Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the distortion and artifact area of metal in MR images and to compare artifact reduction using different metal artifact-reducing sequences in patients with metal-on-metal (MoM) and non-MoM total hip prostheses.
Materials and methods
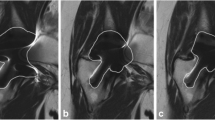
Thirty-six MoM and 15 non-MoM prostheses were examined in a 1.5-T MR scanner using T1-weighted (T1-w) sequences: turbo spin echo (TSE) high-readout bandwidth (hiBW), T1-w; TSE view angle tilting (VAT), T1-w; TSE VAT + slice encoding for metal artifact correction (SEMAC); short tau inversion recovery (STIR) hiBW or matched RF pulses (mRFp). Distortion was quantified using a new method measuring the acetabular roof angle (ARA). The artifact area was defined in the mid-coronal plane of the artifact.
Results
The T1 VAT + SEMAC sequence showed the least distortion compared to T1 VAT and T1-hiBW (150°, 127° and 102°, p < 0.001, in MoM; 152°, 143° and 128°, p ≤ 0.014, in non-MoM). The artifact area was smaller in MoM prostheses using the T1 VAT sequence compared to T1 hiBW and T1 VAT + SEMAC (2506 mm2, 3160 mm2 and 3214 mm2, p < 0.001) and smaller in non-MoM prostheses using T1 VAT compared to T1-hiBW (4296 mm2 and 4831 mm2, p = 0.041). STIR-mRFp substantially reduced the artifact size compared with STIR-hiBW (MoM 4559 mm2 and 6323 mm2; non-MoM 5625 mm2 and 8764 mm2, p < 0.001).
Conclusion
Metal artifacts in MR imaging examinations of hip prostheses can be evaluated for distortion using a distortion angle (ARA) and the degree of signal artifact as determined by measuring the largest cross-sectional artifact area. T1 VAT + SEMAC showed the least distortion; T1 VAT and STIR-mRFp were most efficient for reduction of the artifact area.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hargreaves BA, Worters PW, Pauly KB, Pauly JM, Koch KM, Gold GE. Metal-induced artifacts in MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197:547–55.
Lee MJ, Kim S, Lee SA, et al. Overcoming artifacts from metallic orthopedic implants at high-field-strength MR imaging and multi-detector CT. Radiographics. 2007;27:791–803.
Lee MJ, Janzen DL, Munk PL, MacKay A, Xiang QS, McGowen A. Quantitative assessment of an MR technique for reducing metal artifact: application to spin-echo imaging in a phantom. Skelet Radiol. 2001;30:398–401.
Potter HG, Nestor BJ, Sofka CM, Ho ST, Peters LE, Salvati EA. Magnetic resonance imaging after total hip arthroplasty: evaluation of periprosthetic soft tissue. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A:1947–54.
Suh JS, Jeong EK, Shin KH, et al. Minimizing artifacts caused by metallic implants at MR imaging: experimental and clinical studies. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998;171:1207–13.
White LM, Kim JK, Mehta M, et al. Complications of total hip arthroplasty: MR imaging-initial experience. Radiology. 2000;215:254–62.
Cho ZH, Kim DJ, Kim YK. Total inhomogeneity correction including chemical shifts and susceptibility by view angle tilting. Med Phys. 1988;15:7–11.
Olsen RV, Munk PL, Lee MJ, et al. Metal artifact reduction sequence: early clinical applications. Radiographics. 2000;20:699–712.
Lu W, Pauly KB, Gold GE, Pauly JM, Hargreaves BA. SEMAC: slice encoding for metal artifact correction in MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2009;62:66–76.
Sutter R, Ulbrich EJ, Jellus V, Nittka M, Pfirrmann CW. Reduction of metal artifacts in patients with total hip arthroplasty with slice-encoding metal artifact correction and view-angle tilting MR imaging. Radiology. 2012;265:204–14.
Conflicts of interest
None of the authors has a financial interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, G.M., Lundin, B., von Schewelov, T. et al. Evaluation of metal artifacts in clinical MR images of patients with total hip arthroplasty using different metal artifact-reducing sequences. Skeletal Radiol 44, 353–359 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-014-2051-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-014-2051-y