Abstract
Background
The association of breast implants and complications after mammaplasty has been extensively researched. The aim of this study is to summarize all available results in meta-analysis investigating the association between implants and the incidence of various complications.
Methods
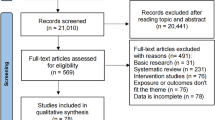
An umbrella review for breast implants and associated complications was performed by searching related reviews from electronic databases including Pubmed, Ovid and CINAHL. We collected and reviewed evidence across meta-analyses of observational and interventional studies of implants and any health outcome. The quality of the reviews was assessed using the AMSTAR tool (A measurement tool to assess systematic reviews).
Results
The research included 92 meta-analyses of 609 studies concerning various areas. Capsular contracture was the most investigated outcome. Radiotherapy, human acellular dermal matrix application, direct-to-implant reconstruction, smooth implant, silicone-filled implant and periareolar incision were significantly associated with higher rates of some of the complications.
Conclusions
This umbrella review provides surgeons with summarized evidence of the association between the complications and implant-related factors in mammaplasty surgery to help surgeons make informed choices in the future.
Level of Evidence III
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albornoz CR, Bach PB, Mehrara BJ, Disa JJ, Pusic AL, McCarthy CM, Cordeiro PG, Matros E (2013) A paradigm shift in U.S. Breast reconstruction: increasing implant rates. Plast Reconstr Surg 131:15–23
Heidekrueger PI, Sinno S, Hidalgo DA, Colombo M, Broer PN (2018) Current trends in breast augmentation: an international analysis. Aesthet Surg J 38:133–148
Kaoutzanis C, Winocour J, Unger J, Gabriel A, Maxwell GP (2019) The evolution of breast implants. Semin Plast Surg 33:217–223
Frey JD, Salibian AA, Karp NS, Choi M (2019) Implant-based breast reconstruction: hot topics, controversies, and new directions. Plast Reconstr Surg 143:404e–416e
Dauplat J, Kwiatkowski F, Rouanet P, Delay E, Clough K, Verhaeghe JL, Raoust I, Houvenaeghel G, Lemasurier P, Thivat E, Pomel C (2017) Quality of life after mastectomy with or without immediate breast reconstruction. Br J Surg 104:1197–1206
Xu F, Sun H, Zhang C, Jiang H, Guan S, Wang X, Wen B, Li J, Li X, Geng C, Yin J (2018) Comparison of surgical complication between immediate implant and autologous breast reconstruction after mastectomy: a multicenter study of 426 cases. J Surg Oncol 118:953–958
Coroneos CJ, Selber JC, Offodile AC 2nd, Butler CE, Clemens MW (2019) US FDA breast implant postapproval studies: long-term outcomes in 99,993 patients. Ann Surg 269:30–36
Panayi AC, Agha RA, Sieber BA, Orgill DP (2018) Impact of obesity on outcomes in breast reconstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Reconstr Microsurg 34:363–375
Aromataris E, Fernandez R, Godfrey CM, Holly C, Khalil H, Tungpunkom P (2015) Summarizing systematic reviews: methodological development, conduct and reporting of an umbrella review approach. Int J Evid Based Healthc 13:132–140
Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, Thuku M, Hamel C, Moran J, Moher D, Tugwell P, Welch V, Kristjansson E, Henry DA (2017) AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ 358:j4008
Lee KT, Mun GH (2017) A meta-analysis of studies comparing outcomes of diverse acellular dermal matrices for implant-based breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg 79:115–123
Lee KT, Mun GH (2016) Updated evidence of acellular dermal matrix use for implant-based breast reconstruction: a meta-analysis. Ann Surg Oncol 23:600–610
Lee K-T, Mun G-H (2015) Prosthetic breast reconstruction in previously irradiated breasts: a meta-analysis. J Surg Oncol 112:468–475
Pu Y, Mao TC, Zhang YM, Wang SL, Fan DL (2018) The role of postmastectomy radiation therapy in patients with immediate prosthetic breast reconstruction: a meta-analysis. Medicine 97:e9548
Lee KT, Mun GH (2017) Optimal sequencing of postmastectomy radiotherapy and two stages of prosthetic reconstruction: a meta-analysis. Ann Surg Oncol 24:1262–1268
Liu X, Zhou L, Pan F, Gao Y, Yuan X, Fan D (2015) Comparison of the postoperative incidence rate of capsular contracture among different breast implants: a cumulative meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 10:e0116071
Wong C-H, Samuel M, Tan B-K, Song C (2006) Capsular contracture in subglandular breast augmentation with textured versus smooth breast implants: a systematic review. Plast Reconstr Surg 118:1224–1236
Li S, Chen L, Liu W, Mu D, Luan J (2018) Capsular contracture rate after breast augmentation with periareolar versus other two (inframammary and transaxillary) incisions: a meta-analysis. [Review]. Aesthet Plast Surg 42:32–37
Lynch JM, Sebai ME, Rodriguez-Unda NA, Seal S, Rosson GD, Manahan MA (2018) Breast pocket irrigation with antibiotic solution at implant insertion: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Aesthet Plast Surg 42:1179–1186
Drinane JJ, Chowdhry T, Pham TH, Ritter E (2017) Examining the role of antimicrobial irrigation and capsular contracture: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Plast Surg 79:107–114
Berbers J, van Baardwijk A, Houben R, Heuts E, Smidt M, Keymeulen K, Bessems M, Tuinder S, Boersma LJ (2014) ‘Reconstruction: before or after postmastectomy radiotherapy?’ A systematic review of the literature. Eur J Cancer (Oxford, England: 1990) 50:2752–2762
Tsoi B, Ziolkowski NI, Thoma A, Campbell K, O’Reilly D, Goeree R (2014) Safety of tissue expander/implant versus autologous abdominal tissue breast reconstruction in postmastectomy breast cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 133:234–249
Lee KT, Mun GH (2016) Comparison of one-stage vs two-stage prosthesis-based breast reconstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Surg 212:336–344
Basta MN, Gerety PA, Serletti JM, Kovach SJ, Fischer JP (2015) A systematic review and head-to-head meta-analysis of outcomes following direct-to-implant versus conventional two-stage implant reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 136:1135–1144
Smith JM, Broyles JM, Guo Y, Tuffaha SH, Mathes D, Sacks JM (2018) Human acellular dermis increases surgical site infection and overall complication profile when compared with submuscular breast reconstruction: an updated meta-analysis incorporating new products(*). J Plast Reconstru Aesthet Surg: JPRAS 71:1547–1556
Ho G, Nguyen TJ, Shahabi A, Hwang BH, Chan LS, Wong AK (2012) A systematic review and meta-analysis of complications associated with acellular dermal matrix-assisted breast reconstruction [Review]. Ann Plast Surg 68:346–356
Hallberg H, Rafnsdottir S, Selvaggi G, Strandell A, Samuelsson O, Stadig I, Svanberg T, Hansson E, Lewin R (2018) Benefits and risks with acellular dermal matrix (ADM) and mesh support in immediate breast reconstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Plast Surg Hand Surg 52:130–147
Wu LH, Zhang MX, Chen CY, Fang QQ, Wang XF, Tan WQ (2018) Breast reconstruction with alloderm ready to use: a meta-analysis of nine observational cohorts. Breast (Edinburgh, Scotland) 39:89–96
Li S, Mu D, Liu C, Xin M, Fu S, Xu B, Li Z, Qi J, Luan J (2019) Complications following subpectoral versus prepectoral breast augmentation: a meta-analysis. Aesthet Plast Surg 43:890–898
Cifuentes I, Dagnino B, Rada GJM (2017) Do textured breast implants decrease the rate of capsular contracture compared to smooth implants? Medwave 17:e7020
Ramos-Gallardo G, Cuenca-Pardo J, Rodríguez-Olivares E, Iribarren-Moreno R, Contreras-Bulnes L, Vallarta-Rodríguez A, Kalixto-Sanchez M, Hernández C, Ceja-Martinez R, Torres-Rivero CJ (2017) Breast implant and anaplastic large cell lymphoma meta-analysis. J Invest Surg 30:56–65
Thompson PA, Prince HM (2013) Breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma: a systematic review of the literature and mini-meta analysis. Curr Hematol Malig Rep 8:196–210
Keech JA Jr (1997) Anaplastic T-cell lymphoma in proximity to a saline-filled breast implant. Plast Reconstr Surg 100:554–555
Leberfinger AN, Behar BJ, Williams NC, Rakszawski KL, Potochny JD, Mackay DR, Ravnic DJ (2017) Breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma: a systematic review. JAMA Surg 152:1161–1168
Loch-Wilkinson A, Beath KJ, Magnusson MR, Cooter R, Shaw K, French J, Vickery K, Prince HM, Deva AKJAsj (2019) Breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma in Australia: a longitudinal study of implant and other related risk factors. Aesthet Surg J 40:838–846
Sheena Y, Smith S, Dua S, Morgan M, Ramakrishnan VJP, Surgery R (2019) Letter to the editor regarding “Current risk estimate of breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma in textured implants”. Plast Reconstr Surg 145:446e
Cardoso M, Wyld L, Rubio I, Leidenius M, Curigliano G, Cutuli B, Marotti L, Biganzoli L (2019) EUSOMA position regarding breast implant associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL) and the use of textured implants. Breast 44:90–93
Rieger UM, Mesina J, Kalbermatten DF, Haug M, Frey HP, Pico R, Frei R, Pierer G, Luscher NJ, Trampuz A (2013) Bacterial biofilms and capsular contracture in patients with breast implants. Br J Surg 100:768–774
Stevens WG, Nahabedian MY, Calobrace MB, Harrington JL, Capizzi PJ, Cohen R, d’Incelli RC, Beckstrand M (2013) Risk factor analysis for capsular contracture: a 5-year Sientra study analysis using round, smooth, and textured implants for breast augmentation. Plast Reconstr Surg 132:1115–1123
Headon H, Kasem A, Mokbel K (2015) Capsular contracture after breast augmentation: an update for clinical practice. Arch Plast Surg 42:532–543
Jeong TK, Han JW, Min KH (2018) Treatment of capsular contracture after breast augmentation with serial fat grafting and implantation. Arch Aesthet Plast Surg 24:68–71
Panettiere P, Marchetti L, Accorsi D (2009) The serial free fat transfer in irradiated prosthetic breast reconstructions. Aesthet Plast Surg 33:695–700
Roca GB, Graf R, da Silva FR, Salles G Jr, Francisco JC, Noronha L, Maluf I Jr (2014) Autologous fat grafting for treatment of breast implant capsular contracture: a study in pigs. Aesthet Surg J 34:769–775
Moyer HR, Pinell-White X, Losken A (2014) The effect of radiation on acellular dermal matrix and capsule formation in breast reconstruction: clinical outcomes and histologic analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 133:214–221
Song J, Zhang X, Liu Q, Peng J, Liang X, Shen Y, Liu H, Li H (2014) Impact of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on immediate breast reconstruction: a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 9:e98225
Colwell AS, Taylor EM (2020) Recent advances in implant-based breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 145:421e–432e
Urban C, Rietjens M, Veronesi U, Petit JY (2013) Oncoplastic and reconstructive breast surgery. Springer, Milano, pp 253–258
Ibrahim AM, Koolen PG, Ganor O, Markarian MK, Tobias AM, Lee BT, Lin SJ, Mureau MA (2015) Does acellular dermal matrix really improve aesthetic outcome in tissue expander/implant-based breast reconstruction? Aesthet Plast Surg 39:359–368
Gabriel A, Maxwell GP (2018) AlloDerm RTU integration and clinical outcomes when used for reconstructive breast surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 6:e1744
Burns PB, Rohrich RJ, Chung KC (2011) The levels of evidence and their role in evidence-based medicine. Plast Reconstr Surg 128:305
McKenzie JE, Beller EM, Forbes AB (2016) Introduction to systematic reviews and meta-analysis. Respirology 21:626–637
Acknowledgements
Funding was provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81700410) and the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (Grant No. 2019YFS0344).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Human and Animal Rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bi, S., Liu, R., Wu, B. et al. Breast Implants for Mammaplasty: An Umbrella Review of Meta-analyses of Multiple Complications. Aesth Plast Surg 44, 1988–1996 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01866-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01866-0