Abstract
Purpose
We aimed to validate the performance of the hepatitis B-based Hong Kong Liver Cancer (HKLC) staging system compared with the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging system in Chinese hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients treated with conventional transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) as the initial treatment.
Materials and Methods
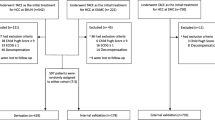
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Boards at all participating centers. This retrospective study included 715 patients with HCC who underwent TACE as the initial treatment between January 2008 and December 2016 at three Chinese institutions. All of the patients calculated HCC stage using 5-substage HKLC (HKLC-5), 9-substage HKLC (HKLC-9), and the BCLC system. Based on overall survival (OS), these three staging systems’ performance on treatment outcome prediction were compared using C statistic, Akaike information criterion (AIC), area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), linear trend Chi-square, likelihood ratio Chi-square, and calibration plots, respectively.
Results
The median OS was 10.1 months. Compared with the BCLC system, the HKLC system, especially HKLC-9, showed better performance on survival prediction (HKLC-9: C = 0.689, AIC = 6646.162; HKLC-5: C = 0.683, AIC = 6662.663; BCLC: C = 0.680, AIC = 6654.146), homogeneity (likelihood ratio Chi-square: HKLC-9 = 232.38, HKLC-5 = 215.87, and BCLC = 224.39, P < 0.001), and calibration (R2: HKLC-9 = 0.923, HKLC-5 = 0.916, and BCLC = 0.914). HKLC-9 outperformed on AUC at 6-, 12-, and 24-month survival prediction than HKLC-5 and BCLC. BCLC showed better performance on monotonicity (linear trend Chi-square: HKLC-9 = 121.641, HKLC-5 = 117.389, and BCLC = 125.752; P < 0.001).
Conclusions
Combining survival prediction, discrimination, and calibration, the HKLC, especially HKLC-9 system, performed better for Chinese patients treated with TACE than the BCLC system.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21262.
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(2):115–32. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21338.
Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30010-2.
Yang JD, Kim WR, Park KW, Chaiteerakij R, Kim B, Sanderson SO, et al. Model to estimate survival in ambulatory patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2012;56(2):614–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.25680.
Vauthey JN, Klimstra D, Blumgart LH. A simplified staging system for hepatocellular carcinomas. Gastroenterology. 1995;108(2):617–8.
Llovet JM, Bru C, Bruix J. Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: the BCLC staging classification. Semin Liver Dis. 1999;19(3):329–38. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-1007122.
Leung TW, Tang AM, Zee B, Lau WY, Lai PB, Leung KL, et al. Construction of the Chinese University Prognostic Index for hepatocellular carcinoma and comparison with the TNM staging system, the Okuda staging system, and the Cancer of the Liver Italian Program staging system: a study based on 926 patients. Cancer. 2002;94(6):1760–9.
Kudo M, Chung H, Osaki Y. Prognostic staging system for hepatocellular carcinoma (CLIP score): its value and limitations, and a proposal for a new staging system, the Japan Integrated Staging Score (JIS score). J Gastroenterol. 2003;38(3):207–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s005350300038.
European Association for the study of the L, European Organisation for R, Treatment of C. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012;56(4):908–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2011.12.001.
Bruix J, Sherman M, American Association for the study of liver D. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology. 2011;53(3):1020–2. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.24199.
Zhong JH, Ke Y, Gong WF, Xiang BD, Ma L, Ye XP, et al. Hepatic resection associated with good survival for selected patients with intermediate and advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. 2014;260(2):329–40. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000000236.
Daniele B, Annunziata M, Barletta E, Tinessa V, Di Maio M. Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) score for staging hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res Off J Jpn Soc Hepatol. 2007;37(Suppl 2):S206–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1872-034X.2007.00186.x.
Bolondi L, Burroughs A, Dufour JF, Galle PR, Mazzaferro V, Piscaglia F, et al. Heterogeneity of patients with intermediate (BCLC B) hepatocellular carcinoma: proposal for a subclassification to facilitate treatment decisions. Semin Liver Dis. 2012;32(4):348–59. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0032-1329906.
Yau T, Tang VY, Yao TJ, Fan ST, Lo CM, Poon RT. Development of Hong Kong Liver Cancer staging system with treatment stratification for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2014;146(7):1691–700. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2014.02.032.
Park JW, Chen M, Colombo M, Roberts LR, Schwartz M, Chen PJ, et al. Global patterns of hepatocellular carcinoma management from diagnosis to death: the BRIDGE Study. Liver Int Off J Int Assoc Study Liver. 2015;35(9):2155–66. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.12818.
Bruix J, Sherman M, Llovet JM, Beaugrand M, Lencioni R, Burroughs AK, et al. Clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Conclusions of the Barcelona-2000 EASL conference. European Association for the Study of the Liver. J Hepatol. 2001;35(3):421–30.
Zhong BY, Ni CF, Chen L, Zhu HD, Teng GJ. Early sorafenib-related biomarkers for combination treatment with transarterial chemoembolization and sorafenib in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology. 2017;284(2):583–92. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2017161975.
Marelli L, Stigliano R, Triantos C, Senzolo M, Cholongitas E, Davies N, et al. Transarterial therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: which technique is more effective? A systematic review of cohort and randomized studies. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2007;30(1):6–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-006-0062-3.
Terzi E, Golfieri R, Piscaglia F, Galassi M, Dazzi A, Leoni S, et al. Response rate and clinical outcome of HCC after first and repeated cTACE performed “on demand”. J Hepatol. 2012;57(6):1258–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2012.07.025.
Ueno S, Tanabe G, Sako K, Hiwaki T, Hokotate H, Fukukura Y, et al. Discrimination value of the new western prognostic system (CLIP score) for hepatocellular carcinoma in 662 Japanese patients. Cancer of the Liver Italian Program. Hepatology. 2001;34(3):529–34. https://doi.org/10.1053/jhep.2001.27219.
Memon K, Kulik LM, Lewandowski RJ, Wang E, Wang J, Ryu RK, et al. Comparative study of staging systems for hepatocellular carcinoma in 428 patients treated with radioembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol JVIR. 2014;25(7):1056–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2014.01.010.
Harrell FE Jr., Lee KL, Mark DB. Multivariable prognostic models: issues in developing models, evaluating assumptions and adequacy, and measuring and reducing errors. Stat Med. 1996;15(4):361–87. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0258(19960229)15:4<361::AID-SIM168>3.0.CO;2-4.
Steyerberg EW, Vickers AJ, Cook NR, Gerds T, Gonen M, Obuchowski N, et al. Assessing the performance of prediction models: a framework for traditional and novel measures. Epidemiology. 2010;21(1):128–38. https://doi.org/10.1097/EDE.0b013e3181c30fb2.
Adhoute X, Penaranda G, Bronowicki JP, Raoul JL. Usefulness of the HKLC vs. the BCLC staging system in a European HCC cohort. J Hepatol. 2015;62(2):492–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2014.08.035.
Sohn JH, Duran R, Zhao Y, Fleckenstein F, Chapiro J, Sahu S, et al. Validation of the Hong Kong Liver Cancer staging system in determining prognosis of the North American patients following intra-arterial therapy. Clinical Gastroenterol Hepatol Off Clin Pract J Am Gastroenterol Assoc. 2017;15(5):746–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2016.10.036.
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. New Engl J Med. 2008;359(4):378–90. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0708857.
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(1):25–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70285-7.
Yoo DJ, Kim KM, Jin YJ, Shim JH, Ko GY, Yoon HK, et al. Clinical outcome of 251 patients with extrahepatic metastasis at initial diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: Does transarterial chemoembolization improve survival in these patients? J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;26(1):145–54. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06341.x.
Pinter M, Hucke F, Graziadei I, Vogel W, Maieron A, Konigsberg R, et al. Advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: transarterial chemoembolization versus sorafenib. Radiology. 2012;263(2):590–9. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.12111550.
Luo J, Guo RP, Lai EC, Zhang YJ, Lau WY, Chen MS, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: a prospective comparative study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18(2):413–20. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-010-1321-8.
Lee YS, Seo YS, Kim JH, Lee J, Kim HR, Yoo YJ, et al. Can more aggressive treatment improve prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma? A direct comparison of the Hong Kong Liver Cancer and Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer algorithms. Gut Liver. 2017. https://doi.org/10.5009/gnl17040.
Wallace MC, Huang Y, Preen DB, Garas G, Adams LA, MacQuillan G, et al. HKLC triages more hepatocellular carcinoma patients to curative therapies compared to bclc and is associated with better survival. Dig Dis Sci. 2017;62(8):2182–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-017-4622-y.
Chapiro J, Geschwind JF. Hepatocellular carcinoma: have we finally found the ultimate staging system for HCC? Nature Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;11(6):334–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2014.67.
Min YW, Kim J, Kim S, Sung YK, Lee JH, Gwak GY, et al. Risk factors and a predictive model for acute hepatic failure after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int Off J Int Assoc Study Liver. 2013;33(2):197–202. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.12023.
Choi TW, Kim HC, Lee JH, Yu SJ, Kang B, Hur S, et al. The safety and clinical outcomes of chemoembolization in Child–Pugh class C patients with hepatocellular carcinomas. Korean J Radiol. 2015;16(6):1283–93. https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.6.1283.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program #2013CB733800, 2013733803), the National Scientific and Technical Achievement Translation Foundation ([2012]258), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81441054, 81671796, 81501522), the Jiangsu Provincial Special Program of Medical Science (BL2013029), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, and the Scientific Research Innovation Program for College and University Graduates of Jiangsu Province (KYZZ16_0133). Funding sources had no involvement in the financial support for the conduct of the research and preparation of the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Our study was approved by the Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) at three participating centers. The requirement to obtain informed consent was waived due to the retrospective nature.
Informed Consent
The requirement to obtain informed consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, BY., Ni, CF., Yin, GW. et al. Multicentric Assessment of the Hong Kong Liver Cancer Staging System in Chinese Patients Following Transarterial Chemoembolization. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 41, 1867–1876 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-018-2023-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-018-2023-z