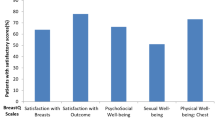
Abstract
Background
Implant-based breast reconstruction (IBBR) can be performed using a variety of biological and synthetic meshes. However, there has yet to be a consensus on the optimal mesh. This study investigates the safety and patient satisfaction of using TiLOOP® Bra in IBBR and compares its postoperative complication risk with that of porcine acellular dermal matrix (ADM) and SERAGYN® BR.
Methods
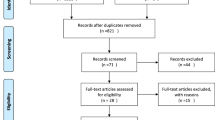
The literature review was performed via PRISMA criteria, 23 studies met the inclusion criteria for the TiLOOP® Bra review, and 5 studies met the inclusion criteria for the meta-analysis. Patient characteristics and per-breast complications were collected. Data were analyzed using Cochrane RevMan and IBM SPSS.
Results
In 3175 breasts of 2685 patients that underwent IBBR using TiLOOP® Bra, rippling was observed as the most common complication, followed by seroma and capsular contracture. No significant difference in the overall complication rate between pre- and sub-pectoral IBBR using TiLOOP® Bra. However, the meta-analysis showed that the TiLOOP® Bra group had significantly lower odds of implant loss, seroma, wound dehiscence, and the need for reoperation or hospitalization than the ADM group. Additionally, the TiLOOP® Bra group had a significantly lower seroma rate compared to the SERAGYN® BR group, while the other outcome indicators were similar between the two groups.
Conclusion
TiLOOP® Bra has become increasingly popular in IBBR in recent years. This review and meta-analysis support the favorable safety profile of TiLOOP® Bra reported in the current literature. The meta-analysis revealed that TiLOOP® Bra has better safety than ADM and a comparable risk of complications compared to SERAGYN® BR. However, as most studies had low levels of evidence, further investigations are necessary.
Level of Evidence III
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Ermoshchenkova MV, Zikiryahodjaev AD, Reshetov IV, Svyatoslavov DS, Sinelnikov MY (2021) Psychological and aesthetic outcomes in breast cancer patients. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 9(7):e3679. https://doi.org/10.1097/gox.0000000000003679
Bi S, Liu R, Wu B, Shen Y, Jia K, Sun K, Gu J (2020) Breast implants for mammaplasty: an umbrella review of meta-analyses of multiple complications. Aesthetic Plast Surg 44(6):1988–1996. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01866-0
Abbate O, Rosado N, Sobti N, Vieira BL, Liao EC (2020) Meta-analysis of prepectoral implant-based breast reconstruction: guide to patient selection and current outcomes. Breast Cancer Res Treat 182(3):543–554. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-020-05722-2
Huang NS, Quan CL, Ma LX, Si J, Chen JJ, Yang BL, Huang XY, Liu GY, Shen ZZ, Shao ZM, Wu J (2016) Current status of breast reconstruction in China: an experience of 951 breast reconstructions from a single institute. Gland Surg 5(3):278–286. https://doi.org/10.21037/gs.2016.03.01
Zaborowski AM, Heeney A, Walsh S, Barry M, Kell MR (2023) Immediate breast reconstruction. Br J Surg. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjs/znad064
Vidya R, Iqbal FM (2017) A guide to prepectoral breast reconstruction: a new dimension to implant-based breast reconstruction. Clin Breast Cancer 17(4):266–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clbc.2016.11.009
Liu J, Hou J, Li Z, Wang B, Sun J (2020) Efficacy of acellular dermal matrix in capsular contracture of implant-based breast reconstruction: a single-arm meta-analysis. Aesthetic Plast Surg 44(3):735–742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-019-01603-2
Wilson RL, Kirwan CC, Johnson RK, O’Donoghue JM, Linforth RA, Harvey JR (2023) Breast Reconstruction Outcomes With and without StratticE (BROWSE)- Long-term outcomes of a multi-centre study comparing Strattice TM immediate implant breast reconstruction with submuscular implant reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000010157
Cohen LE, Bogue JT, Jin J, Disa JJ (2021) Explantation in tissue expander and direct-to-implant reconstruction with acellular dermal matrix: how to avoid early reconstructive failures. Plast Reconstr Surg 147(4):579e–586e. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000007702
Guo R, Li L, Su Y, Xiu B, Zhang Q, Wang J, Chi W, Yang B, Zhang Y, Cao A, Shao Z, Wu J (2020) Current practice and barriers of mesh-assisted implant-based breast reconstruction in China: a nationwide cross-sectional survey of 110 hospitals. Eur J Surg Oncol 46(1):65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2019.09.001
Dieterich M, Paepke S, Zwiefel K, Dieterich H, Blohmer J, Faridi A, Klein E, Gerber B, Nestle-Kraemling C (2013) Implant-based breast reconstruction using a titanium-coated polypropylene mesh (TiLOOP Bra): a multicenter study of 231 cases. Plast Reconstr Surg 132(1):8e–19e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e318290f8a0
Nguyen-Sträuli BD, Vorburger D, Frauchiger-Heuer H, Bringolf L, Maggi N, Talimi-Schnabel J, Dedes KJ (2022) Prepectoral implant-based breast reconstruction with TiLOOP® Bra Pocket - a single-centre retrospective study. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 75(1):104–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2021.08.027
Gschwantler-Kaulich D, Schrenk P, Bjelic-Radisic V, Unterrieder K, Leser C, Fink-Retter A, Salama M, Singer C (2016) Mesh versus acellular dermal matrix in immediate implant-based breast reconstruction - A prospective randomized trial. Eur J Surg Oncol 42(5):665–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2016.02.007
Ohlinger R, Nawroth F, Kohlmann T, Alwafai Z, Schueler K, Zygmunt M, Paepke S (2021) Retrospective study of radiotherapy impact on the outcome of material-assisted implant-based subpectoral breast reconstruction. Anticancer Res 41(4):2017–2024. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.14969
Gentile P, Bernini M, Orzalesi L, Sordi S, Meattini I, Lessi F, Kothari A, Calabrese C (2021) Titanium-coated polypropylene mesh as innovative bioactive material in conservatives mastectomies and pre-pectoral breast reconstruction. Bioact Mater 6(12):4640–4653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.05.002
Casella D, Bernini M, Bencini L, Roselli J, Lacaria MT, Martellucci J, Banfi R, Calabrese C, Orzalesi L (2014) TiLoop Bra mesh used for immediate breast reconstruction: comparison of retropectoral and subcutaneous implant placement in a prospective single-institution series. Eur J Plast Surg 37(11):599–604. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-014-1001-1
Woo A, Harless C, Jacobson SR (2017) Revisiting an old place: single-surgeon experience on post-mastectomy subcutaneous implant-based breast reconstruction. Breast J 23(5):545–553. https://doi.org/10.1111/tbj.12790
Casella D, Di Taranto G, Marcasciano M, Sordi S, Kothari A, Kovacs T, Lo Torto F, Cigna E, Calabrese C, Ribuffo D (2019) Evaluation of prepectoral implant placement and complete coverage with TiLoop bra mesh for breast reconstruction: a prospective study on long-term and patient-reported BREAST-Q outcomes. Plast Reconstr Surg 143(1):1e–9e. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000005078
Wang Y, Zhang B, Zhang T, Guan S (2018) Advances in the use of artificial materials in implant-based breast reconstruction for breast cancer. Chin J Pract Surger. https://doi.org/10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2018.11.22
Ostapenko E, Nixdorf L, Devyatko Y, Exner R, Wimmer K, Fitzal F (2023) Prepectoral versus subpectoral implant-based breast reconstruction: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg Oncol 30(1):126–136. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-022-12567-0
Blok YL, Plat VD, van der Hage JA, Krekel NMA, Mureau MAM (2022) Nation-wide validation of a multicenter risk model for implant loss following implant-based breast reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 75(12):4347–4353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2022.08.065
Mahoney B, Walklet E, Bradley E, Thrush S, Skillman J, Whisker L, Barnes N, Holcombe C, Potter S (2020) Experiences of implant loss after immediate implant-based breast reconstruction: qualitative study. BJS Open 4(3):380–390. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs5.50275
Becherer BE, Heeg E, Young-Afat DA, Vrancken Peeters M-JTFD, Rakhorst HA, Mureau MAM (2022) Revision incidence after immediate direct-to-implant versus two-stage implant-based breast reconstruction: results from a nationwide breast implant registry. Plast Reconstruct Surg 151:693–702
Hirsch EM, Seth AK, Kim JYS, Dumanian GA, Mustoe TA, Galiano RD, Fine NA (2014) Analysis of risk factors for complications in expander/implant breast reconstruction by stage of reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 134(5):692e–699e. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000000607
Fischer JP, Wes AM, Tuggle CT 3rd, Serletti JM, Wu LC (2013) Risk analysis of early implant loss after immediate breast reconstruction: a review of 14,585 patients. J Am Coll Surg 217(6):983–990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2013.07.389
Schueler K, Paepke S, Kohlmann T, Alwafai Z, Nawroth F, Zygmunt M, Ohlinger R (2021) Postoperative complications in breast reconstruction with porcine acellular dermis and polypropylene meshes in subpectoral implant placement. In Vivo 35(5):2739–2746. https://doi.org/10.21873/invivo.12558
Lee KT, Mun GH (2016) Updated evidence of acellular dermal matrix use for implant-based breast reconstruction: a meta-analysis. Ann Surg Oncol 23(2):600–610. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-4873-9
Rao D, Xie J, Xia Y, Cao D (2022) Comparison of flap fixation to its bed and conventional wound closure with drainage in preventing seroma formation following mastectomy for breast cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Aesthetic Plast Surg 46(3):1180–1188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-022-02814-w
Jordan SW, Khavanin N, Kim JYS (2016) Seroma in prosthetic breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 137(4):1104–1116. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000481102.24444.72
Eichler C, Schulz C, Thangarajah F, Malter W, Warm M, Brunnert K (2019) A retrospective head-to-head comparison between TiLoop Bra/TiMesh (R) and Seragyn (R) in 320 cases of reconstructive breast surgery. Anticancer Res 39(5):2599–2605. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.13383
Mazari FAK, Wattoo GM, Kazzazi NH, Kolar KM, Olubowale OO, Rogers CE, Azmy IA (2018) The comparison of strattice and surgimend in acellular dermal matrix-assisted, implant-based immediate breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 141(2):283–293. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000004018
Ball JF, Sheena Y, Tarek Saleh DM, Forouhi P, Benyon SL, Irwin MS, Malata CM (2017) A direct comparison of porcine (Strattice™) and bovine (Surgimend™) acellular dermal matrices in implant-based immediate breast reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 70(8):1076–1082. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2017.05.015
Acknowledgment
There is no commercial interest in the subject of study and no source of any financial or material support.
Funding
The authors received no financial support for this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T., Ye, J. & Tian, T. Implant Based Breast Reconstruction Using a Titanium-Coated Polypropylene Mesh (TiLOOP® Bra): A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Aesth Plast Surg 48, 925–935 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03500-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03500-1