Abstract
Purpose
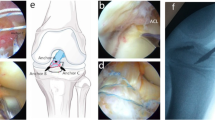
The purpose of this study was to prospectively evaluate outcomes of arthroscopic management of neglected ununited tibial eminence fractures in skeletally immature patients.
Methods
The study was conducted and cases performed by two surgeons from two centres as a prospective case series of 13 patients with neglected ununited tibial eminence fractures: nine were girls and four were boys; ten were right knees and three were left. The average age at surgery was ten [standard deviation (SD) 2.6] years. Average follow-up was 10.8 (SD 6.8) months. Primary outcome measures used for evaluation were the Objective International Knee Documentation Committee Score (IKDC), subjective IKDC and modified Lysholm knee score. Secondary outcome measures were visual analogue scales (VAS) for pain and patient satisfaction.
Results
Twelve patients had grade A objective IKDC score and one patient had grade B. Average subjective IKDC score was 80.5 (SD 16.7). Average modified Lysholm score was 91.2 (SD 8.9). Average VAS for operation satisfaction was 9.6 (SD 0.5) and for pain was 0.4 (SD 0.5). All patients showed radiological union and anatomical reduction at an average of 12.4 weeks postoperatively. At follow-up, all 13 patients showed complete range of motion (ROM). Eleven patients had negative Lachman, anterior drawer and pivot-shift tests, while two patients had grade 1 positive Lachman and negative anterior drawer and pivot-shift tests. No patient had complained of instability.
Conclusion
Neglected ununited tibial eminence fractures in skeletally immature patients achieve good functional outcome results when treated with arthroscopic reduction and internal fixation using sutures.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Noyes F, DeLucas J, Torvik P (1974) Biomechanics of anterior cruciate ligament failure: an analysis of strain-rate sensitivity and mechanisms of failure in primates. J Bone Joint Surg Am 56(2):236–53
Poncet A (1875) Arrachement de l’epine du tibia a l’insertion du ligament croise anterieur. Bull Mem Soc Chir Paris 1:883–4
Luhmann S (2003) Acute traumatic knee effusions in children and adolscents. J Pediatr Orthop 23:199–202
Kendall N, Hsy S, Chan K (1992) Fracture of the tibial spine in adults and children. A review of 31 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br 74(6):848–52
Skak S, Jensen TT, Poulsen TD et al (1987) Epidemiology of knee injuries in children. Acta Orthop Scand 58:78–81
Lubowitz JH, Elson WS, Guttmann D (2005) Part II: Arthroscopic treatment of tibial plateau fractures. Intercondylar eminence avulsion fractures. Arthroscopy 21(1):86–92
Chandler JT, Miller TK (1995) Tibial eminence fracture with meniscal entrapment. Arthroscopy 11(4):499–502
Falstie-Jensen S, Sondergard Petersen PE (1984) Incarceration of the meniscus in fractures of the intercondylar eminence of the tibia in children. Injury 15:236–238
Zionts L (2009) Fractures and Dislocations about the Knee. In: Green NE, Swiontkowski MR (eds) Skeletal trauma in children. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 452–5
Perugia D (2009) Clinical and radiological results of arthroscopically treated tibial spine fractures in childhood. Int Orthop 33(1):243–8
Kocher M, Foreman E, Micheli L (2003) Laxity and functional outcome after arthroscopic reduction and internal fixation of displaced tibial spine fractures in children. Arthroscopy 19(10):1085–90
Tudisco C (2010) Intercondylar eminence avulsion fracture in children: long-term follow-up of 14 cases at the end of skeletal growth. J Pediatr Orthop B 19(5):403–8
Meyers M, McKeever F (1959) Fracture of the intercondylar eminence of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Am 41-A(2):209–20
Zaricznyi B (1977) Avulsion fracture of the tibial eminence: treatment by open reduction and pinning. J Bone Joint Surg Am 59(8):1111–4
Ahn J, Yoo J (2005) Clinical outcome of arthroscopic reduction and suture for displaced acute and chronic tibial spine fractures. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 13(2):116–21
Seon J, Park SJ, Lee KB et al (2009) A clinical comparison of screw and suture fixation of anterior cruciate ligament tibial avulsion fractures. Am J Sports Med 37(12):2334–9
Reynders P, Reynders K, Broos P (2002) Pediatric and adolescent tibial eminence fractures: arthroscopic cannulated screw fixation. J Trauma 53(1):49–54
Liljeros K (2009) Arthroscopic fixation of anterior tibial spine fractures with bioabsorbable nails in skeletally immature patients. Am J Sports Med 37(5):923–8
McLennan J (1982) The role of arthroscopic surgery in the treatment of fractures of the intercondylar eminence of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br 64(4):477–80
Ezechieli M, Schäfer M, Becher C, Dratzidis A, Glaab R, Ryf C, Hurschler C, Ettinger M (2013) Biomechanical comparison of different fixation techniques for reconstruction of tibial avulsion fractures of the anterior cruciate ligament. Int Orthop 37(5):919–23
Anderson AF, Anderson CN (2011) Anterior cruciate ligament injuries with bony avulsion. In: Lieberman JR, Berry DJ, Azar FM (eds) AAOS Advanced Reconstruction: Knee. Rosemont, AAOS p, pp 603–12
Molander M-L, Wallin G, Wikstad I (1981) Fracture of the intercondylar eminence of the tibia. A review of 35 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br 63:89–91
Luger EJ, Arbel R, Eichenblat MS, Menachem A, Dekel S (1994) Femoral notchplasty in the treatment of malunited intercondylar eminence fractures of the tibia. Arthroscopy 10:550–551
Hefti F, Müller W, Jakob RP, Stäubli HU (1993) Evaluation of knee ligament injuries with the IKDC form. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 1:226–234
Tegner Y, Lysholm J (1985) Rating systems in the evaluation of knee ligament injuries. Clin Orthop 198:43
Anderson CN, Anderson AF (2011) Tibial eminence fractures. Clin Sports Med 30(4):727–42
Lafrance RM, Giordano B, Goldblatt J, Voloshin I, Maloney M (2010) Pediatric tibial eminence fractures: evaluation and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 18(7):395–405
Coyle C, Jagernauth S, Ramachandran M (2014) Tibial eminence fractures in the paediatric population: a systematic review. J Child Orthop 8(2):149–59
Shepley RW (2004) Arthroscopic treatment of type III tibial spine fractures using absorbable fixation. Orthopedics 27(7):767–769
Wilfinger C, Castellani C, Raith J, Pilhatsch A, Hollwarth ME, Weinberg AM (2009) Nonoperative treatment of tibial spine fractures in children-38 patients with a minimum follow-up of 1 year. J Orthop Trauma 23(7):519–524
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdelkafy, A., Said, H.G. Neglected ununited tibial eminence fractures in the skeletally immature: arthroscopic management. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 38, 2525–2532 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-014-2462-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-014-2462-3