Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the current evidence for the effectiveness of transarterial embolization (TAE) in treatment of symptomatic hepatic hemangiomas.
Materials and Methods
A systematic literature review was conducted in PubMed, CINAHL and Scopus databases to identify studies of hepatic hemangiomas treated with transarterial embolization. Main outcome was defined as the mean difference between pre- and post-TAE hemangioma diameters. Treatment agents were categorized as Lipiodol based [bleomycin (L + BE), pingyangmycin (L + PYG) or ethanol (L + ethanol)] and non-Lipiodol based (polyvinyl-alcohol-only). Conventional random-effect meta-analysis technique was applied to analyze data.
Results
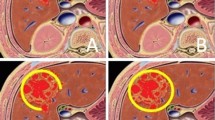
Of 3080 initially inspected publications, 21 studies were included in the meta-analysis comprising of 1450 patients with total of 1871 hemangiomas (36.2% male, mean age: 46.3 ± 3.6 years). One hundred and twenty-six, 1666, 41 and 38 lesions were treated with L + BE, L + PYG, L + ethanol and PVA, respectively. Median follow-up time after embolization was 12 months. Lipiodol-based treatments showed significant effect in reducing hemangioma size after TAE compared to PVA (P < 0.001). Pooled diameter reduction (cm) (95% confidence interval) was − 4.37( − 5.32, − 3.42), − 4.70( − 5.70, − 3.71), − 0.93( − 2.02, 0.16) for overall TAE treatment, Lipiodol-based and non-Lipiodol-based treatments, respectively. Main complications included post-embolization syndrome and transient liver enzyme elevation (pooled incidence for Lipiodol-based and non-Lipiodol-based techniques: 36% and 33%; and 37% and 0, respectively). No fatal complications were reported. Symptomatic improvement was reported in 63.3%–100% of the cases with majority of studies (15/21) reporting improvement in all cases (pooled response rate: 98%).
Conclusions
Transarterial embolization with bleomycin, pingyangmycin or ethanol in combination with Lipiodol is safe and associated with reduced size of hemangiomas resulting in symptoms alleviation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhlaghpoor S, Torkian P, Golzarian J. Transarterial bleomycin–lipiodol embolization (b/le) for symptomatic giant hepatic hemangioma. CardioVasc Interv Radiol. 2018;41(11):1674–82.
Bennett JM, Reich SD. Drugs five years later: bleomycin. Ann Intern Med. 1979;90(6):945–8.
Blackburn H, West S. Management of postembolization syndrome following hepatic transarterial chemoembolization for primary or metastatic liver cancer. Cancer Nurs. 2016;39(5):E1–8.
Bozkaya H, Cinar C, Besir FH, Parildar M, Oran I. Minimally invasive treatment of giant haemangiomas of the liver: embolisation with bleomycin. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2014;37(1):101–7.
Bozkaya H, Cinar C, Ünalp ÖV, Parildar M, Oran I. Unusual treatment of Kasabach-Merritt syndrome secondary to hepatic hemangioma: embolization with bleomycin. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2015;127(11–12):488–90.
Duxbury MS, Garden OJ. Giant haemangioma of the liver: observation or resection? Digestive surgery. 2010;27(1):7–11.
Fan SL, Tong XQ, Wang J, Song L. Transarterial embolization for treatment of giant hepatic hemangiomas: an analysis of 46 cases. World Chin J Dig. 2013;21(20):1925–30.
Filippiadis DK, Binkert C, Pellerin O, Hoffmann RT, Krajina A, Pereira PL. Cirse quality assurance document and standards for classification of complications: the cirse classification system. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2017;40(8):1141–6.
Firouznia K, Ghanaati H, Alavian SM, et al. Management of liver hemangioma using trans-catheter arterial embolization. Hepat. Mon. 2014;14(2):e25788.
Gao J, Ding X, Ke S, et al. Radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of large hepatic hemangiomas: a comparison of multitined and internally cooled electrodes. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2014;48(6):540–7.
Gao J, Ke S, Ding X-m, Zhou Y-m, Qian X-j, Sun W-b. Radiofrequency ablation for large hepatic hemangiomas: initial experience and lessons. Surgery. 2013;153(1):78–85.
Giavroglou C, Economou H, Ioannidis I. Arterial embolization of giant hepatic hemangiomas. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2003;26(1):92–6.
Hanks B, Suhocki P, DeLong D, et al. The efficacy and tolerability of transarterial chemo-embolization (TACE) compared with transarterial embolization (TAE) for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(15_suppl):4595.
He Y, Lan Y, Liu Y, et al. Pingyangmycin and bleomycin share the same cytotoxicity pathway. Molecules. 2016;21(7):862.
Higgins J, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The cochrane collaboration. 2011.
Ho H-Y, Wu T-H, Yu M-C, Lee W-C, Chao T-C, Chen M-F. Surgical management of giant hepatic hemangiomas: complications and review of the literature. Chang Gung Med J. 2012;35(1):70–8.
Huang Y-D, Li P, Tong X, et al. Effects of bleomycin A5 on caspase-3, P53, bcl-2 expression and telomerase activity in vascular endothelial cells. Indian J Pharmacol. 2015;47(1):55.
Jiang XY, Xu K. The middle-long term effect of TAE with pingyangmycin-lipiodol emulsion for hepatic hemangioma. J Intervent Radiol. 2012;21(1):31–4.
Jin H. A preliminary approach to pathological and biochemical changes of the lungs injured by domestic pingyangmycinum. Zhonghua bing li xue za zhi = Chinese J Pathol. 1992;21(5):278–80.
Kirnap M, Boyvat F, Boyacioglu S, Hilmioglu F, Moray G, Haberal M. The effect of bleomycin embolization on symptomatic improvement and hemangioma size among patients with giant liver hemangiomas. Intl J Surg. 2018;12:12–6.
Lerner SM, Hiatt JR, Salamandra J, et al. Giant cavernous liver hemangiomas: effect of operative approach on outcome. Arch Surg. 2004;139(8):818–23.
Li HW, Chen DJ, He MJ, Lian H, Wang GY. Transcatheter arterial embolization and regional injection to treat the cavernous hemangioma of liver. Chin J Intervent Imaging Ther. 2007;4(3):192–5.
Li Y, Jia Y, Li S, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization of giant liver haemangioma: a multi-center study with 836 cases. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015;73(2):469–72.
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS medicine. 2009;6(7):e1000100.
Luo Q, Zhao F. How to use bleomycin A5 for infantile maxillofacial haemangiomas: clinical evaluation of 82 consecutive cases. J Cranio-Maxillofac Surg. 2011;39(7):482–6.
Malagari K, Alexopoulou E, Dourakis S, et al. Transarterial embolization of giant liver hemangiomas associated with Kasabach-Merritt syndrome: a case report. Acta Radiol. 2007;48(6):608–12.
Millis JM. Molina DC What is the best surgical method of addressing hepatic hemangiomas? difficult decisions in hepatobiliary and pancreatic surgery. Cham: Springer; 2016. p. 25–37.
Park SY, Tak WY, Jung MK, et al. Symptomatic-enlarging hepatic hemangiomas are effectively treated by percutaneous ultrasonography-guided radiofrequency ablation. J Hepatol. 2011;54(3):559–65.
Phan SH, Kunkel SL. Lung cytokine production in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Exp Lung Res. 1992;18(1):29–43.
Season W, Wang W, Chen J, Wang G, Pay L, Wu J. Pingyangmycin iodized oil emulsion plus gelatin sponge particles embolization of hepatic hemangioma study of the efficacy of treatment intervention. Med J Chin Peoples Liberation Army. 2015;40(6):513–4.
Shin SW. The current practice of transarterial chemoembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Radiol. 2009;10(5):425–34.
Singh RK, Kapoor S, Sahni P, Chattopadhyay TK. Giant haemangioma of the liver: is enucleation better than resection? Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2007;89(5):490–3.
Srivastava D, Gandhi D, Seith A, Pande G, Sahni P. Transcatheter arterial embolization in the treatment of symptomatic cavernous hemangiomas of the liver: a prospective study. Abdom Imaging. 2001;26(5):510–4.
Srivastava DN, Gandhi D, Seith A, Pande GK, Sahni P. Transcatheter arterial embolization in the treatment of symptomatic cavernous hemangiomas of the liver: A prospective study. Abdom Imaging. 2001;26(5):510–4.
Suh JS, Shin KH, Na JB, Won JY, Hahn SB. Venous malformations: sclerotherapy with a mixture of ethanol and lipiodol. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1997;20(4):268–73.
Sullivan GM. Irb 101. J Grad Med Educ. 2011;3(1):5–6.
Sun JH, Nie CH, Zhang YL, et al. Transcatheter arterial embolization alone for giant hepatic hemangioma. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(8):e0135158.
Szejnfeld D, Nunes TF, Fornazari VAV, et al. Transcatheter arterial embolization for unresectable symptomatic giant hepatic hemangiomas: single-center experience using a lipiodol-ethanol mixture. Radiol Bras. 2015;48(3):154–7.
Tian JL, Du YH, Luo J, Li CL, Zhang LY. Changes of liver function and lesion size after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization of hepatic hemangiomas. Chin J Intervent Imaging Ther. 2010;7(3):273–7.
Toro A, Mahfouz A-E, Ardiri A, et al. What is changing in indications and treatment of hepatic hemangiomas. Ann Hepatol. 2014;13(4):327–39.
Vaidya S, Tozer KR, Chen J. An overview of embolic agents. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2008;25(3):204–15.
Wahab MA, El Nakeeb A, Ali MA, et al. Surgical management of giant hepatic hemangioma: single center’s experience with 144 patients. J Gastrointest Surg. 2018;22(5):849–58.
Wang BT, Liu ZY, Zhang JM. Interventional embolotherapy in treatment of liver hemangioma. Chin J Med Imaging Technol. 2014;30(4):549–51.
Wang JB, An X, Wang H, et al. Transcatheter arterial embolization with the mixture of ethanol and lipiodol for the treatment of hepatic cavernous hemangiomas. J Intervent Radiol. 2010;19(5):358–60.
Wang S, Gao J, Yang M, et al. Intratumoral coagulation by radiofrequency ablation facilitated the laparoscopic resection of giant hepatic hemangioma: a surgical technique report of two cases. Oncotarget. 2017;8(31):52006.
Yamamoto T, Kawarada Y, Yano T, Noguchi T, Mizumoto R. Spontaneous rupture of hemangioma of the liver: treatment with transcatheter hepatic arterial embolization. Am J Gastroenterol. 1991;86(11):1645–9.
Yue H, Qian J, Elner VM, et al. Treatment of orbital vascular malformations with intralesional injection of pingyangmycin. Br J Ophthalmol. 2013;97(6):739–45.
Zeng Q, Li Y, Chen Y, Ouyang Y, He X, Zhang H. Gigantic cavernous hemangioma of the liver treated by intra-arterial embolization with pingyangmycin-lipiodol emulsion: a multi-center study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2004;27(5):481–5.
Zhang AZ, Cui Y, Yang CM. Observation of superselectively hepatic artery embolization treatment with pingyangmycin lipiodol emulsion for patients with liver cavernous hemangioma. Chin J Cancer Prev Treat. 2009;16(17):1349–50.
Zhang H, Zhao XJ. Mid-long term clinical effects of the 110 °C pingyangmycin-lipiodol chemoembolization for the treatment of liver hemangiomas. Chin J Intervent Imaging Ther. 2015;12(1):34–8.
Zhang W, Chen G, Ren JG, Zhao YF. Bleomycin induces endothelial mesenchymal transition through activation of mTOR pathway: a possible mechanism contributing to the sclerotherapy of venous malformations. Br J Pharmacol. 2013;170(6):1210–20.
Zhang X, Xiong B, Yao Q, Zheng CS. Transcatheter arterial sclerotic embolization for the treatment of giant hepatic cavernous hemangioma: Analysis of the effectiveness and the safety. J Intervent Radiol. 2015;24(11):992–5.
Zhang X, Yan L, Li B, et al. Comparison of laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation versus open resection in the treatment of symptomatic-enlarging hepatic hemangiomas: a prospective study. Surg Endosc. 2016;30(2):756–63.
Zheng JW, Yang XJ, Wang YA, He Y, Ye WM, Zhang ZY. Intralesional injection of Pingyangmycin for vascular malformations in oral and maxillofacial regions: an evaluation of 297 consecutive patients. Oral Oncol. 2009;45(10):872–6.
Zhu K, Cao JM. Transcatheter selective hepatic arteriography combined with embolization therapy for the treatment of hepatic hemangiomas. J Intervent Radiol. 2010;19(12):985–7.
Acknowledgement
We appreciate Dr. Mehdi Yaseri’s assistance with meta-analysis.
Funding
This study was not supported by any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, consent for publication is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torkian, P., Li, J., Kaufman, J.A. et al. Effectiveness of Transarterial Embolization in Treatment of Symptomatic Hepatic Hemangiomas: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 44, 80–91 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-020-02611-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-020-02611-5