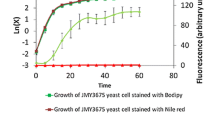
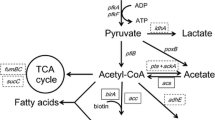
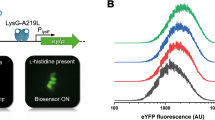
Abstract
Adipic acid is an industrially important chemical, but the current approach to synthesize it can be of serious pollution to the environment. Rencently, bio-based production of adipic acid has significantly advanced with the development of metabolic engineering and synthetic biology. However, genetic heterogeneity-caused decrease of product titer has largely limited the industrialization of chemicals like adipic acid. Therefore, in the attempt to overcome this challenge, we constitutively expressed the reverse adipate degradation pathway, designed and optimized an adipic acid biosensor, and established a high-throughput screening platform to screen for high-performance strains based on the optimized biosensor. Using this platform, we successfully screened a strain with an adipic acid titer of 188.08 mg·L−1. Coupling the screening platform with fermentation optimization, the titer of adipic acid reached 531.88 mg·L−1 under shake flask fermentation, which achieved an 18.78-fold improvement comparing to the initial strain. Scale-up fermentation in a 5-L fermenter utilizing the screened high-performance strain was eventually conducted, in which the adipic acid titer reached 3.62 g·L−1. Overall, strategies developed in this study proved to be a potentially efficient method in reducing the genetic heterogeneity and was expected to provide guidance in helping to build a more efficient industrial screening process.
Key points
• Developed a fine-tuned adipic acid biosensor.
• Established a high-throughput screening platform to screen high-performance strains.
• The titer of adipic acid reached 3.62 g·L −1 in a 5-L fermenter.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ang J, Harris E, Hussey BJ, Kil R, McMillen DR (2013) Tuning response curves for synthetic biology. ACS Synth Biol 2(10):547–567. https://doi.org/10.1021/sb4000564
Bart JCJ, Cavallaro S (2015) Transiting from adipic acid to bioadipic acid. 1, petroleum-based processes. Ind Eng Chem Res 54(1):1–46. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie5020734
Bart JCJ, Cavallaro S (2015) Transiting from adipic acid to bioadipic acid. part II. Biosynthetic pathways. Ind Eng Chem Res 54(2):567–576. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie502074d
Bretschneider L, Heuschkel I, Buhler K, Karande R, Buhler B (2022) Rational orthologous pathway and biochemical process engineering for adipic acid production using Pseudomonas taiwanensis VLB120. Metab Eng 70:206–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2022.01.014
Brutesco C, Preveral S, Escoffier C, Descamps ECT, Prudent E, Cayron J, Dumas L, Ricquebourg M, Adryanczyk-Perrier G, de Groot A, Garcia D, Rodrigue A, Pignol D, Ginet N (2017) Bacterial host and reporter gene optimization for genetically encoded whole cell biosensors. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(1):52–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6952-2
Ceroni F, Boo A, Furini S, Gorochowski TE, Borkowski O, Ladak YN, Awan AR, Gilbert C, Stan G-B, Ellis T (2018) Burden-driven feedback control of gene expression. Nat Methods 15(5):387–393. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4635
Cheng F, Tang X, Kardashliev T (2018) Transcription factor-based biosensors in high-throughput screening: advances and applications. Biotechnol J 13(7):e1700648. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201700648
Cheong S, Clomburg JM, Gonzalez R (2016) Energy- and carbon-efficient synthesis of functionalized small molecules in bacteria using non-decarboxylative claisen condensation reactions. Nat Biotech 34(5):556–561. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3505
Clomburg JM, Blankschien MD, Vick JE, Chou A, Kim S, Gonzalez R (2015) Integrated engineering of β-oxidation reversal and ω-oxidation pathways for the synthesis of medium chain ω-functionalized carboxylic acids. Metab Eng 28:202–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2015.01.007
Concordet J-P, Haeussler M (2018) CRISPOR: intuitive guide selection for CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing experiments and screens. Nucleic Acids Res 46(W1):W242–W245. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky354
Dahl RH, Zhang F, Alonso-Gutierrez J, Baidoo E, Batth TS, Redding-Johanson AM, Petzold CJ, Mukhopadhyay A, Lee TS, Adams PD, Keasling JD (2013) Engineering dynamic pathway regulation using stress-response promoters. Nat Biotechnol 31(11):1039–1046. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2689
de jong E, Higson A, Walsh P, Wellisch M (2012) Bio-based chemicals value added products from biorefineries. IEA Bioenergy website. https://www.ieabioenergy.com/blog/publications/bio-based-chemicals-value-added-products-from-biorefineries/
Deng Y, Mao Y (2015) Production of adipic acid by the native-occurring pathway in Thermobifida fusca B6. J Appl Microbiol 119(4):1057–1063. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.12905
Ding N, Yuan Z, Zhang X, Chen J, Zhou S, Deng Y (2020) Programmable cross-ribosome-binding sites to fine-tune the dynamic range of transcription factor-based biosensor. Nucleic Acids Res 48(18):10602–10613. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa786
Gao J, Du M, Zhao J, Yue Z, Xu N, Du H, Ju J, Wei L, Liu J (2022) Design of a genetically encoded biosensor to establish a high-throughput screening platform for L-cysteine overproduction. Metab Eng 73:144–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2022.07.007
Hao T, Li G, Zhou S, Deng Y (2021) Engineering the reductive TCA pathway to dynamically regulate the biosynthesis of adipic acid in Escherichia coli. ACS Synth Biol 10(3):632–639. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.0c00648
Hossain A, Lopez E, Halper SM, Cetnar DP, Reis AC, Strickland D, Klavins E, Salis HM (2020) Automated design of thousands of nonrepetitive parts for engineering stable genetic systems. Nat Biotechnol 38(12):1466–1475. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-020-0584-2
Jiang Y, Chen B, Duan C, Sun B, Yang J, Yang S (2015) Multigene editing in the Escherichia coli genome via the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Appl Environ Microbiol 81(7):2506–2514. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.04023-14
Joo JC, Khusnutdinova AN, Flick R, Kim T, Bornscheuer UT, Yakunin AF, Mahadevan R (2017) Alkene hydrogenation activity of enoate reductases for an environmentally benign biosynthesis of adipic acid. Chem Sci 8(2):1406–1413. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6sc02842j
Kallscheuer N, Gätgens J, Lübcke M, Pietruszka J, Bott M, Polen T (2017) Improved production of adipate with Escherichia coli by reversal of β-oxidation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(6):2371–2382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-8033-3
Kruyer NS, Peralta-Yahya P (2017) Metabolic engineering strategies to bio-adipic acid production. Curr Opin Biotechnol 45:136–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2017.03.006
Li L, Chang M, Tao G, Wang X, Liu Y, Liu R, Jin Q, Wang X (2016) Analysis of phospholipids in Schizochytrium sp. S31 by using UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. Anal Methods 8(4):763–770. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5AY02795K
Li G, Huang D, Sui X, Li S, Huang B, Zhang X, Wu H, Deng Y (2020) Advances in microbial production of medium-chain dicarboxylic acids for nylon materials. React Chem Eng 5(2):221–238. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RE00338J
Liu Y, Liu Y, Wang M (2017) Design, optimization and application of small molecule biosensor in metabolic engineering. Front Microbiol 8:2012. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02012
Mannan AA, Liu D, Zhang F, Oyarzun DA (2017) Fundamental design principles for transcription-factor-based metabolite biosensor. ACS Synth Biol 6(10):1851–1859. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.7b00172
Niu W, Willett H, Mueller J, He X, Kramer L, Ma B, Guo J (2020) Direct biosynthesis of adipic acid from lignin-derived aromatics using engineered Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Metab Eng 59:151–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2020.02.006
Rios J, Lebeau J, Yang T, Li S, Lynch MD (2021) A critical review on the progress and challenges to a more sustanable, cost competitive synthesis of adipic acid. Green Chem 23(9):3172–3190. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1gc00638j
Rugbjerg P, Sommer MOA (2019) Overcoming genetic heterogeneity in industrial fermentations. Nat Biotechnol 37(8):869–876. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0171-6
Rugbjerg P, Myling-Petersen N, Porse A, Sarup-Lytzen K, Sommer MOA (2018) Diverse genetic error modes constrain large-scale bio-based production. Nat Commun 9(1):787. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03232-w
Skoog E, Shin JH, Saez-Jimenez V, Mapelli V, Olsson L (2018) Biobased adipic acid - the challenge of developing the production host. Biotechnol Adv 36(8):2248–2263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.10.012
Snoek T, Chaberski EK, Ambri F, Kol S, Bjorn SP, Pang B, Barajas JF, Welner DH, Jensen MK, Keasling JD (2020) Evolution-guided engineering of small-molecule biosensors. Nucleic Acids Res 48(1):e3. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz954
Sui X, Zhao M, Liu Y, Wang J, Li G, Zhang X, Deng Y (2020) Enhancing glutaric acid production in Escherichia coli by uptake of malonic acid. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 47(3):311–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-020-02268-6
Teufel R, Mascaraque V, Ismail W, Voss M, Perera J, Eisenreich W, Haehnel W, Fuchs G (2010) Bacterial phenylalanine and phenylacetate catabolic pathway revealed. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(32):14390–14395. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1005399107
Tucci S, Martin W (2007) A novel prokaryotic trans-2-enoyl-CoA reductase from the spirochete Treponema denticola. FEBS Lett 581(8):1561–1566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2007.03.013
Turk SC, Kloosterman WP, Ninaber DK, Kolen KP, Knutova J, Suir E, Schürmann M, Raemakers-Franken PC, Müller M, de Wildeman SM, Raamsdonk LM, van der Pol R, Wu L, Temudo MF, van der Hoeven RA, Akeroyd M, van der Stoel RE, Noorman HJ, Bovenberg RA, Trefzer AC (2016) Metabolic engineering toward sustainable production of nylon-6. ACS Synth Biol 5(1):65–73. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.5b00129
Valgepta K, Adamberg K, Nahku R, Lahtvee P, Arike L, Vilu R (2010) Systems biology approach reveals that overflow metabolism of acetate in Escherichia coli is triggered by carbon catabolite repression of acetyl-CoA synthetase. BMC Syst Biol 4(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-0509-4-166
Waegeman H, Beauprez J, Moens H, Maertens J, De Mey M, Foulquié-Moreno MR, Heijnen JJ, Charlier D, Soetaert W (2011) Effect of iclR and arcA knockouts on biomass formation and metabolic fluxes in Escherichia coli K12 and its implications on understanding the metabolism of Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3). BMC Microbiol 11(1):70. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-11-70
Waegeman H, Maertens J, Beauprez J, De Mey M, Soetaert W (2012) Effect of iclR and arcA deletions on physiology and metabolic fluxes in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3). Biotechnol Lett 34(2):329–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-011-0774-6
Wan X, Volpetti F, Petrova E, French C, Maerkl SJ, Wang B (2019) Cascaded amplifying circuits enable ultrasensitive cellular sensors for toxic metals. Nat Chem Biol 15(5):540–548. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-019-0244-3
Wehrs M, Tanjore D, Eng T, Lievense J, Pray TR, Mukhopadhyay A (2019) Engineering robust production microbes for large-scale cultivation. Trends Microbiol 27(6):524–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2019.01.006
Wei L, Zhao J, Wang Y, Gao J, Du M, Zhang Y, Xu N, Du H, Ju J, Liu Q, Liu J (2022) Engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for high-level gamma-aminobutyric acid production from glycerol by dynamic metabolic control. Metab Eng 69:134–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2021.11.010
Westin MA, Hunt MC, Alexson SE (2005) The identification of a succinyl-CoA thioesterase suggests a novel pathway for succinate production in peroxisomes. J Biol Chem 280(46):38125–38132. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M508479200
Xu P, Vansiri A, Bhan N, Koffas MA (2012) ePathBrick: a synthetic biology platform for engineering metabolic pathways in E. coli. ACS Synth Biol 1(7):256–266. https://doi.org/10.1021/sb300016b
Xu S, Zhang L, Zhou S, Deng Y (2021) Biosensor-based multigene pathway optimization for enhancing the production of glycolate. Appl Environ Microbiol 87(12):e0011321. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00113-21
Zeng X, Chen X, Ren X, Liu Q, Wang L, Sun Q, Tang L, Mao Z (2014) Insights into the role of glucose and glycerol as a mixed carbon source in the improvement of epsilon-poly-L-lysine productivity. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 173(8):2211–2224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1026-8
Zhang X, Zhao Y, Liu Y, Wang J, Deng Y (2020) Recent progress on bio-based production of dicarboxylic acids in yeast. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104(10):4259–4272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10537-8
Zhao M, Huang D, Zhang X, Koffas MAG, Zhou J, Deng Y (2018) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for producing adipic acid through the reverse adipate-degradation pathway. Metab Eng 47:254–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.04.002
Zhao M, Yuan Z, Wu L, Zhou S, Deng Y (2022) Precise prediction of promoter strength based on a de novo synthetic promoter library coupled with machine learning. ACS Synth Biol 11(1):92–102. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.1c00117
Zhou S, Ding R, Chen J, Du G, Li H, Zhou J (2017) Obtaining a panel of cascade promoter-5’-UTR complexes in Escherichia coli. ACS Synth Biol 6(6):1065–1075. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.7b00006
Funding
This work was supported the National Key R&D Program of China (2021YFC2100700), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21877053, 22008088), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20220089), Jiangsu Planned Projects for Postdoctoral Research Funds (2020Z012), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M681485, 2021T140277), and Tianjin Synthetic Biotechnology Innovation Capacity Improvement Project (TSBICIP-KJGG-015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RZ, GL, and YD: conceived, designed the study and experiments. RZ, NC conducted the experiments and analyzed the data. RZ, GL, and YD wrote the manuscript. All authors had read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhi, R., Cheng, N., Li, G. et al. Biosensor-based high-throughput screening enabled efficient adipic acid production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 5427–5438 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12669-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12669-z