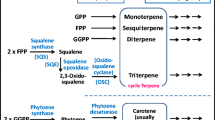
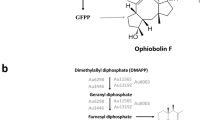
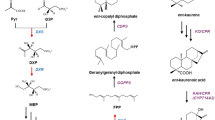
Abstract
Pathway engineering is a useful technology for producing desired compounds on a large scale by modifying the biosynthetic pathways of host organisms using genetic engineering. We focused on acetoacetate esters as novel low-cost substrates and established an efficient terpenoid production system using pathway-engineered recombinant Escherichia coli. Functional analysis using recombinant E. coli proteins of 18 carboxylesterases identified from the microbial esterases and lipases database showed that the p-nitrobenzyl esterase (PnbA) from Bacillus subtilis specifically hydrolyzed two acetoacetate esters: methyl acetoacetate (MAA) and ethyl acetoacetate (EAA). We generated a plasmid (pAC-Mev/Scidi/Aacl/PnbA) co-expressing PnbA and six enzymes of the mevalonate pathway gene cluster from Streptomyces, isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase type I from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and acetoacetyl-coenzyme A ligase from Rattus norvegicus. The plasmid pAC-Mev/Scidi/Aacl/PnbA was introduced into E. coli along with plasmid expressing carotenoid (lycopene) or sesquiterpene (β-bisabolene) biosynthesis genes, and the terpenoid production was evaluated following the addition of acetoacetate esters as substrates. These recombinant E. coli strains used MAA and EAA as substrates for the biosynthesis of terpenoids and produced almost equivalent concentrations of target compounds compared with the previous production system that used mevalonolactone and lithium acetoacetate. The findings of this study will enable the production of useful terpenoids from low-cost substrates, which may facilitate their commercial production on an industrial scale in the future.
Key points
• PnbA from Bacillus subtilis exhibits acetoacetate hydrolysis activity.
• A plasmid enabling terpenoid synthesis from acetoacetate esters was constructed.
• Acetoacetate esters as substrates enable a low-cost production of terpenoids.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available at reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Ajikumar PK, Tyo K, Carlsen S, Mucha O, Phon TH, Stephanopoulos G (2008) Terpenoids: opportunities for biosynthesis of natural product drugs using engineered microorganisms. Mol Pharm 5:167–190. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp700151b
Albrecht M, Misawa N, Sandmann G (1999) Metabolic engineering of the terpenoid biosynthetic pathway of Escherichia coli for production of the carotenoids β-carotene and zeaxanthin. Biotechnol Lett 21:791–795. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005547827380
Alper H, Fischer C, Nevoigt E, Stephanopoulos G (2005a) Tuning genetic control through promoter engineering. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:12678–12683. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0504604102
Alper H, Jin YS, Moxley JF, Stephanopoulos G (2005b) Identifying gene targets for the metabolic engineering of lycopene biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Metab Eng 7:155–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2004.12.003
Alper H, Miyaoku K, Stephanopoulos G (2005c) Construction of lycopene-overproducing E. coli strains by combining systematic and combinatorial gene knockout targets. Nat Biotechnol 23:612–616. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1083
Arpigny JL, Jaeger KE (1999) Bacterial lipolytic enzymes: classification and properties. Biochem J 343(Pt 1):177–183
Chen YR, Usui S, Queener SW, Yu CA (1995) Purification and properties of a p-nitrobenzyl esterase from Bacillus subtilis. J Ind Microbiol 15:10–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01570007
Choi S, Nishida Y, Matsuda S, Adachi K, Kasai H, Peng X, Komemushi S, Miki W, Misawa N (2005) Characterization of β-carotene ketolases, CrtW, from marine bacteria by complementation analysis in Escherichia coli. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 7:515–522. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-004-5100-z
Croteau R, Ketchum REB, Long RM, Kaspera R, Wildung MR (2006) Taxol biosynthesis and molecular genetics. Phytochem Rev 5:75–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-005-3748-2
Cui YH, Wei P, Peng F, Zong MH, Lou WY (2018) Efficient biocatalytic stereoselective reduction of methyl acetoacetate catalyzed by whole cells of engineered E. coli. RSC Adv 8:9970–9978. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra00883c
Fujisawa M, Harada H, Kenmoku H, Mizutani S, Misawa N (2010) Cloning and characterization of a novel gene that encodes (S)-β-bisabolene synthase from ginger, Zingiber officinale. Planta 232:121–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1137-6
George KW, Thompson MG, Kim J, Baidoo EEK, Wang G, Benites VT, Petzold CJ, Chan LJG, Yilmaz S, Turhanen P, Adams PD, Keasling JD, Lee TS (2018) Integrated analysis of isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) toxicity in isoprenoid-producing Escherichia coli. Metab Eng 47:60–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.03.004
Giver L, Gershenson A, Freskgard PO, Arnold FH (1998) Directed evolution of a thermostable esterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:12809–12813. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.22.12809
Gonzalez CF, Proudfoot M, Brown G, Korniyenko Y, Mori H, Savchenko AV, Yakunin AF (2006) Molecular basis of formaldehyde detoxification: characterization of two S-formylglutathione hydrolases from Escherichia coli, FrmB and YeiG. J Biol Chem 281:14514–14522. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M600996200
Harada H, Misawa N (2009) Novel approaches and achievements in biosynthesis of functional isoprenoids in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84:1021–1031. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2166-6
Harada H, Yu F, Okamoto S, Kuzuyama T, Utsumi R, Misawa N (2009) Efficient synthesis of functional isoprenoids from acetoacetate through metabolic pathway-engineered Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81:915–925. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1724-7
Jackson H, Braun CL, Ernst H (2008) The chemistry of novel xanthophyll carotenoids. Am J Cardiol 101:S50–S57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2008.02.008
Kajiwara S, Fraser PD, Kondo K, Misawa N (1997) Expression of an exogenous isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase gene enhances isoprenoid biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Biochem J 324:421–426. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj3240421
Kanda T, Miyata N, Fukui T, Kawamoto T, Tanaka A (1998) Doubly entrapped baker’s yeast survives during the long-term stereoselective reduction of ethyl 3-oxobutanoate in an organic solvent. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 49:377–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051185
Kang HY, Kim JF, Kim MH, Park SH, Oh TK, Hur CG (2006) MELDB: a database for microbial esterases and lipases. FEBS Lett 580:2736–2740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2006.04.034
Kusama H, Hara R, Kawahara S, Nishimori T, Kashima H, Nakamura N, Morihira K, Kuwajima I (2000) Enantioselective total synthesis of (-)-taxol. J Am Chem Soc 122:3811–3820. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja9939439
Liao P, Hemmerlin A, Bach TJ, Chye ML (2016) The potential of the mevalonate pathway for enhanced isoprenoid production. Biotechnol Adv 34:697–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.03.005
Martin VJJ, Pitera DJ, Withers ST, Newman JD, Keasling JD (2003) Engineering a mevalonate pathway in Escherichia coli for production of terpenoids. Nat Biotechnol 21:796–802. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt833
Misawa N (2009) Pathway engineering of plants toward astaxanthin production. Plant Biotechnol 26:93–99. https://doi.org/10.5511/plantbiotechnology.26.93
Misawa N (2011) Pathway engineering for functional isoprenoids. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22:627–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2011.01.002
Misawa N, Nakagawa M, Kobayashi K, Yamano S, Izawa Y, Nakamura K, Harashima K (1990) Elucidation of the Erwinia uredovora carotenoid biosynthetic pathway by functional analysis of gene products expressed in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 172:6704–6712
Moore JC, Arnold FH (1996) Directed evolution of a para-nitrobenzyl esterase for aqueous-organic solvents. Nat Biotechnol 14:458–467. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0496-458
Nakashimada Y, Kubota H, Takayose A, Kakizono T, Nishio N (2001) Asymmetric reduction of ethyl acetoacetate to ethyl (R)-3-hydroxybutyrate coupled with nitrate reduction by Paracoccus denitrificans. J Biosci Bioeng 91:368–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1389-1723(01)80153-5
Navale GR, Dharne MS, Shinde SS (2021) Metabolic engineering and synthetic biology for isoprenoid production in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105:457–475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-11040-w
Pesaresi A, Devescovi G, Lamba D, Venturi V, Degrassi G (2005) Isolation, characterization, and heterologous expression of a carboxylesterase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Curr Microbiol 50:102–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-004-4414-4
Quax WJ, Broekhuizen CP (1994) Development of a new Bacillus carboxyl esterase for use in the resolution of chiral drugs. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 41:425–431. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00939031
Roberts SC (2007) Production and engineering of terpenoids in plant cell culture. Nat Chem Biol 3:387–395. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2007.8
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3th edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York
Sezonov G, Joseleau-Petit D, D’Ari R (2007) Escherichia coli physiology in Luria-Bertani broth. J Bacteriol 189:8746–8749. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01368-07
Wang XT, Chen XH, Xu Y, Lou WY, Wu H, Zong MH (2013) Biocatalytic anti-Prelog stereoselective reduction of ethyl acetoacetate catalyzed by whole cells of Acetobacter sp. CCTCC M209061. J Biotechnol 163:292–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2012.10.023
White NJ (2008) Qinghaosu (artemisinin): the price of success. Science 320:330–334. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1155165
Yuan LZ, Rouvière PE, Larossa RA, Suh W (2006) Chromosomal promoter replacement of the isoprenoid pathway for enhancing carotenoid production in E. coli. Metab Eng 8:79–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2005.08.005
Zhang C, Chen X, Zou R, Zhou K, Stephanopoulos G, Too HP (2013) Combining genotype improvement and statistical media optimization for isoprenoid production in E. coli. PLoS One 8:e75164. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0075164
Zock J, Cantwell C, Swartling J, Hodges R, Pohl T, Sutton K, Rosteck P, McGilvray D, Queener S (1994) The Bacillus subtilis pnbA gene encoding p-nitrobenzyl esterase: cloning, sequence and high-level expression in Escherichia coli. Gene 151:37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1119(94)90630-0
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Norihiko Misawa (Ishikawa Prefectural University) for kindly providing the pCRT-EIB and pET-ZoTPS1 plasmids. We also thank KNC Laboratories Co., Ltd. (Kobe, Japan), for providing lithium acetoacetate.
Funding
This research was supported by grant aid from the commission for Development of Artificial Gene Synthesis Technology for Creating Innovative Biomaterial from the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI), Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HH and DS conceived and designed the study. All authors conducted the experiments. HH and DS analyzed experimental data. HH wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors consent to the publication of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 577 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harada, H., Senda, D., Shima, T. et al. Carboxylesterases for the hydrolysis of acetoacetate esters and their applications in terpenoid production using Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105, 5821–5832 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11447-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11447-z