Abstract
Background
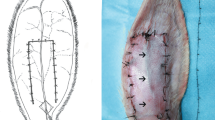
Hyaluronic acid (HA) injection-induced embolism is a rare but severe complication. This article is aimed to introduce an islanded rabbit auricular skin flap model of HA injection-induced embolism and to study its pathophysiological progress.
Methods
An islanded skin flap was elevated based on the proximal central auricular artery/vein. Eighteen rabbits were randomized into three groups. Ten, twenty, and forty microliters of HA were injected into the central auricular artery in each group, respectively. Flap fluorescence angiography was performed. One-way ANOVA was used to compare fluorescence area at different time points and between dose groups. Two rabbits in each group were randomly chosen for histology examination. In addition to regular HE staining, Alcian Blue staining was performed to better show the existence of HA in the vessel lumen.
Results
The mean calculated fluorescence area was 64.41 % on POD 1, 79.77 % on POD 3, 88.20 % on POD 5, and 92.03 % on POD 7 in 10 μl group; 60.51 % on POD 1, 58.84 % on POD 3, 71.20 % on POD 5, and 76.54 % on POD 7 in 20 μl group; 21.60 % on POD 1, 3.08 % on POD 3, 2.91 % on POD 5, and 7.52 % on POD 7 in 40 μl group. In all three groups, infiltration of eosinophilic granulocytes was observed in the muscular layer of both artery and vein.
Conclusion
Our study successfully created a rabbit auricular skin necrosis model of HA embolism, which provided a valuable animal model for further investigation of the pathophysiological progress and the efficacy of potential treatments.
No Level Assigned
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Society of Aesthetic and Plastic Surgery (2014) Global Statistics. Available at: http://www.isaps.org/Media/Default/global-statistics/Quick%20Facts%202015v2.pdf. Accessed 1 Dec 2015
Ozturk CN, Li Y, Tung R, Parker L, Piliang MP, Zins JE (2013) Complications following injection of soft-tissue fillers. Aesthetic Surg J 33(6):862–877
DeLorenzi C (2014) Complications of injectable fillers, part 2: vascular complications. Aesthetic Surg J 34(4):584–600
Funt D, Pavicic T (2015) Dermal fillers in aesthetics: an overview of adverse events and treatment approaches. Plast Surg Nurs 35(1):13–32
Chang SH, Yousefi S, Qin J et al (2015) External compression versus intravascular injection: a mechanistic animal model of filler-induced tissue ischemia. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. doi:10.1097/IOP.0000000000000484
Nonomura S, Oshitari T, Miura G, Chiba A, Yamamoto S (2014) A case of ophthalmic artery occlusion following injection of hyaluronic acid into the glabellar area. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 118(9):783–787
Sung HM, Suh IS, Lee HB, Tak KS, Moon KM, Jung MS (2012) Case reports of adipose-derived stem cell therapy for nasal skin necrosis after filler injection. Arch Plast Surg 39(1):51–54
Kwon SG, Hong JW, Roh TS, Kim YS, Rah DK, Kim SS (2013) Ischemic oculomotor nerve palsy and skin necrosis caused by vascular embolization after hyaluronic acid filler injection: a case report. Ann Plast Surg 71(4):333–334
Kim YJ, Kim SS, Song WK, Lee SY, Yoon JS (2011) Ocular ischemia with hypotony after injection of hyaluronic acid gel. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 27(6):e152–e155
Grunebaum LD, Allemann IB, Dayan S, Mandy S, Baumann L (2009) The risk of alar necrosis associated with dermal filler injection. Dermatol Surg 35(Suppl 2):1635–1640
Kim EG, Eom TK, Kang SJ (2014) Severe visual loss and cerebral infarction after injection of hyaluronic acid gel. J Craniofac Surg 25(2):684–686
Kim DW, Yoon ES, Ji YH, Park SH, Lee BI, Dhong ES (2011) Vascular complications of hyaluronic acid fillers and the role of hyaluronidase in management. J Plast Reconstr Aesthetic Surg 64(12):1590–1595
Kassir R, Kolluru A, Kassir M (2011) Extensive necrosis after injection of hyaluronic acid filler: case report and review of the literature. J Cosmet Dermatol 10(3):224–231
Hirsch RJ, Lupo M, Cohen JL, Duffy D (2007) Delayed presentation of impending necrosis following soft tissue augmentation with hyaluronic acid and successful management with hyaluronidase. J Drugs Dermatol 6(3):325–328
Dayan SH, Arkins JP, Mathison CC (2011) Management of impending necrosis associated with soft tissue filler injections. J Drugs Dermatol 10(9):1007–1012
Hirsch RJ, Cohen JL, Carruthers JD (2007) Successful management of an unusual presentation of impending necrosis following a hyaluronic acid injection embolus and a proposed algorithm for management with hyaluronidase. Dermatol Surg 33(3):357–360
Cohen JL, Biesman BS, Dayan SH et al (2015) Treatment of hyaluronic acid filler-induced impending necrosis with hyaluronidase: consensus recommendations. Aesthetic Surg J 35(7):844–849
Flynn TC, Sarazin D, Bezzola A, Terrani C, Micheels P (2011) Comparative histology of intradermal implantation of mono and biphasic hyaluronic acid fillers. Dermatol Surg 37(5):637–643
DeLorenzi C (2014) Transarterial degradation of hyaluronic acid filler by hyaluronidase. Dermatol Surg 40(8):832–841
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Peking Union Medical College Innovation Grant to Dr. Yan Zhuang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Mingyong Yang and Chunjun Liu have contributed equally to the article as co-corresponding authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhuang, Y., Yang, M. & Liu, C. An Islanded Rabbit Auricular Skin Flap Model of Hyaluronic Acid Injection-Induced Embolism. Aesth Plast Surg 40, 421–427 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-016-0630-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-016-0630-0