Abstract
Plantaricin EF, a kind of natural antibacterial substance, has shown inhibitory effect on most pathogen and spoilage microorganisms, which possessed great potential in food preservation. However, the lower production of plantaricin EF has limited its large-scale production and application. In this study, the effect of maltose on plantaricin EF production and its regulation mechanism in Lactobacillus plantarum 163 were investigated. Maltose significantly improved the biomass and plantaricin EF production, which increased by 3.35 and 3.99 times comparing to the control without maltose, respectively. The maximum production of plantaricin E and F in fed-batch fermentation were 10.55 mg/L and 22.94 mg/L, respectively. Besides, qPCR results showed that maltose remarkably improved transcription of plnA, plnB, plnD, plnE, plnF, plnG1 and plnH, and heighten transcription of lamR, lamK, hpk6 and rrp6. These results provided an effective method to enhance plantaricin EF production and revealed a possible regulatory mechanism from transcriptome results that hpk6, rrp6, lamK and lamR were relative to plantaricin EF production. Genes, hpk6 and rrp6, promote transcription of plnG1, whereas lamK and lamR enhance transcription of plnA, plnB and plnD, which increased plantaricin EF production.
Keypoints
• Maltose was proved to be effective in promoting the biosynthesis of plantaricin EF.
• Maltose promoted the transcription of biosynthesis and secretion genes of plantaricin EF.
• Up-regulation of genes lamR, lamK, hpk6 and rrp6 heightened the plantaricin EF production.
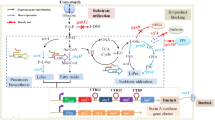
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data of whole genome sequence and transcriptome sequence on L. plantarum 163 have been submitted to the Sequence Read Archive database of National Center for Biotechnology Information, and the accession numbers were SRR12825168 and SRR12831476, respectively. Other related data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Amini M, Yousefi-Massumabad H, Younesi H, Abyar H, Bahramifar N (2020) Production of the polyhydroxyalkanoate biopolymer by Cupriavidus necator using beer brewery wastewater containing maltose as a primary carbon source. J Environ Chem Eng 8(1):103588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103588
Badouin H, Hood ME, Gouzy J, Aguileta G, Siguenza S, Perlin MH, Cuomo CA, Fairhead C, Branca A, Giraud T (2015) Chaos of rearrangements in the mating-type chromosomes of the anther-smut fungus Microbotryum lychnidis-dioicae. Genetics 200(4):1275–1284. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.115.177709
Boos W, Shuman H (1998) Maltose/maltodextrin system of Escherichia coli: transport, metabolism, and regulation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62(1):204–229. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.45.11.3231-3233.2001
Capra EJ, Laub MT (2012) Evolution of two-component signal transduction systems. Annu Rev Microbiol 66(1):325–347. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-micro-092611-150039
Delcher AL, Harmon D, Kasif S, White O, Salzberg SL (1999) Improved microbial gene identification with GLIMMER. Nucleic Acids Res 27(23):4636–4641. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/27.23.4636
Diep DB, Straume D, Kjos M, Torres C, Nes IF (2009) An overview of the mosaic bacteriocin pln loci from Lactobacillus plantarum. Peptides 30(8):1562–1574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2009.05.014
Du H, Yang J, Lu X, Lu Z, Bie X, Zhao H, Zhang C, Lu F (2018) Purification, characterization, and mode of action of plantaricin GZ1-27, a novel bacteriocin against Bacillus cereus. J Agric Food Chem 66(18):4716–4724. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b01124
Ekblad B, Kyriakou PK, Oppegard C, Jon N-M, Kaznessis YN, Kristiansen PE (2016) Structure-function analysis of the two-peptide bacteriocin plantaricin EF. Biochemistry 55(36):5106–5116. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00588
Faino L, Seidl MF, Datema E, van den Berg GCM, Janssen A, Wittenberg AHJ, Thomm BPHJ (2015) Single-molecule real-time sequencing combined with optical mapping yields completely finished fungal genome. mBio 6(4). https://doi.org/10.1128/mbio.00936-15
Fu X, Wang Y, Wang J, Garza E, Manow R, Zhou S (2017) Semi-industrial scale (30 m3) fed-batch fermentation for the production of d-lactate by Escherichia coli strain HBUT-D15. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 44(2):221–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-016-1877-9
Gerdes K, Christensen SK, Lobner-Olesen A (2005) Prokaryotic toxin–antitoxin stress response loci. Nat Rev Microbiol 3(5):371–382. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1147
Heeney DD, Zhai Z, Bendiks Z, Barouei J, Martinic A, Slupsky C, Marco ML (2019) Lactobacillus plantarum bacteriocin is associated with intestinal and systemic improvements in diet-induced obese mice and maintains epithelial barrier integrity in vitro. Gut Microbes 10(3):382–397. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2018.1534513
Hu M, Zhao H, Zhang C, Yu J, Lu Z (2013) Purification and characterization of plantaricin 163, a novel bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum 163 isolated from traditional Chinese fermented vegetables. J Agric Food Chem 61(47):11676–11682. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf403370y
Jia FF, Pang XH, Zhu DQ, Zhu ZT, Sun SR, Meng XC (2017) Role of the luxS gene in bacteriocin biosynthesis by Lactobacillus plantarum KLDS1.0391: a proteomic analysis. Sci Rep-UK 7(1):13871–13871. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13231-4
Kim KE, Peluso P, Babayan P, Yeadon PJ, Yu C, Fisher WW, Chin CS, Rapicavoli NA, Rank DR, Li J, Catcheside DEA, Celniker SE, Phillippy AM, Bergman CM, Landolin JM (2014) Long-read, whole-genome shotgun sequence data for five model organisms. Sci Data 1(1):140045–140045. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2014.45
Kumar N, Sudan KS, Garg R, Sahni G (2019) Enhanced production of novel halostable recombinant endoglucanase derived from the metagenomic library using fed-batch fermentation. Process Biochem 78:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2018.12.033
Li J, Yang X, Shi G, Chang J, Liu Z, Zeng M (2019) Cooperation of lactic acid bacteria regulated by the AI-2/LuxS system involve in the biopreservation of refrigerated shrimp. Food Res Int 120:679–687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2018.11.025
Liu W, Li Y, Bai X, Wu H, Bian L, Hu X (2020) LuxR-type regulator AclR1 of Azorhizobium caulinodans regulates cyclic di-GMP and numerous phenotypes in free-living and symbiotic states. Mol Plant Microbe In 33(3):528–538. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-10-19-0306-R
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001
Man L, Xiang D (2019) Characterization of a broad spectrum bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum MXG-68 from Inner Mongolia traditional fermented koumiss. Folia Microbiol 64(6):821–834. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-019-00697-0
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31(3):426–428. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60147a030
Navarro L, Rojo-Bezares B, Saenz Y, Diez L, Zarazaga M, Ruiz-Larrea F, Torres C (2008) Comparative study of the pln locus of the quorum-sensing regulated bacteriocin-producing L. plantarum J51 strain. Int J Food Microbiol 128(2):390–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2008.08.004
Nikolskaya AN, Galperin MY (2002) A novel type of conserved DNA-binding domain in the transcriptional regulators of the AlgR/AgrA/LytR family. Nucleic Acids Res 30(11):2453–2459. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/30.11.2453
Pal G, Srivastava S (2014) Cloning and heterologous expression of plnE, -F, -J and -K genes derived from soil metagenome and purification of active plantaricin peptides. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(3):1441–1447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5097-1
Pei J, Grishin NV (2001) Type II CAAX prenyl endopeptidases belong to a novel superfamily of putative membrane-bound metalloproteases. Trends Biochem Sci 26(5):275–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0968-0004(01)01813-8
Qian S, Lu H, Meng P, Zhang C, Lv F, Bie X, Lu Z (2015) Effect of inulin on efficient production and regulatory biosynthesis of bacillomycin D in Bacillus subtilis fmbJ. Bioresour Technol 179:260–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.11.086
Ren F, Chen L, Xiong S, Tong Q (2017) Enhanced acarbose production by Streptomyces M37 using a two-stage fermentation strategy. PLoS One 12(2):e0166985. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0166985
Rojo-Bezares B, Saenz Y, Navarro L, Jimenez-Diaz R, Zarazaga M, Ruiz-Larrea F, Torres C (2008) Characterization of a new organization of the plantaricin locus in the inducible bacteriocin-producing Lactobacillus plantarum J23 of grape must origin. Arch Microbiol 189(5):491–499. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-007-0342-6
Saenz Y, Rojo-Bezares B, Navarro L, Diez L, Somalo S, Zarazaga M, Ruiz-Larrea F, Torres C (2009) Genetic diversity of the pln locus among oenological Lactobacillus plantarum strains. Int J Food Microbiol 134(3):176–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2009.06.004
Schaller GE, Shiu SH, Armitage JP (2011) Two-component systems and their co-option for eukaryotic signal transduction. Curr Biol 21(9):R320–R330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2011.02.045
Schlegel A, Böhm A, Lee SJ, Peist R, Boos W (2002) Network regulation of the Escherichia coli maltose system. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 4(3):301–307. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj/jim/7000246
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S, Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos A, Tsafou KP, Kuhn M, Bork P, Jensen LJ, von Mering C (2015) STRING v10: protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res 43:447–452. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1003
Todorov S, Gotcheva B, Dousset X, Onno B, Ivanova I (2000) Influence of growth medium on bacteriocin production in Lactobacillus Plantarum ST31. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 14(1):50–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2000.10819062
Tsapieva A, Duplik N, Suvorov A (2011) Structure of plantaricin locus of Lactobacillus plantarum 8P-A3. Benefic Microbes 2(4):255–261. https://doi.org/10.3920/BM2011.0030
Wang Y, Liu L, Wang Y, Xue Y, Zheng Y, Shen Y (2012) Actinoplanes utahensis ZJB-08196 fed-batch fermentation at elevated osmolality for enhancing acarbose production. Bioresour Technol 103(1):337–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.09.121
Wang Y, He L, Zhang Z, Zhao X, Qi N, Han T (2020) Efficiency enhancement of H2 production by a newly isolated maltose-preferring fermentative bio-hydrogen producer of Clostridium butyricum NH-02. J Energy Storage 30:101426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2020.101426
Wen LS, Philip K, Ajam N (2016) Purification, characterization and mode of action of plantaricin K25 produced by Lactobacillus plantarum. Food Control 60:430–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.08.010
Wolf D, Rippa V, Mobarec JC, Sauer P, Adlung L, Kolb P, Bischofs IB (2016) The quorum-sensing regulator ComA from Bacillus subtilis activates transcription using topologically distinct DNA motifs. Nucleic Acids Res 44(5):2160–2172. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1242
Yu L, Xu M, Tang I, Yang S (2015) Metabolic engineering of Clostridium tyrobutyricum for n-butanol production from maltose and soluble starch by overexpressing α-glucosidase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(14):6155–6165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6680-4
Zacharof MP, Lovitt RW (2012) Bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria a review article. APCBEE Procedia 2:50–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcbee.2012.06.010
Zhao S, Han J, Bie X, Lu Z, Zhang C, Lv F (2016) Purification and Characterization of Plantaricin JLA-9: A Novel Bacteriocin against Bacillus spp. Produced by Lactobacillus plantarum JLA-9 from Suan-Tsai, a Traditional Chinese Fermented Cabbage. J Agric Food Chem 64(13):2754–2764. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b05717
Funding
The authors acknowledge the financial support for this work provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31771948).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.X.L. and Y.J.L. conceived and designed research. D.Y.Z. conducted experiments. F.Q.M., L.B.Z. and J.S. analyzed data. D.Y.Z., F.X.L. and X.M.B. wrote the manuscript. Z.X.L. and Y.J.L. reviewed and edited this manuscript. Z.X.L. is also the supervision, project administration of this manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 806 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, D., Meng, F., Zhou, L. et al. Maltose effective improving production and regulatory biosynthesis of plantaricin EF in Lactobacillus plantarum 163. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105, 2713–2723 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11218-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11218-w