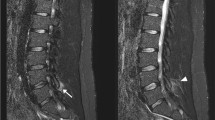
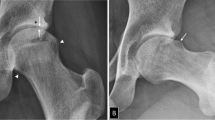
Abstract
Bone sclerosis is a focal, multifocal, or diffuse increase in the density of the bone matrix on radiographs or computed tomography (CT) imaging. This radiological finding can be caused by a broad spectrum of diseases, such as congenital and developmental disorders, depositional disorders, and metabolic diseases. The differential diagnosis can be effectively narrowed by an astute radiologist in the light of the clinical picture and typical findings on imaging. Some of these lesions are rare and have been described as case reports and series in the literature. This article aims to collate the clinical-radiologic findings of non-infectious and non-neoplastic causes of bone sclerosis with relevant imaging illustrations.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awan O, Wu JS, Eisenberg RL. Imaging of multifocal and diffuse sclerotic bone lesions. Contemp Diagn Radiol. 2015;38(6):1–7.
Bastawrous S, Bhargava P, Behnia F, Djang DS, Haseley DR. Newer PET application with an old tracer: role of 18F-NaF skeletal PET/CT in oncologic practice. Radiographics. 2014;34(5):1295–316.
Agrawal A, Purandare N, Shah S, Rangarajan V. Metastatic mimics on bone scan: “all that glitters is not metastatic”. Indian J Nucl Med. 2016;31(3):185–90.
Kogan F, Broski SM, Yoon D, Gold GE. Applications of PET-MRI in musculoskeletal disease. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018;48(1):27–47.
Bernard S, Walker E, Raghavan M. An approach to the evaluation of incidentally identified bone lesions encountered on imaging studies. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017;208(5):960–70.
Carlson ML, Beatty CW, Neff BA, Link MJ, Driscoll CLW. Skull base manifestations of Camurati-Engelmann disease. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010;136(6):566–75.
Janssens K, Vanhoenacker F, Bonduelle M, Verbruggen L, Van Maldergem L, Ralston S, et al. Camurati-Engelmann disease: review of the clinical, radiological, and molecular data of 24 families and implications for diagnosis and treatment. J Med Genet. 2006;43(1):1–11.
Wallace SE, Wilcox WR. Camurati-Engelmann Disease. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJH, Stephens K, et al., eds. GeneReviews((R)). Seattle (WA); 1993.
Del Fattore A, Peruzzi B, Rucci N, Recchia I, Cappariello A, Longo M, et al. Clinical, genetic, and cellular analysis of 49 osteopetrotic patients: implications for diagnosis and treatment. J Med Genet. 2006;43(4):315–25.
Stark Z, Savarirayan R. Osteopetrosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2009;4(1):5.
Del Fattore A, Cappariello A, Teti A. Genetics, pathogenesis and complications of osteopetrosis. Bone. 2008;42(1):19–29.
Bollerslev J, Andersen PE Jr. Radiological, biochemical and hereditary evidence of two types of autosomal dominant osteopetrosis. Bone. 1988;9(1):7–13.
Mugera C, Suh KJ, Huisman TAGM, Weber K, Belzberg AJ, Carrino JA, et al. Sclerotic lesions of the spine: MRI assessment. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013;38(6):1310–24.
Khoja A, Fida M, Shaikh A. Pycnodysostosis with special emphasis on dentofacial characteristics. Case Rep Dent. 2015;2015:817989.
Ihde LL, Forrester DM, Gottsegen CJ, Masih S, Patel DB, Vachon LA, et al. Sclerosing bone dysplasias: review and differentiation from other causes of osteosclerosis. Radiographics. 2011;31(7):1865–82.
Ramaiah KKK, George GB, Padiyath S, Sethuraman R, Cherian B. Pyknodysostosis: report of a rare case with review of literature. Imaging Sci Dent. 2011;41(4):177–81.
Viot G, Lacombe D, David A, Mathieu M, de Broca A, Faivre L, et al. Osteopathia striata cranial sclerosis: non-random X-inactivation suggestive of X-linked dominant inheritance. Am J Med Genet. 2002;107(1):1–4.
Seeger LL, Hewel KC, Yao L, Gold RH, Mirra JM, Chandnani VP, et al. Ribbing disease (multiple diaphyseal sclerosis): imaging and differential diagnosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996;167(3):689–94.
Cai Y, Lin H, Huang F, Zheng X, Huang Y, Zhang S. Imaging features and differential diagnosis of multiple diaphyseal sclerosis: a case report and review of literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(33):e11725.
Sakamoto A, Oda Y, Iwamoto Y, Tsuneyoshi M. A comparative study of fibrous dysplasia and osteofibrous dysplasia with regard to Gsalpha mutation at the Arg201 codon: polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of paraffin-embedded tissues. J Mol Diagn. 2000;2(2):67–72.
Campanacci M. Osteofibrous dysplasia of long bones a new clinical entity. Ital J Orthop Traumatol. 1976;2(2):221–37.
Scholfield DW, Sadozai Z, Ghali C, Sumathi V, Douis H, Gaston L, et al. Does osteofibrous dysplasia progress to adamantinoma and how should they be treated? Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B(3):409–16.
Jung J-Y, Jee W-H, Hong SH, Kang HS, Chung HW, Ryu K-N, et al. MR findings of the osteofibrous dysplasia. Korean J Radiol. 2014;15(1):114–22.
Adetayo OA, Salcedo SE, Borad V, Richards SS, Workman AD, Ray AO. Fibrous dysplasia: an overview of disease process, indications for surgical management, and a case report. Eplasty. 2015;15:e6.
Mohan H, Mittal P, Mundi I, Kumar S. Fibrous dysplasia of bone: a clinicopathologic review. Pathol Lab Med Int. 2011;3:3–31.
Gwark J-Y, Jeong J-H, Hwang S-C, Nam D-C, Lee J-H, Na J-B, et al. Monostotic fibrous dysplasia in the proximal tibial epiphysis: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2014;8:452.
Wordsworth P, Chan M. Melorheostosis and osteopoikilosis: a review of clinical features and pathogenesis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2019;104(5):530–43.
Franca PM, Ferrreira CS, Figueiredo R, Matushita JP. Melorheostosis. Radiol Bras. 2015;48(1):60–1.
Roberts NM, Langtry JAA, Branfoot AC, Gleeson J, Staughton RCD. Osteopoikilosis and the Buschke–Ollendorff syndrome. Br J Radiol. 1993;66(785):468–70.
Krishna D, Chand S. Osteopoikilosis: a case report with review of literature. J Orthop Traumatol Rehabil. 2013;6(1):84–6.
Negi RS, Manchanda KL, Sanga S, Chand S, Goswami G. Osteopoikilosis - spotted bone disease. Med J Armed Forces India. 2013;69(2):196–8.
Itzchaki M, Lebel E, Dweck A, Patlas M, Hadas-Halpern I, Zimran A, et al. Orthopedic considerations in Gaucher disease since the advent of enzyme replacement therapy. Acta Orthop Scand. 2004;75(6):641–53.
Mikosch P, Hughes D. An overview on bone manifestations in Gaucher disease. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2010;160(23–24):609–24.
Katz R, Booth T, Hargunani R, Wylie P, Holloway B. Radiological aspects of Gaucher disease. Skelet Radiol. 2011;40(12):1505–13.
Mucci JM, Rozenfeld P. Pathogenesis of bone alterations in Gaucher disease: the role of immune system. J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:1–6.
Maas M, van Kuijk C, Stoker J, Hollak CEM, Akkerman EM, Aerts JFMG, et al. Quantification of bone involvement in Gaucher disease: MR imaging bone marrow burden score as an alternative to Dixon quantitative chemical shift MR imaging—initial experience. Radiology. 2003;229(2):554–61.
Maas M, Poll LW, Terk MR. Imaging and quantifying skeletal involvement in Gaucher disease. Br J Radiol. 2002;75(suppl_1):A13–24.
Wagner N, Staubach P. Mastocytosis - pathogenesis, clinical manifestation and treatment. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2018;16(1):42–57.
Lange M, Nedoszytko B, Górska A, Zawrocki A, Sobjanek M, Kozlowski D. Mastocytosis in children and adults: clinical disease heterogeneity. Arch Med Sci. 2012;8(3):533–41.
Delsignore JL, Dvoretsky PM, Hicks DG, O'Keefe RJ, Rosier RN. Mastocytosis presenting as a skeletal disorder. Iowa Orthop J. 1996;16:126–34.
Roca M, Mota J, Giraldo P, García Erce JA. Systemic mastocytosis: MRI of bone marrow involvement. Eur Radiol. 1999;9(6):1094–7.
Haney K, Russell W, Raila FA, Brower AC, Harrison RB. MRI characteristics of systemic mastocytosis of the lumbosacral spine. Skelet Radiol. 1996;25(2):171–3.
Chen CC, Andrich MP, Mican JM, Metcalfe DD, CCC MPA, et al. A retrospective analysis of bone scan abnormalities in mastocytosis: correlation with disease category and prognosis. J Nucl Med. 1994;35(9):1471–5.
Avila NA, Ling A, Metcalfe DD, Worobec AS. Mastocytosis: magnetic resonance imaging patterns of marrow disease. Skelet Radiol. 1998;27(3):119–26.
Nguyen BD. CT and scintigraphy of aggressive lymphadenopathic mastocytosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;178(3):769–70.
Sidhu HS, Venkatanarasimha N, Bhatnagar G, Vardhanabhuti V, Fox BM, Suresh SP. Imaging features of therapeutic drug-induced musculoskeletal abnormalities. Radiographics. 2012;32(1):105–27.
Chang CY, Rosenthal DI, Mitchell DM, Handa A, Kattapuram SV, Huang AJ. Imaging findings of metabolic bone disease. Radiographics. 2016;36(6):1871–87.
Hayami N, Hoshino J, Suwabe T, Sumida K, Mise K, Hamanoue S, et al. Destructive spondyloarthropathy in patients on long-term peritoneal dialysis or hemodialysis. Ther Apher Dial. 2015;19(4):393–8.
Jevtic V. Imaging of renal osteodystrophy. Eur J Radiol. 2003;46(2):85–95.
Reddy D. Neurology of endemic skeletal fluorosis. Neurol India. 2009;57(1):7–7.
Kurdi MS. Chronic fluorosis: the disease and its anaesthetic implications. Indian J Anaesth. 2016;60(3):157–62.
Wang Y, Yin Y, Gilula LA, Wilson AJ. Endemic fluorosis of the skeleton: radiographic features in 127 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994;162(1):93–8.
Gupta N, Gupta N, Chhabra P. Image diagnosis: dental and skeletal fluorosis. Perm J. 2016;20(1):e105.
Soriano M, Manchón F. Radiological aspects of a new type of bone fluorosis. Periostitis Deformans Radiology. 1966;87(6):1089–94.
Krishnamachari KA. Skeletal fluorosis in humans: a review of recent progress in the understanding of the disease. Prog Food Nutr Sci. 1986;10(3–4):279–314.
Ahmed I, Sohail S, Hussain M, Khan N, Hameed KM. MRI features of spinal fluorosis: results of an endemic community screening. Pak J Med Sci. 2013;29(1):177–80.
Theodorou DJ, Theodorou SJ, Kakitsubata Y. Imaging of Paget disease of bone and its musculoskeletal complications: review. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;196(6 Suppl):S64–75.
Bouchette P, Boktor SW. Paget disease. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls; 2020.
Mazor RD, Manevich-Mazor M, Shoenfeld Y. Erdheim-Chester disease: a comprehensive review of the literature. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013;8(1):137.
Matzumura M, Arias-Stella J, Novak JE, Novak JE. Erdheim-Chester disease: a rare presentation of a rare disease. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2016;4(3):–2324709616663233.
Drier A, Haroche J, Savatovsky J, Godenèche G, Dormont D, Chiras J, et al. Cerebral, facial, and orbital involvement in Erdheim-Chester disease: CT and MR imaging findings. Radiology. 2010;255(2):586–94.
Antunes C, Graça B, Donato P. Thoracic, abdominal and musculoskeletal involvement in Erdheim-Chester disease: CT, MR and PET imaging findings. Insights Imaging. 2014;5(4):473–82.
Bourke SC, Nicholson AG, Gibson GJ. Erdheim-Chester disease: pulmonary infiltration responding to cyclophosphamide and prednisolone. Thorax. 2003;58(11):1004–5.
Arnaud L, Malek Z, Archambaud F, Kas A, Toledano D, Drier A, et al. 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography scanning is more useful in followup than in the initial assessment of patients with Erdheim-Chester disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(10):3128–38.
Lodhi U, Sarmast U, Khan S, Yaddanapudi K. Multisystem radiologic manifestations of Erdheim-Chester disease. Case Rep Radiol. 2016;2016:2670495.
Haroche J, Amoura Z, Dion E, Wechsler B, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Cacoub P, et al. Cardiovascular involvement, an overlooked feature of Erdheim-Chester disease: report of 6 new cases and a literature review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2004;83(6):371–92.
Sedrak A, Kondamudi NP. Sickle cell disease. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls; 2020.
Kosaraju V, Harwani A, Partovi S, Bhojwani N, Garg V, Ayyappan S, et al. Imaging of musculoskeletal manifestations in sickle cell disease patients. Br J Radiol. 2017;90(1073):20160130.
Lonergan GJ, Cline DB, Abbondanzo SL. Sickle cell anemia. Radiographics. 2001;21(4):971–94.
Ejindu VC, Hine AL, Mashayekhi M, Shorvon PJ, Misra RR. Musculoskeletal manifestations of sickle cell disease. Radiographics. 2007;27(4):1005–21.
Leong CS, Stark P. Thoracic manifestations of sickle cell disease. J Thorac Imaging. 1998;13(2):128–34.
Keeley K, Buchanan GR. Acute infarction of long bones in children with sickle cell anemia. J Pediatr. 1982;101(2):170–5.
Styles LA, Vichinsky EP. Core decompression in avascular necrosis of the hip in sickle-cell disease. Am J Hematol. 1996;52(2):103–7.
Bahebeck J, Atangana R, Techa A, Monny-Lobe M, Sosso M, Hoffmeyer P. Relative rates and features of musculoskeletal complications in adult sicklers. Acta Orthop Belg. 2004;70(2):107–11.
Mughal TI, Vaddi K, Sarlis NJ, Verstovsek S. Myelofibrosis-associated complications: pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, and effects on outcomes. Int J Gen Med. 2014;7:89–101.
Cloran F, Banks KP. AJR teaching file: diffuse osteosclerosis with hepatosplenomegaly. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;188(3_supplement):S18–20.
Guermazi A, De Kerviler E, Cazals-Hatem D, Zagdanski AM, Frija J. Imaging findings in patients with myelofibrosis. Eur Radiol. 1999;9(7):1366–75.
Lafforgue P, Trijau S. Bone infarcts: unsuspected gray areas? Joint Bone Spine. 2016;83(5):495–9.
Munk PL, Helms CA, Holt RG. Immature bone infarcts: findings on plain radiographs and MR scans. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989;152(3):547–9.
Stacy GS, Lo R, Montag A. Infarct-associated bone sarcomas: multimodality imaging findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015;205(4):W432–41.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Avneesh Chhabra—consultant ICON Medical and Treace Medical Concepts, Inc., Royalties: Jaypee, Wolters.
Majid Chalian—Medical Advisor, Imagen Technology Ltd.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gulati, V., Chalian, M., Yi, J. et al. Sclerotic bone lesions caused by non-infectious and non-neoplastic diseases: a review of the imaging and clinicopathologic findings. Skeletal Radiol 50, 847–869 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-020-03644-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-020-03644-0