with sagittal split anterior tibial muscle transfer and medial gastrocnemius transposition in limb-salvage surgery of bone tumors in a proximal tibia. Ann Plast Surg 61(2):204–208
Liem RS, Douwe van Willigen J (1988) In toto staining and preservation of peripheral nervous tissue. Stain Technol 63(2):113–120
Lim AY, Pereira BP et al (2004) Intramuscular innervation of upper-limb skeletal muscles. Muscle Nerve 29(4):523–530
Liu AT, Yu DZ et al (2010) Profiling of innervations of mimetic muscles in fresh human cadavers using a modified Sihler’s technique. Muscle Nerve 42(1):88–94
Liu AT, Liu BL et al (2014) Architectural properties of the neuromuscular compartments in selected forearm skeletal muscles. J Anat 225(1):12–18
Liu CT, Lu YC et al (2015) Half-peroneus-longus-tendon graft augmentation for unqualified hamstring tendon graft of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Orthop Sci 20(5):854–860
Liu J, Kumar VP et al (1997) Modified Sihler’s technique for studying the distribution of intramuscular nerve branches in mammalian skeletal muscle. Anat Rec 247(1):137–144
Lyroudia K, Palakidis K et al (1995) Computerized reconstruction of TEM examined pulpal blood vessels and nerves. Endod Dent Traumatol 11(4):189–195
McCormick SU, Stern JC (1996) Split mentalis flap for reconstruction of the anterior mandible. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 54(8):1031–1033
Orgel MG, Kucan JO (1985) A double-split gluteus maximus muscle flap for reconstruction of the rectal sphincter. Plast Reconstr Surg 75(1):62–67
Panse N, Sahasrabudhe P et al (2012) The split tibialis anterior muscle flap—a simple solution for longitudinal middle third tibial defects. Indian J Plast Surg 45(1):53–57
Peker T, Gulekon N et al (2006) Observation of the relationship between the shape of skeletal muscles and their nerve distribution patterns: a transparent and microanatomic study. Plast Reconstr Surg 117(1):165–176
Tanaka Y, Miki K et al (1998) Reconstruction of an extensive scalp defect using the split latissimus dorsi flap in combination with the serratus anterior musculo-osseous flap. Br J Plast Surg 51(3):250–254
Wang HB, Lin SQ et al (2013) Anatomic study of selective neurectomy of gastrocnemius muscle for calf reduction in Chinese. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 66(6):e162–e165
Wechselberger G, Hussl H et al (2009) Restoration of elbow flexion after brachial plexus injury by free functional rectus femoris muscle transfer. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 62(2):e1–e5
Won SY, Rha DW et al (2012) Intramuscular nerve distribution pattern of the adductor longus and gracilis muscles demonstrated with Sihler staining: guidance for botulinum toxin injection. Muscle Nerve 46(1):80–85
Wong MT, Lim AY et al (2007) Functional units within the latissimus dorsi muscle based on Sihler technique. Ann Plast Surg 59(2):152–155
Wu BL, Sanders I (1992) A technique for demonstrating the nerve supply of whole larynges. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 118(8):822–827
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by the General Financial Grant from the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2014M562659).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare no conflict of interest to disclose.
Authors’ contribution
H Jiang and X. Cao do the work of study design and funds collection; D. Yu and H. Yin contribute to data collection, manuscript preparation, and literature search. T. Han performs statistical analysis and data interpretation.
Additional information
D. Yu and H. Yin contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, D., Yin, H., Han, T. et al. Intramuscular innervations of lower leg skeletal muscles: applications in their clinical use in functional muscular transfer. Surg Radiol Anat 38, 675–685 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-015-1601-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-015-1601-x