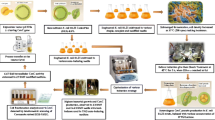
Abstract
To improve β-1,3–1,6-D-glucan (β-glucan) production by Aureobasidium pullulans, an Agrobacterium tumefaciens–mediated transformation method was developed to screen a mutant A. pullulans CGMCC 19650. Based on thermal asymmetric–interlaced PCR detection, DNA sequencing, BLAST analysis, and quantitative real-time PCR assay, the T-DNA was identified to be inserted in the coding region of mal31 gene, which encodes a sugar transporter involved in pullulan biosynthesis in the mutant. The maximal biomass and β-glucan production under batch fermentation were significantly increased by 47.6% and 78.6%, respectively, while pullulan production was decreased by 41.7% in the mutant, as compared to the parental strain A. pullulans CCTCC M 2012259. Analysis of the physiological mechanism of these changes revealed that mal31 gene disruption increased the transcriptional levels of pgm2, ugp, fks1, and kre6 genes; increased the amounts of key enzymes associated with UDPG and β-glucan biosynthesis; and improved intracellular UDPG contents and energy supply, all of which favored β-glucan production. However, the T-DNA insertion decreased the transcriptional levels of ags2 genes, and reduced the biosynthetic capability to form pullulan, resulting in the decrease in pullulan production. This study not only provides an effective approach for improved β-glucan production by A. pullulans, but also presents an accurate and useful gene for metabolic engineering of the producer for efficient polysaccharide production.
Key points
• A mutant A. pullulans CGMCC 19650 was screened by using the ATMT method.
• The mal31 gene encoding a sugar transporter was disrupted in the mutant.
• β-Glucan produced by the mutant was significantly improved.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Bohn JA, BeMiller JN (1995) (1→3)-β-D-glucans as biological response modifiers: a review of structure-functional activity relationships. Carbohydr Polym 28:3–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/0144-8617(95)00076-3
Bundock P, den Dulk-Ras A, Beijersbergen A, Hooykaas PJ (1995) Trans-kingdom T-DNA transfer from Agrobacterium tumefaciens to Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J 14(13):3206–3214. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07323.x
Chan G, Chan W, Sze D (2009) The effects of β-glucan on human immune and cancer cells. J Hematol Oncol 2(1):25. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-8722-2-25
Chen X, Wang Q, Liu N, Liu G, Chi Z, Chi Z (2017) A glycosyltransferase gene responsible for pullulan biosynthesis in Aureobasidium melanogenum P16. Int J Biol Macromol 95:539–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.11.081
Chen TJ, Liu GL, Wei X, Wang K, Hu Z, Chi Z, Chi ZM (2020) A multidomain α-glucan synthetase 2 (AmAgs2) is the key enzyme for pullulan biosynthesis in Aureobasidium melanogenum P16. Int J Biol Macromol 150:1037–1045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.10.108
Choi JS, Kim JW, Jung GW, Moon SB, Cho HR, Sung SH, Jung JJ, Kwon YS, Ku SK, Sohn JH (2016) Effect of a β-glucan from Aureobasidiumon TGF-β1-modulated in vitro dermal wound repair. Toxicol Environ Heal Sci 8(1):12–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-016-0257-1
Covert SF, Kapoor P, Lee M, Briley A, Nairn CJ (2001) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Fusarium circinatum. Mycol Res 105(3):259–264. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0953756201003872
Dietvorst J, Walsh MC, van Heusden GP, Steensma HY (2010) Comparison of the MTT1- and MAL31-like maltose transporter genes in lager yeast strains. FEMS Microbial Lett 310(2):152–157. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2010.02056.x
Donzis BA (1996) Substantially purified beta (1,3) finely ground yeast cell wall glucan composition with dermatological and nutritional uses. US 5576015
Douglas CM, Foor F, Marrinan JA, Morin N, Nielsen JB, Dahl AM, Mazur P, Baginsky W, Li W, El-Sherbeini M, Clemas JA, Mandala SM, Frommer BR, Kurtz MB (1994) The Saccharomyces cerevisiae FKS1 (ETG1) gene encodes an integral membrane protein which is a subunit of 1,3-beta-D-glucan synthase. P Natl Acad Sci USA 91:12907–12911. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.91.26.12907
Du B, Lin C, Bian Z, Xu B (2015) An insight into anti-inflammatory effects of fungal beta-glucans. Trends Food Sci Tech 41:49–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2014.09.002
Duan XH, Chi ZM, Wang L, Wang XH (2008) Influence of different sugars on pullulan production and activity of α-phosphoglucose mutase UDPG-pyrophosphorylase and glucosyltransferase involved in pullulan synthesis in Aureobasidium pullulans Y68. Carbohydr Polym 73:587–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.12.028
Feng J, Li T, Zhang X, Chen J, Zhao T, Zou X (2019) Efficient production of polymalic acid from xylose mother liquor, an environmental waste from the xylitol industry, by a T-DNA-based mutant of Aureobasidium pullulans. Appl Microbiol Biot 103(16):6519–6527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09974-x
Figueiredo JG, Goulin EH, Tanaka F, Stringari D, Kava-Cordeiro V, Galli-Terasawa LV, Staats CC, Schrank A, Glienke C (2010) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Guignardia citricarpa. J Microbiol Meth 80(2):143–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2009.11.014
Freitas F, Torres CAV, Reis MAM (2017) Engineering aspects of microbial exopolysaccharide production. Bioresource Tech 245:1674–1683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.092
Gostinčar C, Ohm RA, Kogej T, Sonjak S, Turk M, Zajc J, Zalar P, Grube M, Sun H, Han J, Sharma A, Chiniquy J, Ngan CY, Lipzen A, Barry K, Grigoriev IV, Gunde-Cimerman N (2014) Genome sequencing of four Aureobasidium pullulans varieties: biotechnological potential, stress tolerance, and description of new species. BMC Genomics 15:549. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-549
Guo J, Wang Y, Li B, Huang S, Chen Y, Guo X, Xiao D (2017) Development of a one-step gene knock-out and knock-in method for metabolic engineering of Aureobasidium pullulans. J Biotechnol 251:145–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.04.029
Hamada N, Deguchi K, Ohmoto T, Sakai K, Ohe T, Yoshizumi H (2000) Ascorbic acid stimulation of production of a highly branched β-1,3-glucan by Aureobasidium pullulans K-1: oxalic acid, a metabolite of ascorbic acid as the stimulating substance. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:1801–1806. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.64.1801
Hirabayashi K, Kondo N, Hayashi S (2016) Characterization and enzymatic hydrolysis of hydrothermally treated β-1,3–1,6-glucan from Aureobasidium pullulans. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 32:206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-016-2167-4
Horák J (2013) Regulations of sugar transporters: insights from yeast. Curr Genet 59:1–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-013-0388-8
Imshenetskii AA, Kondrateva TF, Kudryashev LI, Yarovaya SM, Smutko AN, Alekseeva GS (1983) A comparative study of pullulans synthesized by strains of Pullularia (Aureobasidium) pullulans of differing levels of ploidy. Mikrobiologiia 52:816–820
Iswarya A, Anjugam M, Shanthini S, Vaseeharan B (2019) Protective activity of beta-1,3-glucan binding protein against AAPH induced oxidative stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Int J Biol Macromol 138:890–902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.07.130
Jayachandran M, Chen J, Chung SSM, Xu B (2018) A critical review on the impacts of β-glucans on gut microbiota and human health. J Nutr Biochem 61:101–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.06.010
Ju XM, Wang DH, Zhang GC, Cao D, Wei GY (2015) Efficient pullulan production by bioconversion using Aureobasidium pullulans as the whole-cell catalyst. Appl Microbiol Biot 99(1):211–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6100-1
Kang B, Yang H, Choi N, Ahn K, Park C, Yoon B, Kim M (2010) Production of pure β-glucan by Aureobasidium pullulans after pullulan synthetase gene disruption. Biotechnol Lett 32(1):137–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-0127-x
Kono H, Kondo N, Hirabayashi K, Ogata M, Totani K, Ikematsu S, Osada M (2017) NMR spectroscopic structural characterization of a water-soluble β-(1→3, 1→6)-glucan from Aureobasidium pullulans. Carbohydr Polym 174:876–886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.07.018
Kurita T, Noda Y, Takagi T, Osumi M, Yoda K (2011) Kre6 protein essential for yeast cell wall β-1,6-glucan synthesis accumulates at sites of polarized growth. J Biol Chem 286(9):7429–7438. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.174060
Leclerque A, Wan H, Abschütz A, Chen S, Mitina GV, Zimmermann G, Schairer HU (2004) Agrobacterium-mediated insertional mutagenesis (AIM) of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. Curr Genet 45(2):111–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-003-0468-2
Liu YG, Mitsukawa N, Oosumi T, Whittier RF (1995) Efficient isolation and mapping of Arabidopsis thaliana T-DNA insert junctions by thermal asymmetric interlaced PCR. Plant J 8(3):457–463. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1995.08030457.X
Lotrakul P, Unhapattaratitikul P, Seelanan T, Prasongsuk S, Punnapayak H (2013) An aubasidan-like β-glucan produced by Aureobasidium pullulans in Thailand. ScienceAsia 39(4):363–368. https://doi.org/10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.2013.39.363
Lv B, Zheng L, Liu H, Tang J, Hsiang T, Huang J (2016) Use of random T-DNA mutagenesis in identification of gene UvPRO1, a regulator of conidiation, stress response, and virulence in Ustilaginoidea virens. Front Microbiol 7:2086. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.02086
Michielse CB, Hooykaas PJ, van den Hondel CA, Ram AF (2005) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation as a tool for functional genomics in fungi. Curr Genet 48:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-005-0578-0
Moriya N, Moriya Y, Nomura H, Kusano K, Asada Y, Uchiyama H, Park EY, Okabe M (2013) Improved β-glucan yield using an Aureobasidium pullulans M-2 mutant strain in a 200-L pilot scale fermentor targeting industrial mass production. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 18:1083–1089. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-013-0516-9
Morioka LRI, Furlaneto MC, Bogas AC, Pompermayer P, Duarte RTD, Vieira MLC, Watanabe MAE, Fungaro MHP (2006) Efficient genetic transformation system for the ochratoxigenic fungus Aspergillus carbonarius. Curr Microbiol 52(6):469–472. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-005-0402-6
Nai YS, Lee MR, Kim S, Lee SJ, Kim JC, Yang YT, Kim JS (2017) Relationship between expression level of hygromycin B-resistant gene and Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation efficiency in Beauveria bassiana JEF-007. J Appl Microbiol 123(3):724–731. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13529
Papaspyridi LM, Zerva A, Topakas E (2018) Biocatalytic synthesis of fungal β-glucans. Catalysts 8(7):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8070274
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW, Dempfle L (2002) Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 30:e36. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/30.9.e36
Rieder A, Ballance S, Böcker U, Knutsen S (2018) Quantification of 1,3-β-D-glucan from yeast added as a functional ingredient to bread. Carbohydr Polym 181:34–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.09.044
Rout D, Mondal S, Chakraborty I, Islam SS (2008) The structure and conformation of a water-insoluble (1→3)-, (1→6)-β-D-glucan from the fruiting bodies of Pleurotus florida. Carbohydr Res 343:982–987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2007.12.022
Schimoler-O’Rourke R, Renault S, Mo WJ, Selitrennikoff CP (2003) Neurospora crassa FKS protein binds to the (1,3)beta-glucan synthase substrate. UDP-Glucose Curr Microbiol 46(6):408–412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-002-3884-5
Shingel KI (2004) Current knowledge on biosynthesis, biological activity, and chemical modification of the exopolysaccharide, pullulan. Carbohyd Res 339(3):447–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2003.10.034
Singh RS, Saini GKa, Kennedy JF (2008) Pullulan: microbial sources, production and applications. Carbohydr Polym 73:515–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2008.01.003
Sugui JA, Chang YC, Kwon-Chung KJ (2005) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Aspergillus fumigatus: an efficient tool for insertional mutagenesis and targeted gene disruption. Appl Environ Microb 71(4):1798–1802. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.4.1798-1802.2005
Sugumaran KR, Ponnusami V (2017) Review on production, downstream processing and characterization of microbial pullulan. Carbohydr Polym 173:573–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.06.022
Tu GW, Wang YK, Feng J, Li XR, Guo MJ, Zou X (2015) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Aureobasidium pullulans and high-efficient screening for polymalic acid producing strain. Chin J Biotech 31(7):1063–1072. https://doi.org/10.13345/j.cjb.140594
Uchiyama H, Iwai A, Dohra H, Ohnishi T, Kato T, Park EY (2018) The effects of gene disruption of Kre6-like proteins on the phenotype of β-glucan-producing Aureobasidium pullulans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:4467–4475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8947-z
Wang DY, He D, Li GQ, Gao S, Lv HY, Shan QS, Wang L (2014) An efficient tool for random insertional mutagenesis: Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of the filamentous fungus Aspergillus terreus. J Microbio Meth 98:114–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2014.01.007
Wang D, Bian J, Wei G, Jiang M, Dong M (2016) Simultaneously enhanced production and molecular weight of pullulan using a two-stage agitation speed control strategy. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 91:467–475. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4600
Wang DH, Ni TF, Ju XM, Wei GY (2018) Sodium chloride improves pullulan production by Aureobasidium pullulans but reduces the molecular weight of pullulan. Appl Microbiol Biot 102:8921–8930. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9292-y
Wang D, Zhu C, Zhang G, Wang C, Wei G (2020) Enhanced β-glucan and pullulan production by Aureobasidium pullulans with zinc sulfate supplementation. Appl Microbiol Biot 104:1751–1760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10326-y
Wang Y, Wang D, Wei G, Shao N (2012) Enhanced co-production of S-adenosylmethionine and glutathione by an ATP-oriented amino acid addition strategy. Bioresource Tech 107:19–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.12.030
Wu SJ, Kim JM, Zhou C, Jin ZY, Tong QY (2010) Estimation of pullulan by hydrolysis with pullulanase. Biotechnol Lett 32:1143–1145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-010-0272-2
Yang YH, Kang HW, Ro HS (2014) Cloning and molecular characterization of beta-1,3-glucan synthase from Sparassis crispa. Mycobiology 42(2):167–173. https://doi.org/10.5941/MYCO.2014.42.2.167
Yu X, Wang Y, Wei G, Dong Y (2012) Media optimization for elevated molecular weight and mass production of pigment-free pullulan. Carbohydr Polym 89:928–934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.04.038
Yurlova NA, de Hoog GS (1997) A new variety of Aureobasidium pullulans characterized by exopolysaccharide structure, nutritional physiology and molecular features. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 72:141–147. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1000212003810
Zhang G, Wang G, Zhu C, Wang C, Wang D, Wei G (2020) Metabolic flux and transcriptome analyses provide insights into the mechanism underlying zinc sulfate improved β-1,3-D-glucan production by Aureobasidium pullulans. Int J Biol Macromol 164:140–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.131
Zhang Y, Qu H, Zhao P, Tang Y, Zhou J, Luo S, Yin Y, Chen G (2017) Generation and screening of T-DNA insertion mutants mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens in the garden asparagus stem blight pathogen Phomopsis asparagi. Curr Microbiol 74(11):1270–1277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-017-1312-0
Zhang YJ, Zhao JJ, Xie M, Peng DL (2014) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation in the entomopathogenic fungus Lecanicillium lecanii and development of benzimidazole fungicide resistant strains. J Microbiol Meth 105:168–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2014.07.033
Zhong YH, Wang XL, Wang TH, Jiang Q (2007) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation (AMT) of Trichoderma reesei as an efficient tool for random insertional mutagenesis. Appl Microbiol Biot 73(6):1348–1354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0603-3
Zhou X, He J, Wang L, Wang Y, Du G, Kang Z (2019) Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to improve glucan biosynthesis. J Microbiol Biotechnol 29(5):758–764. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1812.12049
Zhu F, Du B, Xu B (2016) A critical review on production and industrial applications of beta-glucans. Food Hydrocoll 52:275–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.07.003
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21776189), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20181440), and a Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XZ and GYW conceived and designed research. XC, YW, and CYH conducted experiments. GCZ and CLW analyzed the data. XC and DHW wrote the manuscript. XZ and GYW reviewed and edited the manuscript. DHW and GYW administrated project and acquired funding. All authors read and approved the final version of manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Wang, Y., He, CY. et al. Improved production of β-glucan by a T-DNA–based mutant of Aureobasidium pullulans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105, 6887–6898 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11538-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11538-x