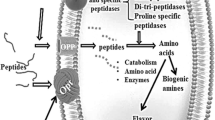
Abstract
Emerging data have suggested that probiotics had good potential in regulating intestinal flora and preventing hypertension. Some studies in human and animal models have demonstrated probiotic intervention could attenuate hypertension, regulate intestinal flora to increase the abundance of beneficial bacteria, and regulate intestinal microbial metabolites such as trimethylamine oxide, short-chain fatty acids, and polyphenols. However, there is still some debate as to whether probiotics exert effective benefits. These recently published reviews did not systematically expound on the heterogeneity between the effect and mechanism of probiotics with different types, doses, and carriers to exert antihypertensive effects, as well as the possible application of probiotics in the prevention and treatment of hypertension in food and clinic. Here we try to systematically review the association between hypertension and intestinal microflora, the effect of probiotics and their metabolites on hypertension, and the recent research progress on the specific mechanism of probiotics on hypertension. In addition, we also summarized the potential application of probiotics in antihypertension. Future challenges include elucidating the functions of metabolites produced by microorganisms and their downstream pathway or molecules, identifying specific strains, not just microbial communities, and developing therapeutic interventions that target hypertension by modulation of gut microbes and metabolites.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abais-Battad JM, Alsheikh AJ, Pan X, Fehrenbach DJ, Dasinger JH, Lund H, Roberts ML, Kriegel AJ, Cowley AW Jr, Kidambi S, Kotchen TA, Liu P, Liang M, Mattson DL (2019) Dietary effects on Dahl salt-sensitive hypertension, renal damage, and the T lymphocyte transcriptome. Hypertension 74(4):854–863
Agerholm-Larsen L, Raben A, Haulrik N, Hansen A, Manders M, Astrup A (2000) Effect of 8 week intake of probiotic milk products on risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. Eur J Clin Nutr 54(4):288–297
Aguilar A (2017) Microbiota under pressure. Nat Rev Nephrol 13(1):3–3
Ahmadmehrabi STWHW (2017) Gut microbiome and its role in cardiovascular diseases. Curr Opin Cardiol 32(6):761
Ahtesh FB, Stojanovska L, Apostolopoulos V (2017) Processing and sensory characteristics of a fermented low-fat skim milk drink containing bioactive antihypertensive peptides, a functional milk product. Int J Dairy Technol 71:230–239
Ahtesh A, Fatah B, Apostolopoulos V, Stojanovska L, Shah N, Mishra V (2018) Effects of fermented skim milk drink by Kluyveromyces marxianus LAF4 co-cultured with lactic acid bacteria to release angiotensinヽonverting enzyme inhibitory activities. Int J Dairy Technol 71:130–140
Alhaj OA (2017) Identification of potential ACE-inhibitory peptides from dromedary fermented camel milk. CyTA-J Food 15(2):191–195
Anselmi G, Gagliardi L, Egidi G, Leone S, Galiuto L (2021) Gut microbiota and cardiovascular diseases: a critical review. Cardiol Rev 29(4):195–204
Antza C, Stabouli S, Kotsis V (2018) Gut microbiota in kidney disease and hypertension. Pharmacol Res 130:198–203
Arya AK, Hu B (2018) Brain–gut axis after stroke. Brain Circ 4(4):165
Aslam H, Marx W, Rocks T, Loughman A, Chandrasekaran V, Ruusunen A, Dawson SL, West M, Mullarkey E, Pasco JA, Jacka FN (2020) The effects of dairy and dairy derivatives on the gut microbiota: a systematic literature review. Gut Microbes 12(1):1799533
Battaglioli EJ, Hale VL, Chen J, Jeraldo P, Ruiz-Mojica C, Schmidt BA, Rekdal VM, Till LM, Huq L, Smits SA, Moor WJ, Jones-Hall Y, Smyrk T, Khanna S, Pardi DS, Grover M, Patel R, Chia N, Nelson H et al (2018) Clostridioides difficile uses amino acids associated with gut microbial dysbiosis in a subset of patients with diarrhea. Sci Transl Med 10(464)
Becattini S, Littmann ER, Carter RA, Kim SG, Morjaria SM, Ling L, Gyaltshen Y, Fontana E, Taur Y, Leiner IM, Pamer EG (2017) Commensal microbes provide first line defense against Listeria monocytogenes infection. J Exp Med 214(7):1973–1989
Beltrán-Barrientos LM, García HS, Hernández-Mendoza A, González-Córdova AF, Vallejo-Cordoba B (2021) Invited review: effect of antihypertensive fermented milks on gut microbiota. J Dairy Sci 104(4):3779–3788
Brial F, Le Lay A, Dumas ME, Gauguier D (2018) Implication of gut microbiota metabolites in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci 75(21):3977–3990
Burokas A, Moloney RD, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2015) Microbiota regulation of the Mammalian gut-brain axis. Adv Appl Microbiol 91:1–62
Cerf-Bensussan N, Gaboriau-Routhiau V (2010) The immune system and the gut microbiota: friends or foes? Nat Rev Immunol 10(10):735–744
Chen M, Sun Q, Giovannucci E, Mozaffarian D, Manson JAE, Willett WC, Hu FB (2014a) Dairy consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes: 3 cohorts of US adults and an updated meta-analysis. BMC Med 12(1):1–14
Chen Y, Liu W, Xue J, Jie Y, Chen X, Shao Y, Kwok LY, Bilige M, Lai M, Zhang H (2014b) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory activity of Lactobacillus helveticus strains from traditional fermented dairy foods and antihypertensive effect of fermented milk of strain H9. J Dairy Sci 97(11):6680–6692
Chen L, Wang L, Li J, Shu G (2021) Antihypertensive potential of fermented milk: the contribution of lactic acid bacteria proteolysis system and the resultant angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptide. Food Funct 12:11121–11131
Cornick S, Kumar M, Moreau F, Gaisano H, Chadee K (2019) VAMP8-mediated MUC2 mucin exocytosis from colonic goblet cells maintains innate intestinal homeostasis. Nature Comm 10(1):4306
de Almeida SM, Mowry FE, Peaden SC, Andrade TU, Biancardi VC (2020) Kefir ameliorates hypertension via gut–brain mechanisms in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Nutr Biochem 77:108318
De Filippis F, Pellegrini N, Vannini L, Jeffery IB, La Storia A, Laghi L, Serrazanetti DI, Di Cagno R, Ferrocino I, Lazzi C, Turroni S, Cocolin L, Brigidi P, Neviani E, Gobbetti M, O'Toole PW, Ercolini D (2016) High-level adherence to a Mediterranean diet beneficially impacts the gut microbiota and associated metabolome. Gut 65(11):1812–1821
Duttaroy AK (2021) Role of gut microbiota and their metabolites on atherosclerosis, hypertension and human blood platelet function: a review. Nutrients 13(1):144
Gallego M, Mora L, Toldrá F (2017) Health relevance of antihypertensive peptides in foods. Curr Opin Food Sci 19:8–14
Ganesh BP, Nelson JW, Eskew JR, Ganesan A, Ajami NJ, Petrosino JF, Bryan RM, Durgan DJ (2018) Prebiotics, probiotics, and acetate supplementation prevent hypertension in a model of obstructive sleep apnea. Hypertension 72(5):1141–1150
Halkjær SI, Christensen AH, Lo BZS, Browne PD, Günther S, Hansen LH, Petersen AM (2018) Faecal microbiota transplantation alters gut microbiota in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: results from a randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled study. Gut 67(12):2107–2115
Hata Y, Yamamoto M, Ohni M, Nakajima K, Nakamura Y, Takano T (1996) A placebo-controlled study of the effect of sour milk on blood pressure in hypertensive subjects. Am J Clin Nutr 64(5):767–771
He M, Shi B (2017) Gut microbiota as a potential target of metabolic syndrome: the role of probiotics and prebiotics. Cell Biosci 7:54
Hou Q, Li C, Liu Y, Li W, Chen Y, Siqinbateer BY, Saqila W, Zhang H, Menghe B (2019) Koumiss consumption modulates gut microbiota, increases plasma high density cholesterol, decreases immunoglobulin G and albumin. J Funct Food 52:469–478
Hsu BB, Gibson TE, Yeliseyev V, Liu Q, Lyon L, Bry L, Silver PA, Gerber GK (2019) Dynamic modulation of the gut microbiota and metabolome by bacteriophages in a mouse model. Cell Host Microbe 25(6):803–814
Isabella VM, Ha BN, Joan CM, Lubkowicz DJ, Rowe SE, Millet YA, Anderson CL, Li N, Fisher A, West KA (2018) Development of a synthetic live bacterial therapeutic for the human metabolic disease phenylketonuria. Nat Biotechnol 36(9):857–864
Jin M, Qian Z, Yin J, Xu W, Zhou X (2019) The role of intestinal microbiota in cardiovascular disease. J Cell Mol Med 23(4):2343–2350
Jin L, Shi X, Yang J, Zhao Y, Xue L, Xu L, Cai J (2021) Gut microbes in cardiovascular diseases and their potential therapeutic applications. Protein Cell 12(5):346–359
Kaye DM, Shihata WA, Jama HA, Tsyganov K, Ziemann M, Kiriazis H, Horlock D, Vijay A, Giam B, Vinh A, Johnson C, Fiedler A, Donner D, Snelson M, Coughlan MT, Phillips S, Du XJ, El-Osta A, Drummond G et al (2020) Deficiency of prebiotic fiber and insufficient signaling through gut metabolite-sensing receptors leads to cardiovascular disease. Circulation 141(17):1393–1403
Kechagia M, Basoulis D, Konstantopoulou S, Dimitriadi D, Gyftopoulou K, Skarmoutsou N, Fakiri EM (2013) Health benefits of probiotics: a review. Int Sch Res Notices 2013:7. https://doi.org/10.5402/2013/481651
Khalesi S, Sun J, Buys N, Jayasinghe R (2014) Effect of probiotics on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Hypertension 64(4):897–903
Koh A, Bckhed F (2020) From association to causality: the role of the gut microbiota and its functional products on host metabolism. Mol Cell 78(4):584–596
Koutsos A, Tuohy KM, Lovegrove JA (2015) Apples and cardiovascular health—is the gut microbiota a core consideration? Nutrients 7(6):3959–3998
Lankelma JM, van Vught LA, Belzer C, Schultz MJ, van der Poll T, de Vos WM, Wiersinga WJ (2017) Critically ill patients demonstrate large interpersonal variation in intestinal microbiota dysregulation: a pilot study. Intensive Care Med 43(1):59–68
Leblanc JG, Chain F, Martín R, Bermúdez-Humarán L, Langella P (2017) Beneficial effects on host energy metabolism of short-chain fatty acids and vitamins produced by commensal and probiotic bacteria. Microbial Cell Fact 16(1):1–10
Lewis-Mikhael AM, Davoodvandi A, Jafarnejad S (2020) Effect of Lactobacillusplantarum containing probiotics on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharmacological Res 153
Li C, Kwok LY, Mi Z, Bala J, Xue J, Jie Y, Ma Y, Zhang H, Chen Y (2017a) Characterization of the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory activity of fermented milks produced with Lactobacillus casei. J Dairy Sci 100(12):9495–9507
Li J, Zhao F, Wang Y, Chen J, Tao J, Tian G, Wu S, Liu W, Cui Q, Geng B (2017b) Gut microbiota dysbiosis contributes to the development of hypertension. Microbiome 5(1):1–19
Li Y, Wang L, Feng X, Zhang M, Huang Z, Deng Q, Zhou M, Astell-Burt T, Wang L (2018) Geographical variations in hypertension prevalence, awareness, treatment and control in China: findings from a nationwide and provincially representative survey. J Hypertens 36(1):178–187
Li H, Xie X, Li Y, Chen M, Xue L, Wang J, Zhang J, Wu S, Ye Q, Zhang S (2021) Pediococcus pentosaceus IM96 exerts protective effects against enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157: H7 infection in vivo. Foods 10(12):2945
Liang Y, Zhan J, Liu D, Luo M, Han J, Liu X, Liu C, Cheng Z, Zhou Z, Wang P (2019) Organophosphorus pesticide chlorpyrifos intake promotes obesity and insulin resistance through impacting gut and gut microbiota. Microbiome 7(1):19
Liang T, Wu L, Xi Y, Li Y, Xie X, Fan C, Yang L, Yang S, Chen X, Zhang J (2021) Probiotics supplementation improves hyperglycemia, hypercholesterolemia, and hypertension in type 2 diabetes mellitus: an update of meta-analysis. Crit Rev Food Sci 61(10):1670–1688
Marco ML, Heeney D, Binda S, Cifelli CJ, Cotter PD, Foligné B, Gänzle M, Kort R, Pasin G, Pihlanto A, Smid EJ (2017) Health benefits of fermented foods: microbiota and beyond. Curr Opin Biotechnol 44:94–102
Marques FZ, Nelson E, Chu PY, Horlock D, Fiedler A, Ziemann M, Tan JK, Kuruppu S, Rajapakse NW, El-Osta A, Mackay CR, Kaye DM (2017) High-fiber diet and acetate supplementation change the gut microbiota and prevent the development of hypertension and heart failure in hypertensive mice. Circulation 135(10):964–977
Masson GS, Nair AR, Soares P, Michelini LC, Francis J (2015) Aerobic training normalizes autonomic dysfunction, HMGB1 content, microglia activation and inflammation in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus of SHR. Am J Physiol-Heart Circul Physiol 309(7):H1115–H1122
Min L, Qinghua H, Jinglu Y (2018) Trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) increased aquaporin-2 expression in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Clin Exp Hypertens 41(4):1–11
Mukherjee S, Joardar N, Sengupta S, Babu S (2018) Gut microbes as future therapeutics in treating inflammatory and infectious diseases: lessons from recent findings. J Nutr Biochem 61:111–128
Naruszewicz M, Johansson M-L, Zapolska-Downar D, Bukowska H (2002) Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum 299v on cardiovascular disease risk factors in smokers. Am J Clin Nutr 76(6):1249–1255
Natarajan N, Hori D, Flavahan S, Steppan J, Flavahan NA, Berkowitz DE, Pluznick JL (2016) Microbial short chain fatty acid metabolites lower blood pressure via endothelial G-protein coupled receptor 41. Physiol Genomics 48(11):826–834
Odamaki T, Bottacini F, Kato K, Mitsuyama E, Yoshida K, Horigome A, Xiao JZ, van Sinderen D (2018) Genomic diversity and distribution of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum across the human lifespan. Scie Rep 8(1):85
Perkins DJ, Richard K, Hansen AM, Lai W, Nallar S, Koller B, Vogel SN (2018) Autocrine-paracrine prostaglandin E(2) signaling restricts TLR4 internalization and TRIF signaling. Nat Immun 19(12):1309–1318. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-018-0243-7
Qato DM, Ozenberger O (2018) Prevalence of prescription medications with depression as a potential adverse effect among adults in the United States. JAMA-J Am Med Assoc 319(22):2289–2298
Richards EM, Pepine CJ, Raizada MK, Kim S (2017) The gut, its microbiome, and hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep 19(4):1–11
Robles-Vera I, Toral M, de la Visitación N, Sánchez M, Romero M, Olivares M, Jiménez R, Duarte J (2018) The probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum prevents dysbiosis and vascular oxidative stress in rats with hypertension induced by chronic nitric oxide blockade. Mol Nutr Food Res 62(19):1800298
Robles-Vera I, Toral M, Ndl V, Sánchez M, Duarte J (2020) Probiotics prevent dysbiosis and the rise in blood pressure in genetic hypertension: role of short-chain fatty acids. Mol Nutr Food Res 64(6):1900616
Santisteban MM, Kim S, Pepine CJ, Raizada MK (2016) Brain-gut-bone marrow axis: implications for hypertension and related therapeutics. Circ Res 118(8):1327–1336
Sharafedtinov KK, Plotnikova OA, Alexeeva RI, Sentsova TB, Songisepp E, Stsepetova J, Smidt I, Mikelsaar M (2013) Hypocaloric diet supplemented with probiotic cheese improves body mass index and blood pressure indices of obese hypertensive patients-a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled pilot study. Nutr J 12(1):1–11
Shen XZ, Li Y, Li L, Shah KH, Bernstein KE, Lyden P, Shi P (2015) Microglia participate in neurogenic regulation of hypertension. Hypertension 66(2):309–316
Shkoporov AN, Hill C (2019) Bacteriophages of the human gut: the “known unknown” of the microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 25(2):195–209
Silva-Cutini MA, Almeida SA, Nascimento AM, Abreu GR, Bissoli NS, Lenz D, Endringer DC, Brasil GA, Lima EM, Biancardi VC (2019) Long-term treatment with kefir probiotics ameliorates cardiac function in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Nutr Biochem 66:79–85
Solak Y, Afsar B, Vaziri ND, Aslan G, Yalcin CE, Covic A, Kanbay M (2016) Hypertension as an autoimmune and inflammatory disease. Hypertens Res : Official J Jap Soc Hypertens 39(8):567–573
Stumpff F (2018) A look at the smelly side of physiology: transport of short chain fatty acids. Pflügers Archiv - European J Physiol 470(4):571–598
Sun L, Xie C, Wang G, Wu Y, Wu Q, Wang X, Liu J, Deng Y, Xia J, Chen B, Zhang S, Yun C, Lian G, Zhang X, Zhang H, Bisson WH, Shi J, Gao X, Ge P et al (2018) Gut microbiota and intestinal FXR mediate the clinical benefits of metformin. Nat Med 24(12):1919–1929
Tillisch K, Labus J, Kilpatrick L, Jiang Z, Mayer EA (2013) Consumption of fermented milk product with probiotic modulates brain activity. Gastroenterology 144(7):1394–1401
Upadrasta A, Madempudi RS (2016) Probiotics and blood pressure: current insights. Integr Blood Press C 2016(9):33–42
Verhaar BJ, Prodan A, Nieuwdorp M, Muller M (2020) Gut microbiota in hypertension and atherosclerosis: a review. Nutrients 12(10):2982
Wang Z, Cheng C, Yang X, Zhang C (2021) L-phenylalanine attenuates high salt-induced hypertension in Dahl SS rats through activation of GCH1-BH4. Plos One 16(4):e0250126
Wilck N, Matus MG, Kearney SM, Olesen SW, Müller D (2017) Salt-responsive gut commensal modulates TH17 axis and disease. Nature 551(7682):585–589
Worsztynowicz P, Białas W, Grajek W (2020) Integrated approach for obtaining bioactive peptides from whey proteins hydrolysed using a new proteolytic lactic acid bacteria. Food Chem 312:126035
Wu H, Jiang L, Shum T-F, Chiou J (2022) Elucidation of anti-hypertensive mechanism by a novel Lactobacillus rhamnosus AC1 fermented soymilk in the deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt hypertensive rats. Nutrients 14(15):3174
Xia Y, Yu J, Xu W, Shuang Q (2020) Purification and characterization of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides isolated from whey proteins of milk fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum QS670. J Dairy Sci 103(6):4919–4928
Yan X, Jin J, Su X, Yin X, Gao J, Wang X, Zhang S, Bu P, Wang M, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Zhang Q (2020) Intestinal flora modulates blood pressure by regulating the synthesis of intestinal-derived corticosterone in high salt-induced hypertension. Circ Res 126(7):839–853. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.119.316394
Yang T, Santisteban MM, Rodriguez V, Li E, Ahmari N, Carvajal JM, Zadeh M, Gong M, Qi Y, Zubcevic J (2015) Gut dysbiosis is linked to hypertension. Hypertension 65(6):1331–1340
Yang T, Richards EM, Pepine CJ, Raizada MK (2018) The gut microbiota and the brain-gut-kidney axis in hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 14(7):442–456
Yang L, Xie X, Li Y, Wu L, Wu Q (2021) Evaluation of the cholesterol-lowering mechanism of Enterococcus faecium strain 132 and Lactobacillus paracasei strain 201 in hypercholesterolemia rats. Nutrients 13(6):1982
Ying H, Wang X, Wang J, Wu F, Sui Y, Yang L, Wang Z (2013) Lactobacillus plantarum strains as potential probiotic cultures with cholesterol-lowering activity. J Dairy Sci 96(5):2746–2753
Yuan L, Li Y, Chen MT, Xue L, Wang J, Ding Y, Zhang JM, Wu S, Ye QH, Zhang SH, Yang RS, Zhao H, Wu L, Liang TT, Xie XQ, Wu QP (2022) Antihypertensive Activity of Milk Fermented by Lactiplantibacillus plantarum SR37-3 and SR61-2 in L-NAME-Induced Hypertensive Rats. Foods 11(15)
Zhong HJ, Zeng HL, Cai YL, Zhuang YP, Liou YL, Wu Q, He XX (2021) Washed microbiota transplantation lowers blood pressure in patients with hypertension. Frontiers Cell Infect Microbiol 11
Funding
This research was jointly funded by Guangdong Province “Pearl River Talents” Local Innovation Team (2017BT01S174), Project by the Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory (2020B121201009), and the GDAS’ Project of Science and Technology Development (2020GDASYL-20200301002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.L. drafted this review. X.X. and Q.W. guided review writing. L.Y. wrote the manuscript. M.C., L.X., J.W., Y.D., Q.G., J.Z., R.Y., and H.Z. conducted language modification. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, L., Li, Y., Chen, M. et al. Effects of probiotics on hypertension. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 1107–1117 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12369-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12369-8