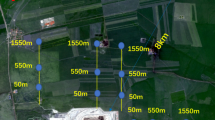
Abstract
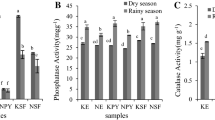
Mining areas are suffering from serious environmental hazards, such as soil erosion, water pollution as well as land degradation. In this study, two types of mining areas in Anhui Province, China—one a copper mining area and the other a coal mining area—were selected to compare the soil properties under different vegetation restoration conditions, which can be generally classified into reclaimed and non-reclaimed areas. Soil catalase and urease activities and soil chemical properties were chosen to be the main indicators of soil quality. Principal component analysis was used to evaluate the overall soil fertility in the copper and coal mining areas. Results showed that in the copper mining area soil catalase activity was between 12.36 and 19.17 μg g−1 h−1 and urease activity was between 0.03 and 12.05 μg g−1 h−1. And in coal mining area, soil catalase activity was between 3.52 and 9.72 μg g−1 h−1 and urease activity was between 2.71 and 10.81 μg g−1 h−1. Moreover, soil catalase and urease activities in degraded areas were lower than those in reclaimed areas. Soil catalase activity and soil urease activity were significantly correlated with total potassium and total nitrogen, respectively. Soil quality in land types with vegetation restoration was higher than in non-reclaimed areas and old subsidence areas, while soil quality in the copper mining area was generally higher than in the coal mining area. Thus, the optimum measure in this region to ameliorate these degraded soils is vegetation restoration, which helps not only to improve the environment, but also to enhance soil quality in these degraded lands.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Afonso TF, Demarco CF, Pieniz SC, Flávio AO, Quadro MS, Andreazza R (2019) Potential of Solanum viarum Dunal in use for phytoremediation of heavy metals to mining areas, southern Brazil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:24132–24142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05460-z
Ahirwal J, Pandey VC (2020) Restoration of mine degraded land for sustainable environmental development. Restor Ecol https://doi.org/10.1111/rec.13268
Angelovičová L, Lodenius M, Tulisalo E, Fazekašová D (2014) Effect of heavy metals on soil enzyme activity at different field conditions in Middle Spis mining area (Slovakia). Bull Environ Contamination Toxicol 93:670–675. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-014-1397-0
Banerjee S, Bora S, Thrall PH, Richardson AE (2016) Soil C and N as causal factors of spatial variation in extracellular enzyme activity across grassland-woodland ecotones. Appl Soil Ecol 105:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2016.04.002
Boisson S, Le Stradic S, Collignon J, Séleck M, Malaisse F, Ngoy Shutcha M, Faucon MP, Mahy G (2016) Potential of copper-tolerant grasses to implement phytostabilisation strategies on polluted soils in South D. R. Congo. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:13693–13705. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5442-2
Cao Y, Ma C, Chen H, Chen G, White JC, Xing B (2020) Copper stress in flooded soil: Impact on enzyme activities, microbial community composition and diversity in the rhizosphere of Salix integra. Sci Total Environ 704:135350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135350
Chen WY, Lin CJ, Ju YR, Tsai JW, Liao CM (2012) Assessing the effects of pulsed waterborne copper toxicity on life-stage tilapia populations. Sci Total Environ 417-418:129–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.12.043
Das PK, Das BP, Dash P (2020) Chromite mining pollution, environmental impact, toxicity and phytoremediation: a review. Environ Chem Lett https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01102-w
Davatgar N, Neishabouri MR, Sepaskhah AR (2012) Delineation of site specific nutrient management zones for a paddy cultivated area based on soil fertility using fuzzy clustering. Geoderma 173-174:111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2011.12.005
Delelegn YT, Purahong W, Blazevic A, Yitaferu B, Wubet T, Göransson H, Godbold DL (2017) Changes in land use alter soil quality and aggregate stability in the highlands of northern Ethiopia. Sci Rep. 7:13602
Eisenberg DA, Yu M, Lam CW, Ogunseitan OA, Schoenung JM (2013) Comparative alternative materials assessment to screen toxicity hazards in the life cycle of CIGS thin film photovoltaics. J Hazard Mater 260:534–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.06.007
Feng H, Zhou J, Zhou A, Bai G, Li Z, Chen H, Su D, Han X (2021) Grassland ecological restoration based on the relationship between vegetation and its below-ground habitat analysis in steppe coal mine area. Sci Total Environ 778:146221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146221
Finkenbein P, Kretschmer K, Kuka K, Klotz S, Heilmeier H (2013) Soil enzyme activities as bioindicators for substrate quality in revegetation of a subtropical coal mining dump. Soil Biol Biochem 56:87–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.02.012
Fu SS, Li PJ, Feng Q, Li XJ, Li P, Sun YB, Chen Y (2011) Soil quality degradation in a magnesite mining area. Pedosphere 21:98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(10)60084-7
Gadi BR, Kumar R, Goswami B, Rankawat R, Rao SR (2020) Recent developments in understanding fluoride accumulation, toxicity, and tolerance mechanisms in plants: an overview. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00354-3
García C, Hernández T (1997) Biological and biochemical indicators in derelict soils subject to erosion. Soil Biol Biochem 29:171–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(96)00294-5
Giacometti C, Demyan MS, Cavani L, Marzadori C, Ciavatta C, Kandeler E (2013) Chemical and microbiological soil quality indicators and their potential to differentiate fertilization regimes in temperate agroecosystems. Appl Soil Ecol 64:32–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2012.10.002
Gomes CJB, Mendes CAB, Costa JFCL (2011) The environmental impact of coal mining: a case study in Brazil’s Sangão watershed. Mine Water Environ 30:159–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-011-0139-3
Guan B, Xie B, Yang S, Hou A, Chen M, Han G (2019) Effects of five years’ nitrogen deposition on soil properties and plant growth in a salinized reed wetland of the Yellow River Delta. Ecol Eng 136:160–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2019.06.016
Guo P, Zhu L, Wang J, Wang J, Xie H, Lv D (2015) Enzymatic activities and microbial biomass in black soil as affected by azoxystrobin. Environ Earth Sci 74:1353–1361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4126-z
Hossain MN, Paul SK, Hasan MM (2015) Environmental impacts of coal mine and thermal power plant to the surroundings of Barapukuria, Dinajpur, Bangladesh. Environ Monit Assess 187:202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4435-4
Huang L, Gao X, Liu M, Du G, Guo J, Ntakirutimana T (2012) Correlation among soil microorganisms, soil enzyme activities, and removal rates of pollutants in three constructed wetlands purifying micro-polluted river water. Ecol Eng 46:98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2012.06.004
Jia X, Zhong Y, Liu J, Zhu G, Shangguan Z, Yan W (2020) Effects of nitrogen enrichment on soil microbial characteristics: From biomass to enzyme activities. Geoderma 366:114256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114256
Lerner CA, Sundar IK, Watson RM, Elder A, Jones R, Done D, Kurtzman R, Ossip DJ, Robinson R, McIntosh S, Rahman I (2015) Environmental health hazards of e-cigarettes and their components: oxidants and copper in e-cigarette aerosols. Environ Pollut 198:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.12.033
Liu G, Wang J, Zhang E, Hou J, Liu X (2016) Heavy metal speciation and risk assessment in dry land and paddy soils near mining areas at Southern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:8709–8720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6114-6
Liu L, Wang X, Wen Q, Jia Q, Liu Q (2017) Interspecific associations of plant populations in rare earth mining wasteland in southern China. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 118:82–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2017.01.011
Liu YN, Xiao XY, Guo ZH (2019) Identification of indicators of giant reed (Arundo donax L.) ecotypes for phytoremediation of metal-contaminated soil in a non-ferrous mining and smelting area in southern China. Ecol Indic 101:249–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.01.029
Liu ZP, Shao MA, Wang YQ (2013) Spatial patterns of soil total nitrogen and soil total phosphorus across the entire Loess Plateau region of China. Geoderma 197-198:67–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2012.12.011
Ma YH, Fu SL, Zhang XP, Zhao K, Chen HYH (2017) Intercropping improves soil nutrient availability, soil enzyme activity and tea quantity and quality. Appl Soil Ecol 119:171–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2017.06.028
Mahar A, Wang P, Ali A, Awasthi MK, Lahori AH, Wang Q, Li R, Zhang Z (2016) Challenges and opportunities in the phytoremediation of heavy metals contaminated soils: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 126:111–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.12.023
Maiti D, Pandey VC (2021) Metal remediation potential of naturally occurring plants growing on barren fly ash dumps. Environ Geochem Health 43:1415–1426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00679-z
Mkhinini M, Boughattas I, Alphonse V, Livet A, Gıustı-Mıller S, Bannı M, Bousserrhıne N (2020) Heavy metal accumulation and changes in soil enzymes activities and bacterial functional diversity under long-term treated wastewater irrigation in East Central region of Tunisia (Monastir governorate). Agric Water Manag 235:106150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106150
Pan P, Lei M, Qiao P, Zhou G, Wan X, Chen T (2019) Potential of indigenous plant species for phytoremediation of metal(loid)-contaminated soil in the Baoshan mining area, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:23583–23592. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05655-4
Pan Y, Li H (2016) Investigating heavy metal pollution in mining brownfield and its policy implications: a case study of the bayan obo rare earth mine, Inner Mongolia, China. Environ Manag 57:879–893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-016-0658-6
Pandey VC, Bajpai O (2019) Phytoremediation: from theory toward practice. phytomanagement of polluted sites - market opportunities in sustainable phytoremediation. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813912-7.00001-6
Pandey VC, Bauddh K (2018) Phytomanagement of polluted sites - market opportunities in sustainable phytoremediation. https://doi.org/10.1016/C2017-0-00586-4
Pandey V, Patel A, Patra DD (2016) Biochar ameliorates crop productivity, soil fertility, essential oil yield and aroma profiling in basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). Ecol Eng 90:361–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.01.020
Pathak S, Agarwal AV, Pandey VC (2020) Phytoremediation—a holistic approach for remediation of heavy metals and metalloids. Bioremed Pollut 3–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819025-8.00001-6
Ren H, Xu Z, Huang J, Lü X, Zeng DH, Yuan Z, Han X, Fang Y (2015) Increased precipitation induces a positive plant-soil feedback in a semi-arid grassland. Plant Soil 389:211–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2349-5
Roba C, Roşu C, Piştea I, Ozunu A, Baciu C (2016) Heavy metal content in vegetables and fruits cultivated in Baia Mare mining area (Romania) and health risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:6062–6073. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4799-6
Shen F, Wu J, Fan H, Liu W, Guo X, Duan H, Hu L, Lei X, Wei X (2019) Soil N/P and C/P ratio regulate the responses of soil microbial community composition and enzyme activities in a long-term nitrogen loaded Chinese fir forest. Plant Soil 436:91–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-03912-y
Smal H, Ligęza S, Pranagal J, Urban D, Pietruczyk-Popławska D (2019) Changes in the stocks of soil organic carbon, total nitrogen and phosphorus following afforestation of post-arable soils: a chronosequence study. For Ecol Manag 451:117536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2019.117536
Soares JR, Cantarella H, Menegale MLDC (2012) Ammonia volatilization losses from surface-applied urea with urease and nitrification inhibitors. Soil Biol Biochem 52:82–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.04.019
Sun SY, Sun H, Zhang DS, Zhang JF, Cai ZY, Qin GH, Song YM (2019) Response of soil microbes to vegetation restoration in coal mining subsidence areas at huaibei coal mine, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16:1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16101757
Tie L, Zhang S, Penuelas J, Sardans J, Zhou S, Hu J, Huang C (2020) Responses of soil C, N, and P stoichiometric ratios to N and S additions in a subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest. Geoderma 379:114633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114633
Touceda-González M, Álvarez-López V, Prieto-Fernández Á, Rodríguez-Garrido B, Trasar-Cepeda C, Mench M, Puschenreiter M, Quintela-Sabarís C, Macías-García F, Kidd PS (2017) Aided phytostabilisation reduces metal toxicity, improves soil fertility and enhances microbial activity in Cu-rich mine tailings. J Environ Manag 186:301–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.09.019
UNEP (2019) United Nations Environment Programme. https://www.unenvironment.org/news-and-stories/press-release/new-un-decade-ecosystem-restoration-offers-unparalleled-opportunity
Veum KS, Goyne KW, Kremer RJ, Miles RJ, Sudduth KA (2014) Biological indicators of soil quality and soil organic matter characteristics in an agricultural management continuum. Biogeochemistry 117:81–99
Wang B, Xue S, Liu GB, Zhang GH, Li G, Ren ZP (2012) Changes in soil nutrient and enzyme activities under different vegetations in the Loess Plateau area, Northwest China. CATENA 92:186–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2011.12.004
Wang D, Zhang B, Zhu L, Yang Y, Li M (2018) Soil and vegetation development along a 10-year restoration chronosequence in tailing dams in the Xiaoqinling gold region of Central China. CATENA 167:250–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.05.007
Wang L, Ji B, Hu Y, Liu R, Sun W (2017) A review on in situ phytoremediation of mine tailings. Chemosphere 184:594–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.06.025
Wang Q, Xiao F, He T, Wang S (2013) Responses of labile soil organic carbon and enzyme activity in mineral soils to forest conversion in the subtropics. Ann For Sci 70:579–587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13595-013-0294-8
Wang R, Zhang J, Sun H, Sun S, Qin G, Song Y (2021) Effect of different vegetation on copper accumulation of copper-mine abandoned land in tongling, China. J Environ Manag 286:112227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112227
Yan B, Wang X, Sun Y, Fan B, Shi L, Liu G (2020) Vegetation rehabilitation increases soil enzyme activities in degraded land via carbon supply and nitrogen retention. Eur J Soil Biol 98:103186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2020.103186
Yu H, Si P, Shao W, Qiao X, Yang X, Gao D, Wang Z (2016) Response of enzyme activities and microbial communities to soil amendment with sugar alcohols. MicrobiologyOpen 5:604–615. https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.355
Zhan J, Sun QY (2014) Development of microbial properties and enzyme activities in copper mine wasteland during natural restoration. CATENA 116:86–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2013.12.012
Zhang Q, Li Z, Huang B, Luo N, Long L, Huang M, Zhai X, Zeng G (2016) Effect of land use pattern change from paddy soil to vegetable soil on the adsorption-desorption of cadmium by soil aggregates. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:2734–2743. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7853-0
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the State Forestry Bureau “948” Program of China (2013-4-83), and by people from local firms. We appreciate all the help.
Author contributions
JZ presented the idea for the study and organized the research. HS designed the study. SS, ZL, and GQ carried out the field measurements and analyzed the data. HS and RW contributed to writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, H., Zhang, J., Wang, R. et al. Effects of Vegetation Restoration on Soil Enzyme Activity in Copper and Coal Mining Areas. Environmental Management 68, 366–376 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-021-01509-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-021-01509-3