Abstract
Background
Hyaluronic acid (HA) filler-induced vascular embolism that threatens skin integrity is an urgent situation. There is increasing evidence that percutaneous intra-arterial hyaluronidase injection is an effective therapeutic technique for it. However, until now, there is a lack of a unifying protocol about the technique.
Objectives
This study aims to provide a conclusion of percutaneous intra-arterial hyaluronidase injection along with adjunctive measures on the treatment of occlusions precipitated by HA-based filler and develop a stepwise treatment protocol.
Methods
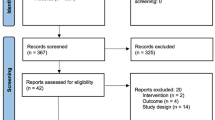
We searched PubMed for peer-reviewed studies, consensus statements, case series, and case reports using a variety of keywords.
Results
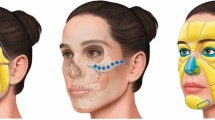
High-dose, pulsed hyaluronidase is the mainstay for the treatment of HA filler-induced embolism, but percutaneous intra-arterial hyaluronidase injection is a more effective technique. Until now, hyaluronidase is injected into three arteries percutaneously, including facial artery, supratrochlear artery, and superficial temporal artery. Furthermore, the adjunctive measures that may optimize clearance of an occlusion and/or skin barrier repair such as the use of image guidance and CGF should be considered.
Conclusion
Vascular occlusions that threaten skin integrity are an urgent matter which requires accurate diagnosis and effective intervention. Percutaneous intra-arterial hyaluronidase injection along with adjunctive measures performed in a stepwise manner is key to an optimal outcome.
No Level Assigned
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each submission to which Evidence-Based Medicine rankings are applicable. This excludes Review Articles, Book Reviews, and manuscripts that concern Basic Science, Animal Studies, Cadaver Studies, and Experimental Studies. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kern JA, Kollipara R, Hoss E et al (2022) Serious adverse events with injectable fillers: retrospective analysis of 7659 patient outcomes. Dermatol Surg 48:551–555
Yang Q, Qiu L, Yi C et al (2017) Reversible alopecia with localized scalp necrosis after accidental embolization of the parietal artery with hyaluronic acid. Aesthet Plast Surg 41:695–699
Gan SD, Itkin A, Wolpowitz D (2013) Hyaluronic acid-induced alopecia: a novel complication. Dermatol Surg 39:1724–1725
Park GH, Kim WI, Yang MY et al (2019) Filler-induced alopecia. J Dermatol 46:e392-393
Glaich AS, Cohen JL, Goldberg LH (2006) Injection necrosis of the glabella: protocol for prevention and treatment after use of dermal fillers. Dermatol Surg 32:276–281
Dufly DM (2005) Complications of fillers: overview. Dermatol Surg 31:1626–1633
Rzany B, Becker WP, Bachmann F et al (2009) Hyaluronidase in the correction of hyaluronic acid-based fillers: a review and a recommendation for use. J Cosmet Dermatol 8:317–323
Goodman GJ, Clague MD (2016) A rethink on hyaluronidase injection, intraarterial injection, and blindness: is there another option for treatment of retinal artery embolism caused by intraarterial injection of hyaluronic acid? Dermatol Surg 42:547–549
Zhang LX, Lai LY, Zhou GW et al (2020) Evaluation of intraarterial thrombolysis in treatment of cosmetic facial filler-related ophthalmic artery occlusion. Plast Reconstr Surg 145:42–50
Xu X, Zhou G, Fu Q et al (2021) Efficacy of intrarterial thrombolytic therapy for vision loss resulting from hyaluronic acid filler embolization. J Cosmet Dermatol 20:3205–3212
Zheng C, Fu Q, Zhou GW et al (2022) Efficacy of percutaneous intraarterial facial/supratrochlear arterial hyaluronidase injection for treatment of vascular embolism resulting from hyaluronic acid filler cosmetic injection. Aesthet Surg J 42:649–655
Zheng C, Fu Q, Zhou GW, Xu X, Tian XM, Lai LY, Wu Q, Ding HF, Yu BY, Chen ML (2023) Efficacy of percutaneous superficial temporal arterial hyaluronidase injection for hyaluronic acid filler-induced necrosis of frontotemporal skin and/or the ipsilateral scalp with subsequent alopecia. Aesthet Surg J 43:77–83
Park MJ, Hong SP, Kim MH et al (2020) Temporary hair loss with an increase of telogen hairs after filler migration into the scalp. Dermatol Surg 46:1129–1131
Stoehr JR, Choi JN, Colavincenzo M et al (2019) Off-label use of topical minoxidil in alopecia: a review. Am J Clin Dermatol 20:237–250
Jones DH, Fitzgerald R, Cox SE, Butterwick K et al (2021) Preventing and treating adverse events of injectable fillers: evidence-based recommendations from the American society for dermatologic surgery multidisciplinary task force. Dermatol Surg 47:214–226
DeLorenzi C (2017) New high dose pulsed hyaluronidase protocol for hyaluronic acid filler vascular adverse events. Aesthet Surg J 37:814–825
Jones DH (2018) Update on emergency and nonemergency use of hyaluronidase in aesthetic dermatology. JAMA Dermatol 154:763–764
DeLorenzi C (2014) Complications of injectable fillers, part 2: vascular complications. Aesthet Surg J 34:584–600
Kwon HJ, Kim BJ, Ko EJ, Choi SY (2017) The utility of color Doppler ultrasound to explore vascular complications after filler injection. Dermatol Surg 43:1508–1510
Schelke LW, Velthuis P, Kadouch J, Swift A (2019) Early ultrasound for diagnosis and treatment of vascular adverse events with hyaluronic acid fillers. J Am Acad Dermatol S0190–9622(19):32392–32398
De Pascale MR, Sommese L, Casamassimi A et al (2015) Platelet derivatives in regenerative medicine:an update. Transfus Med Rev 29(1):52–61
Hu X, Zhou L, Wang H, Gao Y, Gao Y (2021) The value of photo biological regulation based on nano semiconductor laser technology in the treatment of hypertension fundus disease. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 21:1323–1330
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human or Animal Rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, Q., Zheng, C., Zhou, Gw. et al. Percutaneous Intra-arterial Hyaluronidase Injection for Hyaluronic Acid Filler Embolism Threatening Skin Barrier Integrity: Implementation of a Stepwise Treatment Protocol. Aesth Plast Surg 48, 747–751 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03640-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03640-4