Abstract
Purpose
To compare image quality of monopolar and bipolar diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) sequences of the liver at 3T.
Methods
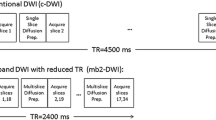
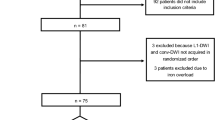
32 healthy volunteers (mean 27 ± 8 years; 27 M/5F) and 11 patients (mean age 58 ± 14 years; 8 M/3F) underwent liver MRI using a 3T system incorporating 2-channel parallel transmission for B1-shimming and reduced B1-inhomogeneity. Scans included free-breathing DWI sequences (b-value 0, 400, 800 s/mm2) acquired using both monopolar and bipolar techniques. Estimated signal-to-noise ratio (eSNR), apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), and measures of subjective image quality on b-800 images, scored on a 1–5 scale by two independent radiologists, were compared between sequences.
Results
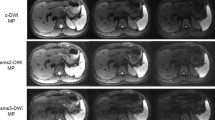
Monopolar sequence demonstrated significantly higher eSNR (volunteers: 12.7 ± 4.0 vs. 11.3 ± 3.5, patients: 11.4 ± 4.0 vs. 10.2 ± 3.3; p ≤ 0.013) compared with the bipolar sequence. Monopolar sequence also achieved significantly higher scores for reader 1 in volunteers and patients in terms of clarity of right lobe edge, clarity of intra-hepatic vessels, conspicuity of the left lobe, and overall diagnostic quality (p ≤ 0.031), as well as significantly higher scores for reader 2 in volunteers in terms of clarity of intra-hepatic vessels, conspicuity of the left lobe, and overall diagnostic quality (p ≤ 0.035). Respiratory motion artifact was not significantly different between sequences in patients or volunteers for either reader (p ≥ 0.191). Hepatic ADC was significantly lower using monopolar technique only in volunteers (1.28 ± 0.12 vs. 1.43 ± 0.15, p < 0.001).
Conclusion
In comparison with past studies performed at 1.5T, when using a modern 3T system, we observed improved image quality of liver DWI using a monopolar, rather than a bipolar, acquisition scheme, largely attributed to higher eSNR.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koh DM, Scurr E, Collins D, et al. (2007) Predicting response of colorectal hepatic metastasis: value of pretreatment apparent diffusion coefficients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 188(4):1001–1008. doi:10.2214/AJR.06.0601
Cui Y, Zhang XP, Sun YS, Tang L, Shen L (2008) Apparent diffusion coefficient: potential imaging biomarker for prediction and early detection of response to chemotherapy in hepatic metastases. Radiology 248(3):894–900. doi:10.1148/radiol.2483071407
Galea N, Cantisani V, Taouli B (2013) Liver lesion detection and characterization: role of diffusion-weighted imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 37(6):1260–1276. doi:10.1002/jmri.23947
Taouli B, Koh DM (2010) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the liver. Radiology 254(1):47–66. doi:10.1148/radiol.09090021
d’Assignies G, Fina P, Bruno O, et al. (2013) High sensitivity of diffusion-weighted MR imaging for the detection of liver metastases from neuroendocrine tumors: comparison with T2-weighted and dynamic gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 268(2):390–399. doi:10.1148/radiol.13121628
Parikh T, Drew SJ, Lee VS, et al. (2008) Focal liver lesion detection and characterization with diffusion-weighted MR imaging: comparison with standard breath-hold T2-weighted imaging. Radiology 246(3):812–822. doi:10.1148/radiol.2463070432
Jezzard P, Barnett AS, Pierpaoli C (1998) Characterization of and correction for eddy current artifacts in echo planar diffusion imaging. Magn Reson Med 39(5):801–812
Koch M, Norris DG (2000) An assessment of eddy current sensitivity and correction in single-shot diffusion-weighted imaging. Phys Med Biol 45(12):3821–3832
Le Bihan D, Poupon C, Amadon A, Lethimonnier F (2006) Artifacts and pitfalls in diffusion MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 24(3):478–488. doi:10.1002/jmri.20683
Liau J, Lee J, Schroeder ME, Sirlin CB, Bydder M (2012) Cardiac motion in diffusion-weighted MRI of the liver: artifact and a method of correction. J Magn Reson Imaging 35(2):318–327. doi:10.1002/jmri.22816
Burdette JH, Durden DD, Elster AD, Yen YF (2001) High b-value diffusion-weighted MRI of normal brain. J Comput Assist Tomogr 25(4):515–519
Stejskal EO, Tanner JE (1965) Spin echoes in the presence of a time dependent field gradient. J Chem Phys 42:288–292
Alexander AL, Tsuruda JS, Parker DL (1997) Elimination of eddy current artifacts in diffusion-weighted echo-planar images: the use of bipolar gradients. Magn Reson Med 38(6):1016–1021
Bodammer N, Kaufmann J, Kanowski M, Tempelmann C (2004) Eddy current correction in diffusion-weighted imaging using pairs of images acquired with opposite diffusion gradient polarity. Magn Reson Med 51(1):188–193. doi:10.1002/mrm.10690
Reese TG, Heid O, Weisskoff RM, Wedeen VJ (2003) Reduction of eddy-current-induced distortion in diffusion MRI using a twice-refocused spin echo. Magn Reson Med 49(1):177–182. doi:10.1002/mrm.10308
Kyriazi S, Blackledge M, Collins DJ, Desouza NM (2010) Optimising diffusion-weighted imaging in the abdomen and pelvis: comparison of image quality between monopolar and bipolar single-shot spin-echo echo-planar sequences. Eur Radiol 20(10):2422–2431. doi:10.1007/s00330-010-1826-3
Dyvorne HA, Galea N, Nevers T, et al. (2013) Diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver with multiple b values: effect of diffusion gradient polarity and breathing acquisition on image quality and intravoxel incoherent motion parameters–a pilot study. Radiology 266(3):920–929. doi:10.1148/radiol.12120686
Rosenkrantz AB, Oei M, Babb JS, Niver BE, Taouli B (2011) Diffusion-weighted imaging of the abdomen at 3.0 T: image quality and apparent diffusion coefficient reproducibility compared with 1.5 Tesla. J Magn Reson Imaging 33(1):128–135
Nasu K, Kuroki Y, Nawano S, et al. (2006) Hepatic metastases: diffusion-weighted sensitivity-encoding versus SPIO-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 239(1):122–130. doi:10.1148/radiol.2383041384
Nasu K, Kuroki Y, Sekiguchi R, Kazama T, Nakajima H (2006) Measurement of the apparent diffusion coefficient in the liver: is it a reliable index for hepatic disease diagnosis? Radiat Med 24(6):438–444. doi:10.1007/s11604-006-0053-y
Kwee TC, Takahara T, Niwa T, et al. (2009) Influence of cardiac motion on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the liver. Magma 22(5):319–325. doi:10.1007/s10334-009-0183-1
Colagrande S, Pasquinelli F, Mazzoni LN, Belli G, Virgili G (2010) MR-diffusion weighted imaging of healthy liver parenchyma: repeatability and reproducibility of apparent diffusion coefficient measurement. J Magn Reson Imaging 31(4):912–920. doi:10.1002/jmri.22117
Kim SY, Lee SS, Byun JH, et al. (2010) Malignant hepatic tumors: short-term reproducibility of apparent diffusion coefficients with breath-hold and respiratory-triggered diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology 255(3):815–823. doi:10.1148/radiol.10091706
Zapparoli M, Semelka RC, Altun E, et al. (2008) 3.0-T MRI evaluation of patients with chronic liver diseases: initial observations. Magn Reson Imaging 26(5):650–660. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2008.01.037
Franklin KM, Dale BM, Merkle EM (2008) Improvement in B1-inhomogeneity artifacts in the abdomen at 3T MR imaging using a radiofrequency cushion. J Magn Reson Imaging 27(6):1443–1447. doi:10.1002/jmri.21164
Rosenkrantz AB, Patel JM, Babb JS, Storey P, Hecht EM (2010) Liver MRI at 3 T using a respiratory-triggered time-efficient 3D T2-weighted technique: impact on artifacts and image quality. AJR Am J Roentgenol 194(3):634–641
Kukuk GM, Gieseke J, Weber S, et al. (2011) Focal liver lesions at 3.0 T: lesion detectability and image quality with T2-weighted imaging by using conventional and dual-source parallel radiofrequency transmission. Radiology 259(2):421–428. doi:10.1148/radiol.11101429
Willinek WA, Gieseke J, Kukuk GM, et al. (2010) Dual-source parallel radiofrequency excitation body MR imaging compared with standard MR imaging at 3.0 T: initial clinical experience. Radiology 256(3):966–975. doi:10.1148/radiol.10092127
Guo L, Liu C, Chen W, Chan Q, Wang G (2013) Dual-source parallel RF transmission for diffusion-weighted imaging of the abdomen using different b values: image quality and apparent diffusion coefficient comparison with conventional single-source transmission. J Magn Reson Imaging 37(4):875–885. doi:10.1002/jmri.23869
Griswold MA, Jakob PM, Heidemann RM, et al. (2002) Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magn Reson Med 47(6):1202–1210. doi:10.1002/mrm.10171
Heverhagen JT (2007) Noise measurement and estimation in MR imaging experiments. Radiology 245(3):638–639. doi:10.1148/radiol.2453062151
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33(1):159–174
de Bazelaire CM, Duhamel GD, Rofsky NM, Alsop DC (2004) MR imaging relaxation times of abdominal and pelvic tissues measured in vivo at 3.0 T: preliminary results. Radiology 230(3):652–659. doi:10.1148/radiol.2303021331
Finsterbusch J (2009) Eddy-current compensated diffusion weighting with a single refocusing RF pulse. Magn Reson Med 61(3):748–754. doi:10.1002/mrm.21899
Lee VS, Hecht EM, Taouli B, et al. (2007) Body and cardiovascular MR imaging at 3.0 T. Radiology 244(3):692–705. doi:10.1148/radiol.2443060582
Merkle EM, Dale BM (2006) Abdominal MRI at 3.0 T: the basics revisited. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186(6):1524–1532. doi:10.2214/AJR.05.0932
Yoshikawa T, Kawamitsu H, Mitchell DG, et al. (2006) ADC measurement of abdominal organs and lesions using parallel imaging technique. AJR Am J Roentgenol 187(6):1521–1530. doi:10.2214/AJR.05.0778
Furuta A, Isoda H, Yamashita R, et al. (2014) Comparison of monopolar and bipolar diffusion weighted imaging sequences for detection of small hepatic metastases. Eur J Radiol. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2014.06.003
Geppert C, Feiweier T, Janka R, et al. (2011) Reduction of image distortions in breast DWI using dynamic field correction: impact on ADC assessment. In: Proceedings of the annual meeting of ESMRMB, Leipzig
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosenkrantz, A.B., Geppert, C., Kiritsy, M. et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver: comparison of image quality between monopolar and bipolar acquisition schemes at 3T. Abdom Imaging 40, 289–298 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-014-0215-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-014-0215-9