Abstract
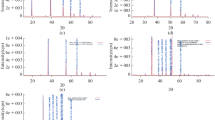
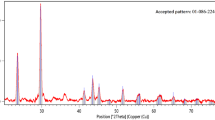
In recent years, metal-based complexes including selenium (Se) and zinc (Zn)-containing compounds have been widely explored for their therapeutic properties due to their roles in biological processes and modulation of diverse molecular targets. Humic acid, as a metal complexing agent, is also widely used in biomedical field. In this work, three kinds of modified sodium humate (HNa), including Zn-HNA, Se-HNa, and Zn/Se-HNa, were prepared by ion exchange reaction method. The modified HNa was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and elemental mapping. The bacteriostatic activity and mechanism of modified HNa against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria were investigated by testing bacterial inhibition zone, minimum inhibitory concentration, and capacity to destroy integrity of the bacterial membrane, promoting ROS generation level and prevention of biofilms. FTIR results showed that HNa could combine with zinc ions and selenite ions. The main XRD peaks did not change significantly. In the modified HNa, the particle shape was irregular. Compared to HNa, Zn-HNA, and Se-HNa, Zn/Se-HNa showed the strongest bacteriostatic activity. Zn/Se-HNa exhibited high bacteriostatic activity against gram-negative bacteria (Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, Klebsiella pneumoniae) and gram-positive bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus), but showed weak antibacterial activity against another gram-positive bacteria, Bacillus subtilis. The bacteriostasis was achieved by altering the permeability of bacterial cell membranes, generating ROS, and preventing the formation of biofilms. In conclusion, Zn/Se-HNa has high bacteriostatic activity, making it a suitable alternative to antibiotics in fields like the treatment of trauma infections and animal husbandry.
Key points
• Preparate and characterize zinc- and selenium-loaded sodium humate (Zn/Se-HNa).
• The combination of Zn and Se enhanced the bacteriostatic activity of HNa.
• Zn/Se-HNa alters the permeability of bacterial cell membranes and promotes generation of ROS.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Al-Lami MK, Oustriere N, Gonzales E, Burken JG (2022) Phytomanagement of Pb/Zn/Cu tailings using biosolids-biochar or -humus combinations: enhancement of bioenergy crop production, substrate functionality, and ecosystem services. Sci Total Environ 836:155676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155676
Arora N, Thangavelu K, Karanikolos GN (2020) Bimetallic nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications. Front Chem 8:412. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.00412
Bhat MA, Lone SH, Srivastava SK (2018) Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, DFT studies and biological activity of Bis (1-(ethyl) piperidine) diselenide (L) and its complexes with selected group 12 metal halides. Inorg Chim Acta 478:222–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2018.04.011
Cagno V, Donalisio M, Civra A, Cagliero C, Rubiolo P, Lembo D (2015) In vitro evaluation of the antiviral properties of Shilajit and investigation of its mechanisms of action. J Ethnopharmacol 166:129–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2015.03.019
Christl I, Knicker H, Kögel-Knabner I, Kretzschmar R (2008) Chemical heterogeneity of humic substances: characterization of size fractions obtained by hollow-fibre ultrafiltration. Eur J Soil Sci 51:617–625. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2000.00352.x
Du Q, Li G, Zhang S, Song J, Zhao Y, Yang F (2020) High-dispersion zero-valent iron particles stabilized by artificial humic acid for lead ion removal. J Hazard Mater 383:121170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121170
Elakraa AA, Salem SS, El-Sayyad GS, AttiaElakraa MS (2022) Cefotaxime incorporated bimetallic silver-selenium nanoparticles: promising antimicrobial synergism, antibiofilm activity, and bacterial membrane leakage reaction mechanism. RSC Adv 12:26603–26619. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ra04717a
Frei A, Verderosa AD, Elliott AG, Zuegg J, Blaskovich MAT (2023) Metals to combat antimicrobial resistance. Nat Rev Chem 7:202–224. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-023-00463-4
Fujimura Y, Katayama A, Kuwatsuka S (1994) Inhibitory action of dissolved humic substances on the growth of soil bacteria degrading DDT. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 40:525–530. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.1994.10413330
Gupta J, Bahadur D (2018) Defect-mediated reactive oxygen species generation in Mg-substituted ZnO nanoparticles: efficient nanomaterials for bacterial inhibition and cancer therapy. ACS Omega 3:2956–2965. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.7b01953
Hassan MS, Amna T, Sheikh FA, Al-Deyab SS, Choi KE, Hwang IH, Khil MS (2013) Bimetallic Zn/Ag doped polyurethane spider net composite nanofibers: a novel multipurpose electrospun mat. Ceram Int 39:2503–2510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2012.09.009
He E, Lü C, He J, Zhao B, Wang J, Zhang R, Ding T (2016) Binding characteristics of Cu(2+) to natural humic acid fractions sequentially extracted from the lake sediments. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:22667–22677. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7487-2
Hou M, Liu W, Zhang L, Zhang L, Xu Z, Cao Y, Kang Y, Xue P (2020) Responsive agarose hydrogel incorporated with natural humic acid and MnO(2) nanoparticles for effective relief of tumor hypoxia and enhanced photo-induced tumor therapy. Biomater Sci 8:353–369. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9bm01472a
Ji Y, Zhang A, Chen X, Che X, Zhou K, Wang Z (2016) Sodium humate accelerates cutaneous wound healing by activating TGF-beta/Smads signaling pathway in rats. Acta Pharm Sin B 6:132–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2016.01.009
Li P, Li J, Feng X, Li J, Hao Y, Zhang J, Wang H, Yin A, Zhou J, Ma X, Wang B (2019) Metal-organic frameworks with photocatalytic bactericidal activity for integrated air cleaning. Nat Commun 10:2177. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10218-9
Litvin VA, Minaev BF (2013) Spectroscopy study of silver nanoparticles fabrication using synthetic humic substances and their antimicrobial activity. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 108:115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2013.01.049
Ma Z, Shan C, Liang J, Tong M (2018) Efficient adsorption of selenium(IV) from water by hematite modified magnetic nanoparticles. Chemosphere 193:134–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.005
Melo BAG, Motta FL, Santana MHA (2016) Humic acids: Structural properties and multiple functionalities for novel technological developments. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 62:967–974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.12.001
Naudé PJW, Cromarty AD, Rensburg CEJ (2010) Potassium humate inhibits carrageenan-induced paw oedema and a graft-versus-host reaction in rats. Inflammopharmacology 18:33–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-009-0026-8
Pandey AK, Pandey SD, Misra V (2000) Stability constants of metal-humic acid complexes and its role in environmental detoxification. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 47:195–200. https://doi.org/10.1006/eesa.2000.1947
Ramos-Inza S, Plano D, Sanmartín C (2022) Metal-based compounds containing selenium: an appealing approach towards novel therapeutic drugs with anticancer and antimicrobial effects. Eur J Med Chem 244:114834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114834
Schönborn S, Wente N, Paduch JH, Krömker V (2017) In vitro ability of mastitis causing pathogens to form biofilms. J Dairy Res 84:198–201. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022029917000218
Sun BK, Tanji Y, Unno H (2006) Extinction of cells of cyanobacterium Anabaena circinalis in the presence of humic acid under illumination. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:823–828. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0327-4
Tang Y, Hou S, Yang Y, Cheng DD, Gao B, Wan YS, Li YC, Yu Z, Yao YY, Xie JZ (2019) Cu(II)-based water-dispersible humic acid: synthesis, characterizations, and antifungal and growth-promoting performances. J Agric Food Chem 67:12987–13000. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b05145
Tran P, Kopel J, Ray C, Reed J, Reid TW (2022) Organo-selenium containing dental sealant inhibits biofilm formation by oral bacteria. Dent Mater 38:848–857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2022.04.006
Urdiales C, Gacitua M, Villacura L, Pizarro C, Escudey M, Canales C, Antilén M (2020) Variable surface charge of humic acid-ferrihydrite composite: influence of electrolytes on ciprofloxacin adsorption. J Hazard Mater 385:121520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121520
Van Rensburg CEJ, Snyman JR, Mokoele T, Cromarty AD (2007) Brown coal derived humate inhibits contact hypersensitivity; an efficacy, toxicity and teratogenicity study in rats. Inflammation 30:148–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-007-9031-5
Vitiello G, Venezia V, Verrillo M, Nuzzo A, Houston J, Cimino S, D'Errico G, Aronne A, Paduano L, Piccolo A, Luciani G (2021) Hybrid humic acid/titanium dioxide nanomaterials as highly effective antimicrobial agents against gram(-) pathogens and antibiotic contaminants in wastewater. Environ Res 193:110562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.110562
Wang D, He Y, Liu K, Deng SX, Fan YY, Liu Y (2022a) Sodium humate alleviates enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-induced intestinal dysfunction via alteration of intestinal microbiota and metabolites in mice. Front Microbiol 13:809086. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.809086
Wang YS, Bian ZR, Wang Y (2022b) Biofilm formation and inhibition mediated by bacterial quorum sensing. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 106:6365–6381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-12150-3
Wilson E, Rajamanickam GV, Dubey GP, Klose P, Musial F, Saha FJ, Rampp T, Michalsen A, Dobos GJ (2011) Review on shilajit used in traditional Indian medicine. J Ethnopharmacol 136:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2011.04.033
Funding
The work was supported by the China Agriculture Research System (CARS36) of the MOF and MARA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YF: conducted the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. JL: participated in the experiments of antimicrobial activity assay. DW: participated in the experiments design. XR: participated in analyzing the data. YL: provided the financial support, developed the concept, guided the whole study process, and revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript for submission.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Y., Li, J., Ren, X. et al. Preparation, characterization, bacteriostatic efficacy, and mechanism of zinc/selenium-loaded sodium humate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 7417–7425 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12803-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12803-x