Abstract
Background
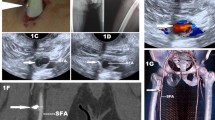
Soft tissue foreign bodies (FBs) are very commonly observed in paediatric emergency departments. Not all FBs can be removed effectively, even via open surgery and image intensifier guidance. In the current study, we evaluated the efficiency of FB removal with the assistance of ultrasound (US) and methylene blue (MB) staining.
Methods
We enrolled 80 patients at our clinical center between May 2016 and December 2020. Eleven patients were operated upon with the assistance of US guidance and MB and were defined as group A; the other 69 patients were defined as group B. For the patients in group A, US was first used to locate the FB; MB was then injected next to the FB. Open surgery was subsequently performed. For group B, the FBs were removed by conventional methods. The surgical outcomes were evaluated according to surgical duration, incision infection rates, radiograph exposure times, and FB residue rates.
Results
The average surgery time for group A was 0.35 ± 0.10 hours; the corresponding time was 0.49 ± 0.50 hours in group B and there was a significant difference between the groups (p = 0.032). The radiograph exposure times were 1.33 ± 0.34 in group A and 4.65 ± 1.81 times in group B (p = 0.021).
Conclusions
This study demonstrates that assistance of US and MB staining is a more efficient approach compared with traditional methods for FB removal, and this surgical method can be used effectively for FB removal in children.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FBs:
-
Foreign bodies
- US:
-
Ultrasound
- MB:
-
Methylene blue
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
References
White RZ, Rezaian P, Parasuramar A, Sampson MJ (2022) Ultrasound-assisted foreign body extraction (U-SAFE): review of technique and technical pearls. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 66(3):362–369. https://doi.org/10.1111/1754-9485.13313
Öztürk AM, Aljasim O, Şanlıdağ G, Taşbakan M (2021) Retrospective evaluation of 377 patients with penetrating foreign body injuries: a university hospital experience (a present case of missed sponge foreign body injury). Turk J Med Sci 51(2):570–582. https://doi.org/10.3906/sag-2006-34
Carneiro BC, Cruz I, Chemin RN, Rizzetto TA, Guimarães JB, Silva FD, Junior CY, Pastore D, Ormond Filho AG, Nico M (2020) Multimodality imaging of foreign bodies: new insights into old challenges. Radiographics 40(7):1965–1986. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.2020200061
Young AS, Shiels WE 2nd, Murakami JW, Coley BD, Hogan MJ (2010) Self-embedding behavior: radiologic management of self-inserted soft-tissue foreign bodies. Radiology 257(1):233–239. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.10091566
Park HJ, Lee SM, Lee SY, Son ES, Chung EC, Rho MH, Lee SJ (2015) Ultrasound-guided percutaneous removal of wooden foreign bodies in the extremities with hydro-dissection technique. Korean J Radiol 16(6):1326–1331. https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.6.1326
Rooks VJ, Shiels WE 3rd, Murakami JW (2020) Soft tissue foreign bodies: a training manual for sonographic diagnosis and guided removal. J Clin Ultrasound 48(6):330–336. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcu.22856
Tahmasebi M, Zareizadeh H, Motamedfar A (2014) Accuracy of ultrasonography in detecting radiolucent soft-tissue foreign bodies. Indian J Radiol Imaging 24(2):196–200
Callegari L, Leonardi A, Bini A, Sabato C, Nicotera P, Spano’ E, Mariani D, Genovese EA, Fugazzola C (2009) Ultrasound-guided removal of foreign bodies: personal experience. Eur Radiol 19(5):1273–1279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-1266-5
Bradley M (2012) Image-guided soft-tissue foreign body extraction - success and pitfalls. Clin Radiol 67(6):531–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2011.10.029
Shaahinfar A, Ghazi-Askar ZM (2021) Procedural applications of point-of-care ultrasound in pediatric emergency medicine. Emerg Med Clin North Am 39(3):529–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emc.2021.04.006
Paziana K, Fields JM, Rotte M, Au A, Ku B (2012) Soft tissue foreign body removal technique using portable ultrasonography. Wilderness Environ Med 23(4):343–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wem.2012.04.006
White RZ, Rezaian P, Parasuramar A, Sampson MJ (2021) Ultrasound-assisted foreign body extraction (U-SAFE): review of technique and technical pearls. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1111/1754-9485.13313
Del Cura JL, Aza I, Zabala RM, Sarabia M, Korta I (2020) US-guided localization and removal of soft-tissue foreign bodies. Radiographics 40(4):1188–1195. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.2020200001
Saboo SS, Saboo SH, Soni SS, Adhane V (2009) High-resolution sonography is effective in detection of soft tissue foreign bodies: experience from a rural Indian center. J Ultrasound Med 28(9):1245–1249
Lewis D, Jivraj A, Atkinson P, Jarman R (2015) My patient is injured: identifying foreign bodies with ultrasound. Ultrasound 23(3):174–180. https://doi.org/10.1177/1742271X15579950
Schirmer RH, Coulibaly B, Stich A, Scheiwein M, Merkle H, Eubel J, Becker K, Becher H, Müller O, Zich T, Schiek W, Kouyaté B (2003) Methylene blue as an antimalarial agent. Redox Rep 8(5):272–275. https://doi.org/10.1179/135100003225002899
Meissner PE, Mandi G, Coulibaly B, Witte S, Tapsoba T, Mansmann U, Rengelshausen J, Schiek W, Jahn A, Walter-Sack I, Mikus G, Burhenne J, Riedel KD, Schirmer RH, Kouyaté B, Müller O (2006) Methylene blue for malaria in Africa: results from a dose-finding study in combination with chloroquine. Malar J 5:84. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2875-5-84
Wainwright M, Crossley KB (2002) Methylene blue–a therapeutic dye for all seasons. J Chemother 14(5):431–443. https://doi.org/10.1179/joc.2002.14.5.431
Agha R, Abdall-Razak A, Crossley E, Dowlut N, Iosifidis C, Mathew G (2019) STROCSS 2019 guideline: strengthening the reporting of cohort studies in surgery. Int J Surg 72:156–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2019.11.002
Mahajan M, Shah N (2004) Accidental lodgment of an air gun pellet in the maxillary sinus of a 6-year old girl: a case report. Dent Traumatol 20(3):178–180. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-4469.2004.00218.x
Hiremath R, Reddy H, Ibrahim J, Haritha CH, Shah RS (2017) Soft tissue foreign body: utility of high resolution ultrasonography. J Clin Diagn Res 11(7):TC14–TC16. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2017/26384.10269
Tantray MD, Rather A, Manaan Q, Andleeb I, Mohammad M, Gull Y (2018) Role of ultrasound in detection of radiolucent foreign bodies in extremities. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr 13(2):81–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11751-018-0308-z
Connolly B, Racadio J, Towbin R (2006) Practice of ALARA in the pediatric interventional suite. Pediatr Radiol 36(Suppl):2163–2167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-006-0192-4
Tao K, Xu S, Liu XY, Liang JL, Qiu T, Tan JN, Che JH, Wang ZH (2012) Small metal soft tissue foreign body extraction by using 3D CT guidance: a reliable method. Eur J Radiol 81(11):3339–3343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2012.01.002
Amoretti N, Hauger O, Marcy PY, Hovorka I, Lesbats-Jacquot V, Fonquerne ME, Maratos Y, Boileau P (2010) Foreign body extraction from soft tissue by using CT and fluoroscopic guidance: a new technique. Eur Radiol 20(1):190–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-009-1499-y
Sarıhan A, Can C (2014) Soft tissue foreign body removal with magnet in ED settings. Am J Emerg Med 32(8):952.e3–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2014.02.009
Chen S, Liu YH, Gao X, Yang CY, Li Z (2020) Computer-assisted navigation for removal of the foreign body in the lower jaw with a mandible reference frame: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore) 99(3):e18875. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000018875
Ji Y, Jiang H, Wan L, Yuan H (2018) Effect of navigation system on removal of foreign bodies in head and neck surgery. J Craniofac Surg 29(7):e723–e726. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000004986
Ebrahimi A, Radmanesh M, Rabiei S, Kavoussi H (2013) Surgical removal of neglected soft tissue foreign bodies by needle-guided technique. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol 25(70):29–36
Ceylan MF, Guner S, Ediz L, Unsal SS, Isik D (2014) Removal of metallic foreign bodies embedded in soft tissues by stereotaxic approach. Afr Health Sci 14(1):64–71. https://doi.org/10.4314/ahs.v14i1.10
Srinivasa RN, Srinivasa RN, Chick J (2018) Balloon tract dilatation facilitates fluoroscopically guided removal of deeply penetrating foreign bodies. Radiol Case Rep 13(3):622–623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radcr.2018.02.031
Albayati WK, Farhan N, Jasim AK, Qassim YN, Ali AA (2021) The utility of a novel vacuum-assisted foreign body extraction technique from wounds. JPRAS Open 27:27–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpra.2020.10.008
Blass N, Fung D (1976) Dyed but not dead–methylene blue overdose. Anesthesiology 45(4):458–459. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-197610000-00020
Su Y, Nan G (2016) Using methylene blue as a marker to find and remove tiny metallic foreign bodies embedded in the soft tissues of children: a randomised controlled trial. Int J Surg 29:43–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2016.03.018
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YS participated the study and drafted the manuscript. KC and MW collected the clinical data and helped draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The ethics committee of the Children’s Hospital of Chongqing Medical University approved the study.
Consent for publication
Informed consent for publication of photographs was obtained from all subjects.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Kai Chen and Menglei Wang are co-first authors and contributed equally to this work
Highlights
1. We increased the scope of the method of foreign body removal.
2. Combination of ultrasound guidance and methylene blue staining is effective.
3. This surgical method can be recommended to orthopedic surgeons.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, K., Wang, M. & Su, Y. Foreign body removal with the assistance of ultrasound guidance and methylene blue staining in children—a cohort study. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 46, 1831–1838 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-022-05427-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-022-05427-9